A) West side,near the cliffs
B) East side,in the embayments
C) On the sandy island on the south side
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the coastlines investigation,what coastline process is likely occurring along the eastern part of the north shore? 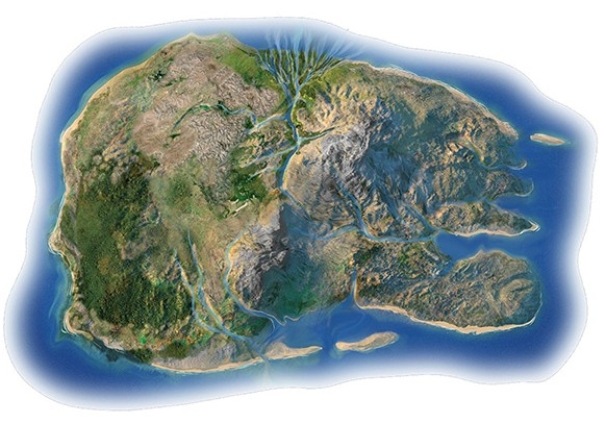
A) Transport of delta-derived sediment along the coast
B) Uplift to the land relative to sea level
C) Subsidence of the land relative to sea level
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the coastlines investigation,what coastline feature is represented by the very steep topography along the western coast (left side of island) ? 
A) Sea cliffs
B) Marine terrace
C) Delta
D) Spit and sand bar
E) Submerged coastline
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the primary reason an increase in glaciation on land would cause sea level to fall?
A) The temperature of the oceans decreases from cold glacial streams.
B) An increase in snow cover causes the atmosphere to heat up,which causes more evaporation.
C) Glaciers depress the land surface,which pulls sea level down with it.
D) Glaciers tie up large volumes of water that would otherwise be in the sea.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This feature is a(n) 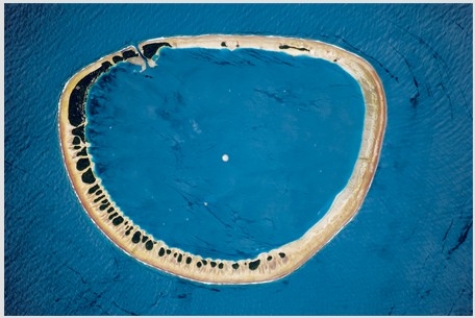
A) sea stack.
B) fringing reef.
C) atoll.
D) sandbar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long Island and Cape Cod both were created from ________ and then later reworked by ________.
A) glacial deposits; ocean waves
B) wind-blown sand; glaciers
C) sea level rise; wind
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chesapeake and Delaware Bays were both ________ before sea level rose and drown them approximately 20,000 years ago.
A) estuaries
B) fjords
C) embayments
D) barrier islands
E) stream valleys
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This wave-cut platform indicates 
A) a rise of sea level relative to the land.
B) a lowering of sea level relative to the land.
C) movement of a large thrust fault.
D) scouring of the land surface by a tsunami.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following can influence whether a coast gains or loses sand with time?
A) the amount of precipitation on land
B) the amount of sediment in rivers
C) a longshore current
D) prevailing wind direction
E) All of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The feature pictured below formed as 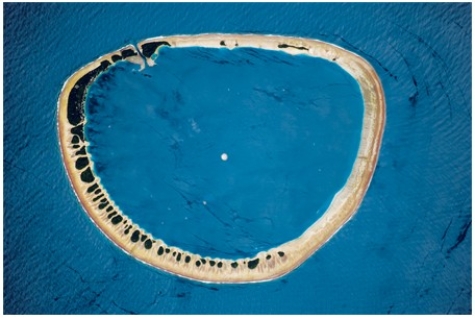
A) an island flanked by coral sank.
B) mass wasting caused the highest parts of a hill to move downslope until nothing was left in the middle.
C) oceanic seafloor spreading occurred in a circular pattern.
D) a recent explosive volcanic eruption left only the sides of the volcano remaining.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not affect the potential hazards of a shoreline?
