A) 2.21 mL
B) 0.577 mL
C) 0.0456 mL
D) 0.0684 mL
E) 0.866 mL
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diffusion rate of H2 gas is 6.45 times as great as that of a certain noble gas (both gases are at the same temperature) . What is the noble gas?
A) He
B) Ar
C) Kr
D) Ne
E) Xe
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Gas A (MM = 36.0 g/mol) and gas B (MM = 62 g/mol) are present in a mixture that contains 50 molecules A : 326 molecules B. If these gases effuse through a pinhole into a neighboring evacuated chamber, what will be the ratio of A:B in the chamber?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of oxygen gas has a volume of 4.50 L at 27°C and 800.0 torr. How many oxygen molecules does it contain?
A) 1.16 × 1022
B) 1.16 × 1023
C) 2.32 × 1024
D) 5.8 × 1022
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a mixture is prepared from 15.0 L of ammonia and 15.0 L of chlorine measured at the same conditions, these compounds react according to the following equation: 2NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g) → N2(g) + 6HCl(g) When the reaction is completed, what are the volumes of the gases (NH3, Cl2, N2, and HCl, respectively) ? Assume the final volumes are measured under identical conditions.
A) 0.00 L, 0.00 L, 5.00 L, and 30.0 L
B) 0.00 L, 0.00 L, 7.50 L, and 45.0 L
C) 0.00 L, 5.00 L, 7.50 L, and 45.0 L
D) 5.00 L, 0.00 L, 5.00 L, and 30.0 L
E) 0.00 L, 10.0 L, 15.0 L, and 90.0 L
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the density of nitrogen at STP.
A) 1.25 g/L
B) 0.625 g/L
C) 0.312 g/L
D) 1.60 g/L
E) 0.800 g/L
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Order the following according to increasing rate of effusion: F2, Cl2, NO, NO2, CH4
A) CH4 < NO2 < NO < F2 < Cl2
B) Cl2 < F2 < NO2 < CH4 < NO
C) Cl2 < NO2 < F2 < NO < CH4
D) CH4 < NO < F2 < NO2 < Cl2
E) F2 < NO < Cl2 < NO2 < CH4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With respect to the Maxwell-Boltzmann probability distribution function of molecular speeds, which of the following is true?
A) ![]()
B) A and D
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The volume of a helium balloon is 1.85 L at 24.0°C and 1.00 atm at sea level. The balloon is released and floats upward. At a certain altitude, the balloon has a volume of 2.14 L and the temperature is 15.2°C. What is the atmospheric pressure at this altitude?
A) 0.538 atm
B) 1.36 atm
C) 0.839 atm
D) 0.891 atm
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given a cylinder of fixed volume filled with 1 mol of argon gas, which of the following is correct? (Assume all gases obey the ideal gas law.)
A) If a second mole of argon is added to the cylinder, the ratio T/P will remain constant.
B) If the temperature of the cylinder is changed from 25°C to 50°C, the pressure inside the cylinder will double.
C) A cylinder of identical volume filled with the same pressure of helium must contain more atoms of gas because He has a smaller atomic radius than argon.
D) Two of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The kinetic-molecular theory of gases does not assume that
A) gas particles are very small compared to the average distance between the particles.
B) gas particles collide with the walls of their container in elastic collisions.
C) the average velocity of gas particles is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
D) gases are made up of tiny particles in constant chaotic motion.
E) All of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider separate samples of Ar(g) and Ne(g) . For what ratio of absolute temperatures (Ne:Ar) are the average kinetic energies equal?
A) 1.41
B) 0.505
C) 1.98
D) 1.00
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 1.00-g sample of a gaseous compound of boron and hydrogen occupies 0.820 L at 1.00 atm and 3°C. What is the molecular formula for the compound?
A) B2H6
B) B4H10
C) B5H14
D) B3H12
E) BH3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Samples of the gases H2(g) and SO2(g) have equal masses and are at the same temperature and pressure. Calculate the following:
-The ratio of the root-mean-square velocities 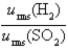 .
.
A) 180
B) 32
C) 0.18
D) 1.0
E) 5.6
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Four identical 1.0-L flasks contain the gases He, Cl2, CH4, and NH3, each at 0°C and 1 atm pressure. -For which gas are the collisions elastic?
A) He
B) Cl2
C) CH4
D) NH3
E) The collisions are elastic for all the gases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider three 1-L flasks at the same temperature and pressure. Flask A contains CO gas, flask B contains N2 gas, and flask C contains O2 gas.In which flask do the molecules have the greatest momentum per impact?
A) The molecules in all the flasks have the same momentum per impact.
B) flask C
C) The molecules in two of the flasks have the same momentum per impact.
D) flask A
E) flask B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 250.0-L cylinder contains 65.0% He(g) and 35.0% Kr(g) by mass at 25.0°C and 1.35 atm total pressure. What is the partial pressure of He in this container?
A) 0.675 atm
B) 0.878 atm
C) 1.32 atm
D) 1.35 atm
E) 0.473 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mercury vapor contains Hg atoms. What is the volume of 200. g of mercury vapor at a temperature of 822 K and 0.500 atm?
A) 135 L
B) 329 L
C) 82.2 L
D) 67.2 L
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is the observed pressure of a gas related to the ideal pressure?
A) The relationship depends on the gas.
B) They are equal.
C) The observed pressure is greater than the ideal pressure.
D) The observed pressure is less than the ideal pressure.
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following gas samples:

Which one of the following statements is false?
Which one of the following statements is false?
A) Assuming identical intermolecular forces in the two samples, sample A should be more nearly ideal than sample B.
B) The root-mean-square velocity of molecules in sample A is twice as large as the root-mean-square velocity of molecules in sample B.
C) The average kinetic energy of the molecules in sample A is twice the average kinetic energy of the molecules in sample B.
D) The fraction of molecules in sample A having a kinetic energies greater than some high fixed value is larger than the fraction of molecules in sample B having kinetic energies greater than that same high fixed value.
E) The volume of sample A is twice the volume of sample B.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 118
Related Exams