Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does it mean to say that the cI protein establishes a positive feedback loop on its own production?
A) It converts inactive cI protein molecules into active cI molecules.
B) It stimulates faster translation of the cI messenger RNA.
C) It makes cI messenger RNA more stable.
D) It is a positive transcriptional activator of the cI gene.
E) None of the answer options is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gene regulation can occur at which of the following steps in the path from DNA to protein?
A) during transcription from a chromosome
B) during translation from DNA to RNA
C) after protein synthesis
D) during transcription from a chromosome and during translation from DNA to RNA
E) during transcription from a chromosome, during translation from DNA to RNA, and after protein synthesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
siRNA is a type of _____ RNA.
A) messenger
B) transfer
C) ribosomal
D) splicing
E) regulatory
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about transcriptional regulation is INCORRECT?
A) Regulatory transcription factors are proteins that bind to enhancer DNA sequences and then recruit one or more general transcription factors.
B) A typical gene contains only one enhancer sequence.
C) General transcription factors are required to initiate the process of transcription.
D) General transcription factors bind to the TATA box in the promoter region of a gene.
E) RNA polymerase components are recruited to the promoter region by the general transcription factors bound to the TATA box.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Modifications of histone tails can:
A) affect chromatin structure.
B) activate transcription of some genes.
C) repress transcription of some genes.
D) affect expression of some genes in response to the environment.
E) All of these choices are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Transcriptional regulation in eukaryotic cells requires the coordinated action of many proteins that interact with one another and with DNA sequences near the gene.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A region of prokaryotic DNA consisting of an operator, promoter, and coding sequence for several functionally related genes is called a(n) :
A) closed reading frame.
B) organized genomic region.
C) opera.
D) operon.
E) operation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following are two genotypes of the lactose operon in E. coli: 1) I+ P+ Oc Z+ Y+ "2) I- P+ O+ Z+ Y+ Do either of these genotypes produce -galactosidase and permease in the absence of lactose?"
A) Both produce -galactosidase and permease.
B) Neither produces -galactosidase and permease.
C) The first one produces -galactosidase and permease; the second does not.
D) The first one does not produce -galactosidase and permease; the second does.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Nucleosomes occupy fixed positions along the DNA that remain the same over time and in each cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A virus that infects bacteria is called a:
A) lytic virus.
B) temperate virus.
C) lysogenic virus.
D) bacteriophage.
E) microphage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram shown here is part of an RNA transcript containing four open reading frames (M, H, K, and L) and three introns (1, 2, 3) . 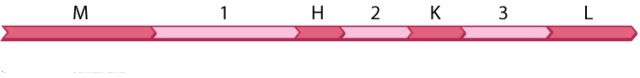 How many cuts would a spliceosome have to make in order to result in a transcript containing only open reading frames M, K, and L?
How many cuts would a spliceosome have to make in order to result in a transcript containing only open reading frames M, K, and L?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following statements MOST accurately describes methylation?
A) Methyl groups are most often added to cytosines adjacent to guanine bases in or near the promoter sequence, increasing the probability of gene expression.
B) Methyl groups are most often added to cytosines adjacent to guanine bases in or near the promoter sequence, decreasing the probability of gene expression.
C) Methyl groups are most often added to adenine-thymine base pairs because they are held by only two hydrogen bonds, and this increases the probability of gene expression.
D) Methyl groups are most often added to guanine-cytosine base pairs because they are held by three hydrogen bonds, and this decreases the probability of gene expression.
E) Methyl groups are added to most bases in the promoter region of a specific gene so that RNA polymerase and its associated proteins will bind more efficiently.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram shown here is part of an RNA transcript containing four open reading frames (M, H, K, and L) and three introns (1, 2, 3) . The sites labeled d1-d3 are nucleotides immediately before each intron on the 5' side and those labeled a1-a3 are nucleotides immediately after each intron on the 3' side. Splicing out an intron involves cleaving the DNA at the d and a sites at either end of the intron. 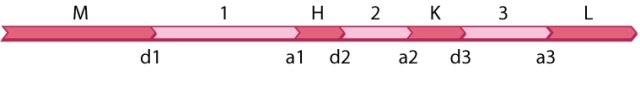 A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame K. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?
A missense mutation takes place in open reading frame K. In which possible alternative splice forms of the transcript would the missense mutation not affect the polypeptide product?
A) d1-a1 + d2-a2 + d3-a3
B) d1-a2 + d3-a3
C) d1-a1 + d2-a3
D) d1-a3
E) None of the answer options is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Review Figure 19.15 below: 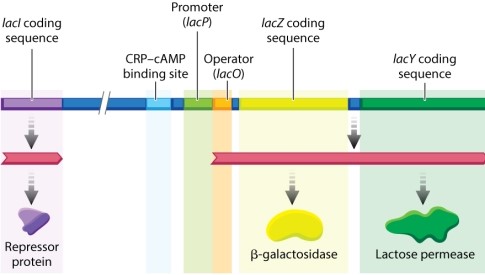 Which one of the following statements about the lactose operon is NOT correct?
Which one of the following statements about the lactose operon is NOT correct?
A) The lacZ coding sequence for -galactosidase and lacY coding sequence for lactose permease are genes called structural genes.
B) lacO is a gene sequence coding for the operator.
C) The promoter sequence recruits RNA polymerase complex and the initiation of transcription.
D) lacI is a gene sequence coding for the repressor which binds to the operator, inhibiting transcription.
E) The CRP-cAMP binding site promotes transcription of lactose operon genes if cAMP is high, which indicates that glucose is low and lactose metabolism is needed for energy production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alternative splicing may be considered a mechanism of gene regulation because it:
A) results in DNA rearrangements.
B) enhances RNA editing.
C) results in different protein products.
D) is mutagenic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
X-inactivation is caused by the accumulation of:
A) proteins produced by the Xist gene; these proteins induce methylation, histone modification, and other changes associated with preventing transcription.
B) coding RNA produced by the Xist gene; this RNA, in addition to coding for Xist proteins, binds to and coats the X chromosome undergoing inactivation and physically prevents it from being transcribed.
C) noncoding RNA produced by the Xist gene, which coats the X chromosome and covalenty crosslinks the DNA strands preventing them from being unwound, "unzipped," and transcribed.
D) noncoding RNA produced by the Xist gene, which coats the X chromosome and induces DNA methylation, histone modification, and other changes associated with preventing transcription.
E) None of the answer choices accurately describes the process of X-inactivation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the drawing of mRNA below, choose the letter that BEST fits the description. 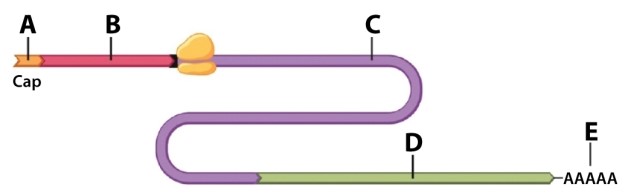 The protein-coding region corresponds to region:
The protein-coding region corresponds to region:
A) A)
B) B)
C) C)
D) D)
E) E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mutant strain of E. coli is found that produces both -galactosidase and permease constitutively. What are the MOST likely mutations in this strain?
A) lacOc
B) lacI-
C) lacP-
D) mutation in CRP-cAMP binding site
E) lacZ- and lacY-
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Transcription in prokaryotes is rapidly turned on or off in response to environmental changes and involves both positive and negative regulators.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 189
Related Exams