A) 2.0
B) 0.50
C) 0.71
D) 1.0
E) 1.4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A vessel with a volume of 10.2 L contains 3.12 g of nitrogen gas, 0.590 g of hydrogen gas, and 82.4 g of argon gas. At 25.4°C, what is the pressure in the vessel?
A) 207 atm
B) 0.504 atm
C) 9.15 104 atm
D) 5.92 atm
E) 2.95 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An excess of potassium hydroxide is treated with 1.4 L of dry hydrogen bromide gas measured at STP. What is the mass of potassium bromide formed?
A) 9.4 102 g
B) 7.4 g
C) 1.2 103 g
D) 1.9 103 g
E) 1.6 103 g
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Into a 3.90-liter container at 23°C are placed 1.18 mol of O2 gas and 4.02 mol of solid C (graphite) . If the carbon and oxygen react completely to form CO(g) , what will be the final pressure in the container at 23°C?
A) 0.571 atm
B) 7.35 atm
C) 25.0 atm
D) 32.4 atm
E) 14.7 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider two 1.0-L containers, one containing He(g) at 2.50 atm and 24°C and the other containing Ar(g) at 5.00 atm and 48°C. -Calculate the ratio of impacts with the wall per second (He:Ar) .
A) 9.22
B) 1.64
C) 4.98
D) 6.25
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three 1.00-L flasks at 25°C and 725 torr contain the gases CH4 (flask A) , CO2 (flask B) , and C2H6 (flask C) . In which single flask do the molecules have the greatest mass, the greatest average velocity, and the highest kinetic energy?
A) flask A
B) flask B
C) flask C
D) all
E) none
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 3.54-g sample of lead(II) nitrate, Pb(NO3) 2, molar mass = 331 g/mol, is heated in an evacuated cylinder with a volume of 1.60 L. The salt decomposes when heated, according to the equation 2Pb(NO3) 2(s) 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g) Assuming complete decomposition, what is the pressure in the cylinder after decomposition and cooling to a temperature of 300. K? Assume the PbO(s) takes up negligible volume.
A) 0.576 atm
B) 0.165 atm
C) 0.786 atm
D) 0.823 atm
E) 0.411 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the ratio of the change in momentum per wall impact for Ar(g) to that for He(g) if the gases are at the same temperature and pressure.
A) 0.316
B) 3.16
C) 9.98
D) 0.100
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Samples of the gases H2(g) and SO2(g) have equal masses and are at the same temperature and pressure. Calculate the following: The ratio of volumes 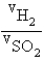 .
.
A) 32
B) 0.18
C) 180
D) 5.6
E) 1.0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Volume versus temperature in degrees Celsius for an ideal gas at constant volume and number of moles Which graph represents the plot?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) None of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the following ratios for a gas at Kelvin temperatures T1 and T2 where T2 = 2T1. -Mean free path at T1 : Mean free path at T2
A) 0.50
B) 1.4
C) 2.0
D) 0.71
E) 1.0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider three 1.0-L flasks at STP. Flask A contains N2 gas, flask B contains Kr gas, and flask C contains He gas. In which flask do the gas particles have the lowest average kinetic energy?
A) flask B
B) The gas particles in all of the flasks have the same average kinetic energy.
C) The gas particles in two of the flasks have the same average kinetic energy.
D) flask C
E) flask A
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Order the following according to increasing rate of effusion: F2, Cl2, NO, NO2, CH4
A) CH4 < NO2 < NO < F2 < Cl2
B) Cl2 < F2 < NO2 < CH4 < NO
C) Cl2 < NO2 < F2 < NO < CH4
D) CH4 < NO < F2 < NO2 < Cl2
E) F2 < NO < Cl2 < NO2 < CH4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of nitrogen gas has a volume of 160.0 mL at STP. What volume does the gas occupy if the absolute temperature and pressure are each quadrupled?
A) 40.00 mL
B) 640.0 mL
C) 400.0 mL
D) 89.60 L
E) 160.0 mL
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider three 1-L flasks at the same temperature and pressure. Flask A contains CO gas, flask B contains N2 gas, and flask C contains O2 gas. In which flask do the molecules have the greatest momentum per impact?
A) The molecules in all the flasks have the same momentum per impact.
B) flask C
C) The molecules in two of the flasks have the same momentum per impact.
D) flask A
E) flask B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a 2.15-g sample of a gas occupies 750. mL at STP, what is the molar mass of the gas at 125°C?
A) 75.0
B) 3.07 10-2
C) 64.2
D) 70.1
E) Not enough information is given.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Four identical 1.0-L flasks contain the gases He, Cl2, CH4, and NH3, each at 0°C and 1 atm pressure. -Which gas sample has the greatest number of molecules?
A) He
B) NH3
C) Cl2
D) CH4
E) All the gases have the same number of molecules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The root-mean-square velocity of CO gas at 15°C is
A) 50.3 m/s.
B) 116 m/s.
C) 3.66 m/s
D) 507 m/s.
E) 16.0 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider separate samples of Ar(g) and Ne(g) . For what ratio of absolute temperatures (Ne:Ar) are the average kinetic energies equal?
A) 1.41
B) 0.505
C) 1.98
D) 1.00
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Calculate the temperature at which the average velocity of Ar(g) equals the average velocity of Ne(g) at 25°C.
A) 25°C
B) 151°C
C) 317°C
D) 49.5°C
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 113
Related Exams