Asked by
Kaley Reindl
on Nov 27, 2024
Verified
When all possible simple random samples of size n are drawn from a population that is normally distributed, the sampling distribution of the sample means 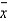 will be normal regardless of sample size n.
will be normal regardless of sample size n.
Sampling Distribution
A statistical measure that describes how likely different outcomes are, based on data from a random sample, which is utilized to draw conclusions about the broader population.
Normally Distributed
A type of distribution for a variable where the data forms a symmetrical bell-shaped curve around the mean.
Simple Random Samples
A subset of a population in which every member has an equal chance of being selected, ensuring that the sample represents the population well.
- Learn about the importance and function of the Central Limit Theorem (CLT) in statistical inference, particularly in terms of its influence on the sampling distribution's shape.
- Ascertain the contexts in which the Central Limit Theorem is pertinent to continuous and discrete distributions.

Verified Answer
AD

Learning Objectives
- Learn about the importance and function of the Central Limit Theorem (CLT) in statistical inference, particularly in terms of its influence on the sampling distribution's shape.
- Ascertain the contexts in which the Central Limit Theorem is pertinent to continuous and discrete distributions.