A) occur inside cells in most animals.
B) add a water molecule to break bonds.
C) require a low pH resulting from HCl production.
D) consume ATP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After surgical removal of an infected gallbladder, a person must be especially careful to restrict dietary intake of ________.
A) protein
B) sugar
C) fat
D) water
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When used appropriately, antibiotic treatment can effectively reduce bacteria populations and help fight infections. However, antibiotic treatments can have unintended effects. What is one concern when using antibiotics?
A) Antibiotics also damage animal cells, so they can be more harmful than a bacterial infection.
B) Antibiotics cause viruses to become more effective at infecting cells.
C) Each antibiotic is only effective against one type of bacteria, so effects on infection are limited.
D) Antibiotics may also kill the beneficial bacteria of the microbiome, thereby disrupting digestive health.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Food being digested in the stomach is in a highly acidic environment. When the food is released from the stomach into the small intestine, why is the environment no longer acidic?
A) Secretin increases the flow of bicarbonate ions from the pancreas into the small intestine to neutralise the stomach acid.
B) Trypsinogen is activated, thus neutralising the stomach acid.
C) Bile salts from the gallbladder neutralise the stomach acid.
D) When pepsinogen activates pepsin, one result is the neutralisation of stomach acid in the stomach.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Animals cannot produce enzymes to digest cellulose, yet many white ant species consume cellulose from plant material as a main part of their diet. How do white ants access the nutrients contained in cellulose?
A) White ants have specialised mouthparts to mechanically break down the cellulose.
B) The ingested plant material also contains enzymes for cellulose digestion.
C) Cellulose is digested intracellularly in the white ant hindgut.
D) Mutualistic bacteria in the hindgut of the white ant digest the cellulose into sugars.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What benefit is gained by intestinal bacteria living in a mutualistic relationship with an animal?
A) The bacteria are provided with a regular source of nutrients.
B) Temperature is always regulated.
C) The bacteria can easily infect the animal's intestinal cells.
D) The bacteria can avoid the animal's immune system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a difference between vitamins and minerals?
A) Vitamins are involved in regulating enzyme activity, but minerals are not.
B) Vitamins are organic molecules, but minerals are inorganic molecules.
C) Minerals are obtained by an animal through dietary sources, but vitamins are made by the animal.
D) Vitamins and minerals are only obtained by digesting plants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you were to jog 1 km a few hours after lunch, which stored fuel would you probably tap?
A) muscle proteins
B) muscle and liver glycogen
C) fat in the liver
D) fat in adipose tissue
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a major activity of the stomach?
A) storage
B) HCl production
C) nutrient absorption
D) enzyme secretion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fat digestion yields fatty acids and glycerol, whereas protein digestion yields amino acids; both digestive processes ________.
A) are catalysed by the same enzyme
B) use water molecules when breaking bonds (hydrolysis)
C) require the presence of hydrochloric acid to lower the pH
D) require adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as an energy source
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over-the-counter medications for acid reflux or heartburn block the production of stomach acid. Which of the following cells are directly affected by this medication?
A) goblet cells
B) chief cells
C) parietal cells
D) smooth muscle cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The function of chylomicrons is to ________.
A) digest nucleic acids in the intestine
B) break down carbohydrates in the mouth
C) transport lipids from the intestine to other organs
D) move proteins across plasma membranes of cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stomach cells are moderately well adapted to the acidity and protein-digesting activities in the stomach by having ________.
A) a sufficient colony of H. pylori
B) a thick, mucous secretion and active mitosis of epithelial cells
C) a high level of secretion of enzymes by chief cells
D) a cell wall impermeable to acid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ticks are parasites that obtain nutrients by ingesting blood from a host animal. Ticks would be classified as ________.
A) filter feeders
B) substrate feeders
C) fluid feeders
D) bulk feeders
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Examine the digestive system structures in the figure. 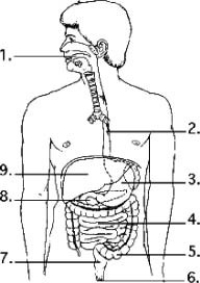 - Bacteria that produce vitamins are found in the greatest concentration in location ________.
- Bacteria that produce vitamins are found in the greatest concentration in location ________.
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process by which digested dietary substances cross cell membranes to be used by the body is known as ________.
A) ingestion
B) digestion
C) hydrolysis
D) absorption
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Obesity in humans is most clearly linked to ________.
A) type 1 diabetes and prostate cancer
B) type 2 diabetes and muscle hypertrophy
C) type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease
D) type 2 diabetes and decreased appetite
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the digestive system, "peristalsis" is ________.
A) a process of fat emulsification in the small intestine
B) voluntary control of the rectal sphincters regulating defecation
C) the transport of nutrients to the liver through the hepatic portal vessel
D) smooth muscle contractions that move food along the oesophagus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A relatively long cecum is characteristic of animals that are ________.
A) carnivores
B) herbivores
C) autotrophs
D) omnivores
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following organs is incorrectly paired with its function?
A) stomach-protein digestion
B) large intestine-bile production
C) small intestine-nutrient absorption
D) pancreas-enzyme production
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 64
Related Exams