Asked by
Logan Rivers
on Nov 27, 2024
Verified
For any random variable, P(x 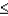 a) = P(x < a) because P(x = a) = 0.
a) = P(x < a) because P(x = a) = 0.
Random Variable
A variable whose values depend on outcomes of a random phenomenon.
P(x < a)
This denotes the probability that the random variable X takes on a value less than a specific value a.
P(x = a)
The probability of a random variable x taking on a specific value a.
- Realize the connection between the concept of probabilities and the under curve areas in a normal distribution context.

Verified Answer
MS

Learning Objectives
- Realize the connection between the concept of probabilities and the under curve areas in a normal distribution context.
Related questions
Using the Standard Normal Curve, the Area Between Z = ...
The Normal Random Variable's Density Function Is (1) Single-Peaked Above ...
Using the Standard Normal Curve, the Probability or Area Between ...
Let Be a Z-Score That Is Unknown but Identifiable ...
Let Be a Z-Score That Is Unknown but Identifiable ...