A) the number of fish in these populations has increased dramatically.
B) the age and size of fish reaching sexual maturity have decreased.
C) many new species of predators have evolved in these regions.
D) the affected fish species have stopped reproducing.
E) many of the fish in these populations have started to reproduce asexually.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do animals as diverse as corals and monkeys have in common?
A) body cavity between body wall and digestive system
B) number of embryonic tissue layers
C) type of body symmetry
D) presence of Hox genes
E) degree of cephalization
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do all craniates have that earlier chordates did not have?
A) brain
B) vertebrae
C) cartilaginous pipe surrounding notochord
D) partial or complete skull
E) bone
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An elementary school science teacher decided to liven up the classroom with a saltwater aquarium. Knowing that saltwater aquaria can be quite a hassle, the teacher proceeded stepwise. First, the teacher conditioned the water. Next, the teacher decided to stock the tank with various marine invertebrates, including a polychaete, a siliceous sponge, several bivalves, a shrimp, several sea anemones of different types, a colonial hydra, a few coral species, an ectoproct, a sea star, and several herbivorous gastropod varieties. Last, she added some vertebrates-a parrotfish and a clownfish. She arranged for daily feedings of copepods and feeder fish. -Had the teacher wanted to point out organisms that belong to the most successful animal phylum, the teacher should have chosen the
A) bivalves and gastropods.
B) sea anemones and hydra.
C) shrimp and copepods.
D) polychaete.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whatever its ultimate cause(s) , the Cambrian explosion is a prime example of
A) mass extinction.
B) evolutionary stasis.
C) adaptive radiation.
D) a large meteor impact.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of members of the phylum Cnidaria?
A) They are not capable of locomotion because they lack true muscle tissue.
B) They are primarily filter feeders.
C) They have either, or both, of two body forms: mobile polyps and sessile medusae.
D) They may use a gastrovascular cavity as a hydrostatic skeleton.
E) They are the simplest organisms with a complete alimentary canal (two openings) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
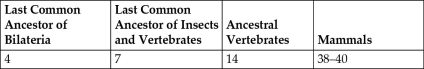 Table 27.1. Proposed Number of Hox Genes in Various Extant and Extinct Animals
-All things being equal, which of these is the most parsimonious explanation for the change in the number of Hox genes from the last common ancestor of insects and vertebrates to ancestral vertebrates, as shown in Table 27.1?
Table 27.1. Proposed Number of Hox Genes in Various Extant and Extinct Animals
-All things being equal, which of these is the most parsimonious explanation for the change in the number of Hox genes from the last common ancestor of insects and vertebrates to ancestral vertebrates, as shown in Table 27.1?
A) The occurrence of seven independent duplications of individual Hox genes.
B) The occurrence of two distinct duplications of the entire seven-gene cluster, followed by the loss of one cluster.
C) The occurrence of a single duplication of the entire seven-gene cluster.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Terry catches a ray-finned fish from the ocean and notices that attached to its flank is an equally long, snakelike organism. The attached organism has no external segmentation, no scales, a round mouth surrounded by a sucker, and two small eyes. Terry thinks it might be a marine leech, a hagfish, or a lamprey. -Which feature excludes the organism from possibly being a leech?
A) elongated shape
B) lack of scales
C) lack of external segmentation
D) round mouth
E) anterior sucker
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most ancient branch point in animal phylogeny is that between having
A) radial or bilateral symmetry.
B) a well-defined head or no head.
C) diploblastic or triploblastic embryos.
D) true tissues or no tissues.
E) a body cavity or no body cavity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cycliophorans have two types of larvae. One type of larva is produced when the digestive system of a female is impregnated by a male. The digestive system then collapses and develops into a larva, which swims away in search of a new host after the surrounding female dies. Which is the embryonic tissue that is apparently most important in forming this type of larva?
A) mesohyl
B) mesoderm
C) ectoderm
D) endoderm
E) mesoglea
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fossil steroid and molecular clock evidence suggests that animals originated
A) between 770 and 710 million years ago.
B) more than 100 million years before the oldest known fossils of large animals.
C) during the Cambrian explosion.
D) after sponges diverged from other metazoans.
E) both A and B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a physoclistus fish removes gas from its swim bladder, this fish's density cannot actually change until that gas arrives at the
A) mouth.
B) gills.
C) skin.
D) heart.
E) anus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the extant vertebrate group with the description. Internal fertilization, leathery amniotic egg, and skin that resists drying are characteristics of
A) amphibians.
B) nonbird reptiles.
C) chondrichthyans.
D) mammals.
E) birds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements concerning animal taxonomy is (are) true? 1. Animals are more closely related to plants than to fungi. 2) All animal clades based on body plan have been found to be incorrect. 3) Kingdom Animalia is monophyletic. 4) Only animals reproduce by sexual means. 5) Animals are thought to have evolved from flagellated protists similar to modern choanoflagellates.
A) 5 only
B) 1 and 3
C) 3 and 5
D) 3, 4, and 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The feeding mode of the extinct conodonts was
A) herbivory.
B) suspension feeding.
C) predation.
D) filter feeding.
E) absorptive feeding.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Trichoplax adhaerens (Tp) is the only living species in the phylum Placozoa. Individuals are about 1 mm wide and only 27 μm high, are irregularly shaped, and consist of a total of about 2,000 cells, which are diploid (2n = 12) . There are four types of cells, none of which is a nerve or muscle cell, and none of which has a cell wall. They move using cilia, and any "edge" can lead. Tp feeds on marine microbes, mostly unicellular green algae, by crawling atop the algae and trapping it between its ventral surface and the substrate. Enzymes are then secreted onto the algae, and the resulting nutrients are absorbed. Tp sperm cells have never been observed, nor have embryos past the 64-cell (blastula) stage. -In how many of the following ways is Tp unlike the typical animal? 1. Tp is multicellular. 2) Tp lacks muscle and nerve cells. 3) Tp has cilia. 4) Tp has a different place where digestion of food occurs. 5) Tp lacks cell walls.
A) only one way
B) two ways
C) three ways
D) four ways
E) all five ways
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
We should expect the inner wall of the swim bladder to be lined with tissue that is derived from
A) ectoderm.
B) endoderm.
C) mesoderm.
D) mesoglea.
E) neurectoderm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following animal groups is entirely aquatic?
A) Mollusca
B) Crustacea
C) Echinodermata
D) Nematoda
E) Platyhelminthes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most recently discovered phylum in the animal kingdom (1995) is the phylum Cycliophora. It includes three species of tiny organisms that live in large numbers on the outsides of the mouthparts and appendages of lobsters. The feeding stage permanently attaches to the lobster via an adhesive disk, and collects scraps of food from its host's feeding by capturing the scraps in a current created by a ring of cilia. The body is sac-like and has a U-shaped intestine that brings the anus close to the mouth. Cycliophorans are eucoelomate, do not molt (though their host does) , and their embryos undergo spiral cleavage. -Which of these features is least useful in assigning the phylum Cycliophora to a clade of animals?
A) having a true coelom as a body cavity
B) having a body symmetry that permits a U-shaped intestine
C) having embryos with spiral cleavage
D) lacking ecdysis (molting)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is most consistent with the hypothesis that the Cambrian explosion was caused by the rise of predator-prey relationships?
A) increased incidence of worm burrows in the fossil record
B) increased incidence of larger animals in the fossil record
C) increased incidence of organic material in the fossil record
D) increased incidence of fern galls in the fossil record
E) increased incidence of hard parts in the fossil record
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 107
Related Exams