A) Apoptosis is regulated by cell surface receptors that signal when a cell has reached its density-dependent limits.
B) During apoptosis, dying cells leak out their contents, including digestive enzymes that also destroy healthy cells.
C) During apoptosis, cellular agents chop up the DNA and fragment the organelles and other cytoplasmic components of a cell.
D) Each cell organelle has protein signals that initiate the breakdown of the organelle's components, which leads to cell death.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an adult person has a faulty version of the human analogue to ced-4 of the nematode, which of the following is most likely to result?
A) Activation of a developmental pathway found in the worm but not in humans.
B) A form of cancer in which there is insufficient apoptosis.
C) Formation of molecular pores in the mitochondrial outer membrane.
D) Excess skin loss will occur.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Protein kinase is an enzyme that functions in which of the following ways?
A) as a second messenger molecule
B) as a receptor for various signal molecules
C) activates or inactivates other proteins by adding a phosphate group to them
D) activates a G protein
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Caffeine is an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase. Therefore, the cells of a person who has recently consumed coffee would have increased levels of which of the following molecules?
A) phosphorylated proteins
B) cAMP
C) adenylyl cyclase
D) activated G proteins
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a neuron responds to a particular neurotransmitter by opening gated ion channels, the neurotransmitter is serving as which part of the signal pathway?
A) relay molecule
B) transducer
C) signal molecule
D) response molecule
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an animal cell suddenly lost the ability to produce GTP, what might happen to its signalling system?
A) It would not be able to activate G proteins on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane.
B) It would be able to carry out reception and transduction but would not be able to respond to a signal.
C) It would use ATP instead of GTP to activate G proteins on the cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane.
D) It would not be able to activate receptor tyrosine kinases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Viagra causes dilation of blood vessels and increased blood flow to the penis, facilitating erection. Viagra acts by inhibiting which of the following events?
A) hydrolysis of cGMP to GMP
B) hydrolysis of GTP to GDP
C) dephosphorylation of cGMP
D) formation of cGMP from GTP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the nematode C. elegans, ced-9 prevents apoptosis in a normal cell in which of the following ways?
A) It prevents the caspase activity of ced-3 and ced-4.
B) Ced-9 remains inactive until it is signalled by ced-3 and other caspases.
C) Ced-9 cleaves to produce ced-3 and ced-4.
D) Ced-9 prevents blebbing by its action on the cell membrane.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
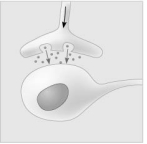 - Which of the following types of signalling is represented in the figure?
- Which of the following types of signalling is represented in the figure?
A) autocrine
B) paracrine
C) hormonal
D) synaptic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At puberty, an adolescent female body changes in both structure and function of several organ systems, primarily under the influence of changing concentrations of oestrogen and other steroid hormones. How can one hormone, such as oestrogen, mediate so many effects?
A) Oestrogen is produced in very large concentration by nearly every tissue of the body.
B) Each cell responds in the same way when steroids bind to the cell surface.
C) Oestrogen is kept away from the surface of any cells, not able to bind it at the surface.
D) Oestrogen binds to specific receptors inside many kinds of cells, each with different responses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because they ________.
A) are species-specific
B) always lead to the same cellular response
C) amplify the original signal many times
D) counter the harmful effects of phosphatases
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true during a typical cAMP-mediated signal transduction event?
A) The second messenger is the last part of the system to be activated.
B) A hormone activates the second messenger by directly binding to it.
C) The second messenger amplifies the hormonal response by attracting more hormones to the cell being affected.
D) Adenylyl cyclase is activated after the hormone binds to the cell and before phosphorylation of proteins occurs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sutherland discovered that the signalling molecule adrenaline is responsible for which of the following events?
A) Stimulating glycogen synthesis.
B) Decreasing blood glucose levels.
C) Interacting directly with glycogen phosphorylase.
D) Elevating cytosolic concentrations of cyclic AMP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which observation suggested to Sutherland the involvement of a second messenger in adrenalineadrenaline's effect on liver cells?
A) Enzymatic activity was proportional to the amount of calcium added to a cell-free extract.
B) Receptor studies indicated that adrenaline adrenalinewas a ligand.
C) Glycogen breakdown was observed only when adrenaline adrenalinewas administered to intact cells.
D) Glycogen breakdown was observed only when adrenaline adrenalineand glycogen phosphorylase were mixed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why has C. elegans proven to be a useful model for understanding apoptosis?
A) C. elegans does not naturally use apoptosis, but can be induced to do so in the laboratory.
B) C. elegans undergoes a fixed and easy-to-visualise number of apoptotic events during its normal development.
C) C. elegans has large cells wherein apoptosis is easily observed without the aid of a microscope.
D) As C. elegans ages, its cells die progressively until the whole organism is dead.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a pharmaceutical company wished to design a drug to maintain low blood sugar levels, one approach might be to design a compound that does which of the following?
A) activates adrenaline receptors in liver cells
B) increases cAMP production in liver cells
C) blocks G protein activity in liver cells
D) increases glycogen phosphorylase activity in liver cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Binding of a signalling molecule to which type of receptor leads directly to a change in the distribution of ions on opposite sides of the membrane?
A) receptor tyrosine kinase
B) G protein-coupled receptor
C) ligand-gated ion channel
D) steroid receptor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What role do phosphatases play in signal transduction pathways?
A) They transfer a phosphate group from one protein in the pathway to the next molecule in the series.
B) They activate protein kinases by phosphorylation.
C) They amplify the second messenger cAMP.
D) They inactivate protein kinases to turn off signal transduction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mutation that knocks out the GTPase activity of a G protein would have what effect on a cell?
A) The concentration of available GTP would decrease.
B) The number of G proteins in the cell would increase.
C) The G protein would be inactivated by a G protein-coupled receptor/signal molecule complex.
D) The G protein would always be active.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following provides the best evidence that cell-signalling pathways evolved early in the history of life?
A) Cell-signalling pathways are seen in "primitive" cells such as bacteria and yeast.
B) Bacteria and yeast cells signal each other in a process called "quorum sensing".
C) Signal transduction molecules identified in distantly related organisms are similar.
D) Most signals in all types of cells are received by cell surface receptors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 65
Related Exams