A) trisomy
B) diploidy
C) monosomy
D) polyploidy
E) Down syndrome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During prophase II, a diploid organism contains how many copies of each gene?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Armadillos have a diploid chromosome number of 64. At prophase I, an armadillo's cell would have ________ tetrads present.
A) 16
B) 32
C) 64
D) 80
E) 128
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During G1 stage of interphase, a diploid organism contains how many copies of each gene?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 4
D) 8
E) 16
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which stage of meiosis will the pairs of homologous chromosomes line up?
A) metaphase I
B) metaphase II
C) metaphase
D) anaphase I
E) prophase II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following human syndromes is a monosomy?
A) Turner syndrome
B) Klinefelter syndrome
C) Down syndrome
D) Swyer syndrome
E) Barr body syndrome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Goats have a diploid chromosome number of 60. At prophase I, each cell would have ________ tetrads present, for a total of ________ chromatids.
A) 30; 120
B) 30; 60
C) 60; 120
D) 60; 240
E) 30; 240
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a function of meiosis?
A) cause an organism to grow
B) create genetic variability
C) reduce the chromosome number in gametes
D) keep the chromosome number constant from one generation to the next
E) produce gametes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A human egg with 22 chromosomes that is fertilized by a normal sperm will result in
A) a zygote with trisomy.
B) a zygote with disomy.
C) a zygote with monosomy.
D) a zygote with normal chromosome number.
E) nondisjunction during subsequent mitosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not correct about crossing-over?
A) Crossing-over is preceded by a process known as synapsis, where homologous chromosomes attach to each other.
B) Crossing-over results in greater genetic variability in offspring.
C) Crossing-over is only detectable when it occurs between sister chromatids.
D) Crossing-over occurs during prophase I when homologous chromosomes line up prior to separation.
E) In humans, crossing-over occurs an average of approximately two events per chromosome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Following meiosis I, the daughter cells are ________; following meiosis II, the daughter cells are ________; and following mitosis, the daughter cells are ________.
A) diploid; haploid; diploid
B) diploid; diploid; haploid
C) haploid; haploid; diploid
D) haploid; haploid; haploid
E) diploid; diploid; diploid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement best describes how the members of a tetrad are separated during meiosis I?
A) The two homologous chromosomes of a tetrad separate into different daughter nuclei.
B) The sister chromatids of each chromosome separate into different daughter nuclei.
C) The nonsister chromatids of each tetrad separate into different daughter nuclei.
D) The two homologous chromosomes of a tetrad separate into one of two daughter nuclei.
E) The two homologous chromosomes of a tetrad are duplicated and separate into each daughter nucleus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Klinefelter syndrome can result from nondisjunction during
A) meiosis I in the female parent.
B) meiosis I in the male parent.
C) meiosis I in either female parent.
D) meiosis I or II in the male parent.
E) meiosis I or II in either parent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the figure shown here, indicate the correct stage of meiosis and diploid chromosome number. 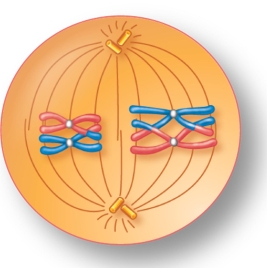
A) metaphase II, 2n=4
B) metaphase II, 2n=2
C) metaphase II, 2n=8
D) metaphase I, 2n=4
E) metaphase I, 2n=8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During meiosis II,
A) homologous chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing the same spindle pole.
B) chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
C) chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing the same spindle pole.
D) homologous chromosomes line up separately, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
E) homologous chromosomes line up together, with sister chromatids facing opposite spindle poles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Turner syndrome is associated with which of the following karyotypes?
A) 47, XXY
B) 47, XXX
C) 46, XY
D) 47, XY, trisomy 21
E) 45, XO
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the figure shown here, indicate the correct stage of meiosis and diploid chromosome number. 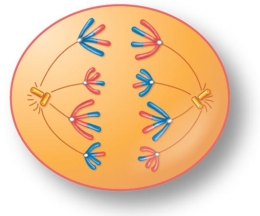
A) anaphase I, 2n=16
B) anaphase II, 2n=16
C) anaphase I, 2n=8
D) anaphase II, 2n=8
E) anaphase II, 2n=4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the diagrams best illustrates the appearance of a chromosome or chromosome pair at the end of prophase I?
A) diagram 1
B) diagram 2
C) diagram 3
D) diagram 4
E) diagram 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the figure shown here, indicate the correct stage of meiosis and the diploid number of the cell. 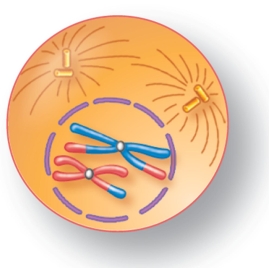
A) prophase I, 2n=4
B) prophase II, 2n=4
C) metaphase I, 2n=4
D) metaphase II, 2n=2
E) anaphase II, 2n=2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It would be possible for a male and a female to have exactly the same ________, but they would have to differ in ________.
A) diploid chromosomes; haploid chromosomes
B) autosomes; sex chromosomes
C) homologues; autosomes
D) karyotype; sex chromosomes
E) karyotype; autosomes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 53
Related Exams