A) Elevation of the land surface near the shore
B) The distribution of hard and soft rocks
C) Width of a beach
D) The presence of offshore islands and sand bars
E) All of these affect potential hazards of shorelines.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a wave of oscillation,an individual water molecule near the surface will move
A) counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere,clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
B) in a smaller vertical circle than a water molecule submerged deeper in the wave.
C) in a larger vertical circle than a water molecule submerged deeper in the wave.
D) clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere,counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does LIDAR data tell us about shorelines?
A) how the size of waves is related to water temperature
B) how the size of waves is related to salinity of seawater
C) changes in elevation,including destruction of houses
D) how the color of sand affects the air temperature
E) None of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the coastlines investigation,what do the embayments along the eastern coast probably reflect? 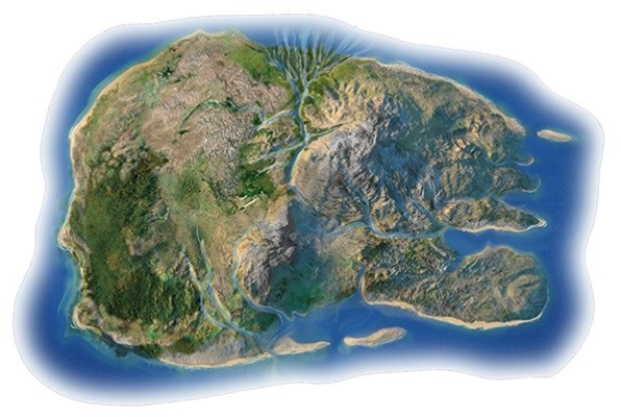
A) Sea cliffs
B) Marine terrace
C) Delta
D) Spit and sand bar
E) Submerged coastline
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagram below represents which stage of the U.S.Geological Survey's model of beach erosion? 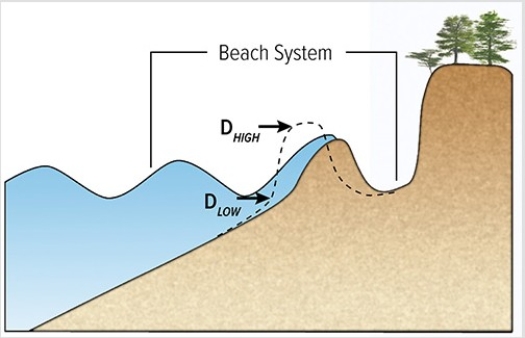
A) Swash regime
B) Collision regime
C) Overwash regime
D) Inundation regime
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which site will most likely experience rapid erosion? 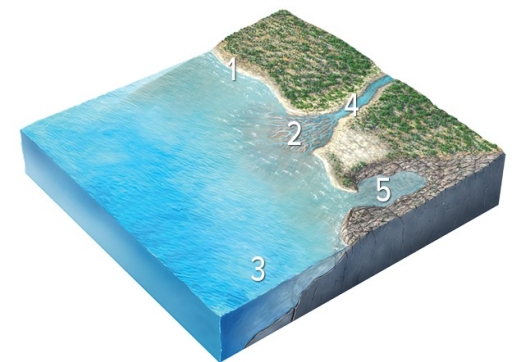
A) 1,cliffs composed of hard rocks
B) 2,sediments in a delta
C) 3,the seafloor deep beneath the waves
D) 4,the coastline of a bay
E) 5,the coastline in a branching embayment
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the coastlines investigation,what coastline feature is represented by the flat bench above the west coast? 
A) Sea cliffs
B) Marine terrace
C) Delta
D) Spit and sand bar
E) Submerged coastline
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The typical setting of a sea cave or sea stack is
A) within a protected bay.
B) on a barrier island.
C) on a sandbar.
D) on a baymouth bar.
E) on a promontory.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
High tides are higher than average and low tides are lower than average when
A) the Moon and the Sun are aligned relative to the Earth.
B) it is a full moon.
C) it is a new moon.
D) All of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sand and other sediment
A) can move laterally along the coast if waves approach the beach at an angle.
B) only move up and down the slope of the beach.
C) can slump downward if the sea bottom has too gentle a slope.
D) are moved by the wind if the material is coarser than sand.
E) All of these are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 80
Related Exams