A) the distribution of ![]() jcollapses to a single value of zero.
jcollapses to a single value of zero.
B) the distribution of ![]() jdiverges away from a single value of zero.
jdiverges away from a single value of zero.
C) the distribution of ![]() jcollapses to the single point
jcollapses to the single point![]() j.
j.
D) the distribution of ![]() jdiverges away from
jdiverges away from![]() j.
j.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The standard error of a regression, ![]() ,is not an unbiased estimator for
,is not an unbiased estimator for![]() ,the standard deviation of the error,u,in a multiple regression model.
,the standard deviation of the error,u,in a multiple regression model.
B) In time series regressions,OLS estimators are always unbiased.
C) Almost all economists agree that unbiasedness is a minimal requirement for an estimator in regression analysis.
D) All estimators in a regression model that are consistent are also unbiased.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If δ1 = Cov(x1/x2) / Var(x1) where x1 and x2 are two independent variables in a regression equation,which of the following statements is true?
A) If x2 has a positive partial effect on the dependent variable,and δ1 > 0,then the inconsistency in the simple regression slope estimator associated with x1is negative.
B) If x2 has a positive partial effect on the dependent variable,and δ1 > 0,then the inconsistency in the simple regression slope estimator associated with x1is positive.
C) If x1 has a positive partial effect on the dependent variable,and δ1 > 0,then the inconsistency in the simple regression slope estimator associated with x1is negative.
D) If x1 has a positive partial effect on the dependent variable,and δ1 > 0,then the inconsistency in the simple regression slope estimator associated with x1is positive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a multiple regression model,the OLS estimator is consistent if:
A) there is no correlation between the dependent variables and the error term.
B) there is a perfect correlation between the dependent variables and the error term.
C) the sample size is less than the number of parameters in the model.
D) there is no correlation between the independent variables and the error term.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If OLS estimators satisfy asymptotic normality,it implies that:
A) they are approximately normally distributed in large enough sample sizes.
B) they are approximately normally distributed in samples with less than 10 observations.
C) they have a constant mean equal to zero and variance equal to σ2.
D) they have a constant mean equal to one and variance equal to σ.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If 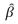 jis an OLS estimator of a regression coefficient associated with one of the explanatory variables,such that j= 1,2,…. ,n,asymptotic standard error of
jis an OLS estimator of a regression coefficient associated with one of the explanatory variables,such that j= 1,2,…. ,n,asymptotic standard error of 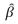 j will refer to the:
j will refer to the:
A) estimated variance of ![]() jwhen the error term is normally distributed.
jwhen the error term is normally distributed.
B) estimated variance of a given coefficient when the error term is not normally distributed.
C) square root of the estimated variance of ![]() j when the error term is normally distributed.
j when the error term is normally distributed.
D) square root of the estimated variance of ![]() j when the error term is not normally distributed.
j when the error term is not normally distributed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true under the Gauss-Markov assumptions?
A) Among a certain class of estimators,OLS estimators are best linear unbiased,but are asymptotically inefficient.
B) Among a certain class of estimators,OLS estimators are biased but asymptotically efficient.
C) Among a certain class of estimators,OLS estimators are best linear unbiased and asymptotically efficient.
D) The LM test is independent of the Gauss-Markov assumptions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The LM statistic requires estimation of the unrestricted model only.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If 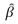 j,an unbiased estimator of
j,an unbiased estimator of 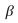 j,is consistent,then the:
j,is consistent,then the:
A) distribution of ![]() jbecomes more and more loosely distributed around
jbecomes more and more loosely distributed around![]() jas the sample size grows.
jas the sample size grows.
B) distribution of ![]() jbecomes more and more tightly distributed around
jbecomes more and more tightly distributed around![]() jas the sample size grows.
jas the sample size grows.
C) distribution of ![]() jtends toward a standard normal distribution as the sample size grows.
jtends toward a standard normal distribution as the sample size grows.
D) distribution of ![]() jremains unaffected as the sample size grows.
jremains unaffected as the sample size grows.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The LM statistic follows a:
A) t distribution.
B) f distribution.
C) ![]() 2 distribution.
2 distribution.
D) binomial distribution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Even if the error terms in a regression equation,u1,u2,….. ,un,are not normally distributed,the estimated coefficients can be normally distributed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An auxiliary regression refers to a regression that is used:
A) when the dependent variables are qualitative in nature.
B) when the independent variables are qualitative in nature.
C) to compute a test statistic but whose coefficients are not of direct interest.
D) to compute coefficients which are of direct interest in the analysis.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the error term is correlated with any of the independent variables,the OLS estimators are:
A) biased and consistent.
B) unbiased and inconsistent.
C) biased and inconsistent.
D) unbiased and consistent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The n-R-squared statistic also refers to the:
A) F statistic.
B) t statistic.
C) z statistic.
D) LM statistic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If variance of an independent variable in a regression model,say x1,is greater than 0,or Var(x1)> 0,the inconsistency in 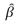 1(estimator associated with x1)is negative,if x1 and the error term are positively related.
1(estimator associated with x1)is negative,if x1 and the error term are positively related.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) In large samples there are not many discrepancies between the outcomes of the F test and the LM test.
B) Degrees of freedom of the unrestricted model are necessary for using the LM test.
C) The LM test can be used to test hypotheses with single restrictions only and provides inefficient results for multiple restrictions.
D) The LM statistic is derived on the basis of the normality assumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a regression model,if variance of the dependent variable,y,conditional on an explanatory variable,x,or Var(y|x) ,is not constant,_____.
A) the t statistics are invalid and confidence intervals are valid for small sample sizes
B) the t statistics are valid and confidence intervals are invalid for small sample sizes
C) the t statistics and confidence intervals are both invalid no matter how large the sample size is
D) the t statistics confidence intervals are valid no matter how large the sample size is
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A normally distributed random variable is symmetrically distributed about its mean,it can take on any positive or negative value (but with zero probability),and more than 95% of the area under the distribution is within two standard deviations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A useful rule of thumb is that standard errors are expected to shrink at a rate that is the inverse of the:
A) square root of the sample size.
B) product of the sample size and the number of parameters in the model.
C) square of the sample size.
D) sum of the sample size and the number of parameters in the model.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The F statistic is also referred to as the score statistic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 20
Related Exams