A) becomes deciduous during dry times.
B) carries on CAM photosynthesis.
C) has extensive taproots.
D) uses animals to help to disperse its seeds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In general, domesticated land can be said to include
A) more than half of the Earth's land surface, with some human influence on most of the rest.
B) more than half of the Earth's land surface, with little human influence on most of the rest.
C) less than half of Earth's land surface, with some human influence on most of the rest.
D) less than half of Earth's land surface, with little human influence on most of the rest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Grazers are well suited to savannas because
A) none of their natural predators live there.
B) they are able to migrate seasonally toward the wetter areas.
C) they can pull up grasses there by the roots.
D) the grasses there are ephemeral.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagram below, 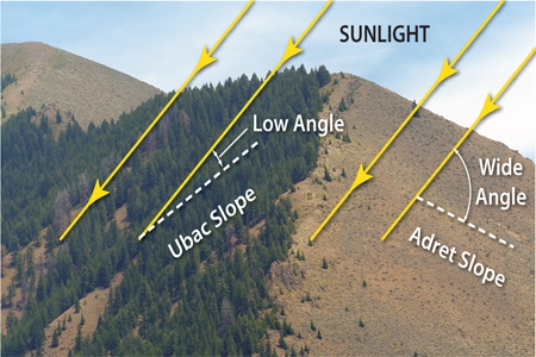
A) the snow line will be higher on the right slope than the left slope.
B) the tree line will be higher on the right slope than the left slope.
C) the right slope will have more soil moisture than the left slope.
D) All of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A savanna differs from a steppe in that the grasses are
A) intolerant to freezes in a savanna.
B) only in riparian zones in a savanna.
C) taller in a savanna.
D) in drier areas in a savanna.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are adaptations that promote survival of the boreal forests except
A) having a dark, rough surface.
B) having needles instead of leaves.
C) having some trees that grow faster than others.
D) All of these are adaptations that promote survival in the boreal forests.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an important function that fire provides to contribute to ecosystem or biome health?
A) restoring nutrients to the soil
B) allowing seeds for pyrophilic species to germinate
C) reducing runoff
D) improving access of wildlife to new lands
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the map below, lavender represents 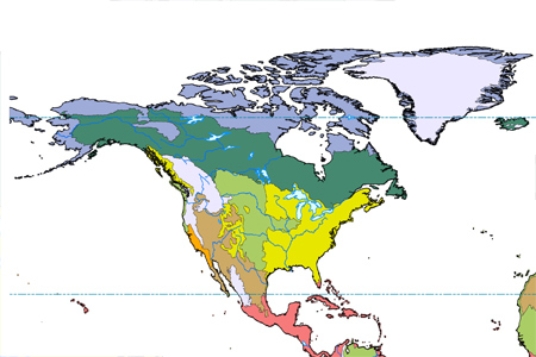
A) temperate forest.
B) tundra.
C) boreal forest.
D) grassland.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagram below, B is the 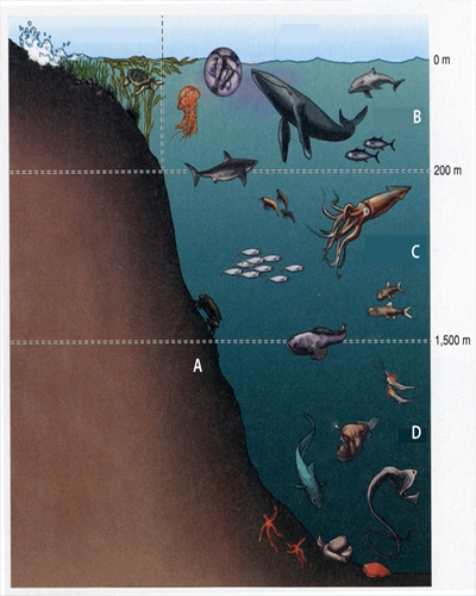
A) hadal zone.
B) mesopelagic zone.
C) epipelagic zone.
D) benthic zone.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which region in the map below are fauna similar even across islands because the areas within that region were once together as part of Gondwana? 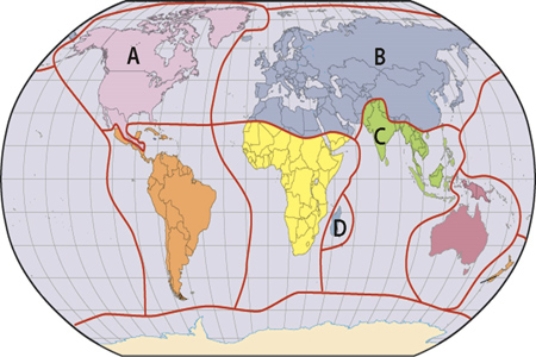
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The seasonal migration of the subtropical high and seasonal circulations associated with the monsoons cause the _______ biome to exist in California and India, respectively.
A) subtropical scrub and woodland
B) grassland
C) desert
D) temperate forest
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
CAM plants can minimize water loss by
A) leaving their stomates closed during dry periods.
B) suspending photosynthesis when the solar radiation is too intense.
C) having leaves shaped like umbrellas, which minimizes evaporation.
D) storing water in their stems during wetter periods.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following choices, evergreen temperate forests are most dominant in
A) the eastern United States.
B) eastern China and Japan.
C) South-central Brazil.
D) central Australia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Moving poleward, vegetation in the Tundra biome grades from
A) lichens to stunted trees to grasses.
B) grasses to stunted trees to lichens.
C) stunted trees to lichens to grasses.
D) stunted trees to grasses to lichens.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Elevation affects the distribution of terrestrial biomes through its effect on
A) temperature.
B) precipitation.
C) both temperature and precipitation.
D) neither temperature nor precipitation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Redwoods of California are an example of
A) coniferous evergreen forest.
B) deciduous temperate forest.
C) broadleaf evergreen forest.
D) needleleaf deciduous forest.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The land bridge called Beringia during the last glacial advance about 20,000 years ago, allowed animals to be exchanged among which two zoogeographic realms?
A) Neotropic and Nearctic
B) Australian and New Zealand
C) Palearctic and Nearctic
D) Neotropic and Paleotropic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Land use changes and exotic species introductions tend to have the impact of
A) favoring K-selected species.
B) creating a dynamic equilibrium in species populations.
C) reducing the area covered by ecotones.
D) reducing biodiversity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Plants that are allelopathic
A) have very sharp spines instead of leaves.
B) cannot tolerate long periods of drought.
C) produce flowers very rapidly after a rain event.
D) are likely to be located away from other plants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effects of global climate change are magnified in mountainside environments because
A) there are such narrow belts of different ecosystems that would shift abruptly.
B) most climate models expect more significant warming in mountainous areas than elsewhere.
C) soils are generally thicker in mountainous environments.
D) Biodiversity is generally less in mountainous environments than in adjacent flatlands.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 76
Related Exams