Asked by
Paulette Eugene Denis
on Nov 25, 2024
Verified
When the necessary conditions are met, a two-tail test is being conducted at 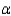 = 0.05 to test
= 0.05 to test 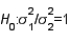 . The two sample variances are
. The two sample variances are  , and the sample sizes are
, and the sample sizes are  . The calculated value of the test statistic will be F = 2.
. The calculated value of the test statistic will be F = 2.
Two-tail Test
A statistical test that considers both the directions of a possible effect, testing for the possibility of positive or negative deviations from the null hypothesis.
Sample Variances
A measure of the dispersion or variability within a sample data set, which indicates how much the sample elements differ from the sample mean.
Test Statistic
A standardized value that is calculated from sample data during a hypothesis test. It's used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis.
- Undertake the computation of the F-test statistic to contrast variances of two samples.
- Discern the differences between one-tailed and two-tailed tests used in comparing variances.

Verified Answer
KK

Learning Objectives
- Undertake the computation of the F-test statistic to contrast variances of two samples.
- Discern the differences between one-tailed and two-tailed tests used in comparing variances.