A) I or V
B) II or IV
C) III only
D) IV only
E) V only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Researchers began a study of a cultured cell line. Their preliminary observations showed them that the cell line did not exhibit either density-dependent inhibition or anchorage dependence. What could they conclude right away?
A) The cells originated in the nervous system.
B) The cells are unable to form spindle microtubules.
C) The cells have altered series of cell cycle phases.
D) The cells show characteristics of tumors.
E) The cells were originally derived from an elderly organism.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The beginning of anaphase is indicated by which of the following?
A) Chromatids lose their kinetochores.
B) Cohesin attaches the sister chromatids to each other.
C) Cohesin is cleaved enzymatically.
D) Kinetochores attach to the metaphase plate.
E) Spindle microtubules begin to polymerize.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to most prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells typically have
A) more DNA molecules and larger genomes.
B) the same number of DNA molecules but larger genomes.
C) the same number of DNA molecules and similarly sized genomes.
D) fewer DNA molecules but larger genomes.
E) fewer DNA molecules and smaller genomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is produced if a cell divides by mitosis but does not undergo cytokinesis?
A) two cells, one cell containing two nuclei and a second cell without a nucleus
B) two cells, each cell with half of the genetic material of the parent cell
C) one cell with one nucleus containing half of the genetic material of the parent cell
D) one cell with two nuclei, each identical to the nucleus of the parent cell
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true concerning cancer cells?
A) They do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture.
B) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle.
C) They are not subject to cell cycle controls.
D) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle, and they are not subject to cell cycle controls.
E) When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle; they are not subject to cell cycle controls; and they do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Motor proteins require which of the following to function in the movement of chromosomes toward the poles of the mitotic spindle?
A) intact centromeres
B) a microtubule-organizing center
C) a kinetochore attached to the metaphase plate
D) ATP as an energy source
E) synthesis of cohesin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on Figure 9.3.
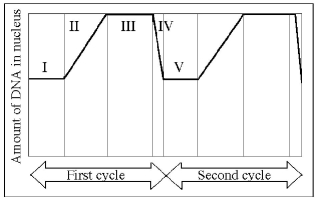 Figure 9.3
-In Figure 9.3, mitosis is represented by which numbered part(s) of the cycle?
Figure 9.3
-In Figure 9.3, mitosis is represented by which numbered part(s) of the cycle?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly forming DNA and can therefore be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student-faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into the culture of dividing human cells at specific times. -In the cells of some organisms, mitosis occurs without cytokinesis. This will result in
A) cells with more than one nucleus.
B) cells that are unusually small.
C) cells lacking nuclei.
D) destruction of chromosomes.
E) cell cycles lacking an S phase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on Figure 9.3.
 Figure 9.3
-Which number represents the point in the cell cycle during which the chromosomes are replicated?
Figure 9.3
-Which number represents the point in the cell cycle during which the chromosomes are replicated?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the M phase checkpoint, the complex allows for what to occur?
A) Separase enzyme cleaves cohesins and allows chromatids to separate.
B) Cohesins alter separase to allow chromatids to separate.
C) Kinetochores are able to bind to spindle microtubules.
D) All microtubules are made to bind to kinetochores.
E) Daughter cells are allowed to pass into G1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly forming DNA and can therefore be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student-faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into the culture of dividing human cells at specific times. -The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. Which of the following aspects of the animal cell cycle would be most disrupted by cytochalasin B?
A) spindle formation
B) spindle attachment to kinetochores
C) DNA synthesis
D) cell elongation during anaphase
E) cleavage furrow formation and cytokinesis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is released by platelets in the vicinity of an injury?
A) PDGF
B) MPF
C) protein kinase
D) cyclin
E) Cdk
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly forming DNA and can therefore be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student-faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into the culture of dividing human cells at specific times. -A particular cell has half as much DNA as some other cells in a mitotically active tissue. The cell in question is most likely in
A) G1.
B) G2.
C) prophase.
D) metaphase.
E) anaphase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are primarily responsible for cytokinesis in plant cells but not in animal cells?
A) kinetochores
B) Golgi-derived vesicles
C) actin and myosin
D) centrioles and centromeres
E) tubulin and dynein
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms would be found at the end of S and the end of G2?
A) 8; 8
B) 8; 16
C) 16; 8
D) 16; 16
E) 12; 16
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You have the technology necessary to measure each of the following in a sample of animal cells: chlorophylls, organelle density, picograms of DNA, cell wall components, and enzymatic activity. Which would you expect to increase significantly from M to G1?
A) organelle density and enzymatic activity
B) cell wall components and DNA
C) chlorophyll and cell walls
D) organelle density and cell walls
E) chlorophyll and DNA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following information applies to the questions below. Several organisms, primarily protists, have what are called intermediate mitotic organization. -What is the most probable hypothesis about these intermediate forms of cell division?
A) They represent a form of cell reproduction that must have evolved completely separately from those of other organisms.
B) They demonstrate that these species are not closely related to any of the other protists and may well be a different kingdom.
C) They rely on totally different proteins for the processes they undergo.
D) They may be more closely related to plant forms that also have unusual mitosis.
E) They show some but not all of the evolutionary steps toward complete mitosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) ?
A) Cdk is inactive, or "turned off," in the presence of cyclin.
B) Cdk is present throughout the cell cycle.
C) Cdk is an enzyme that attaches phosphate groups to other proteins.
D) Cdk is inactive, or "turned off," in the presence of cyclin and it is present throughout the cell cycle.
E) Cdk is present throughout the cell cycle and is an enzyme that attaches phosphate groups to other proteins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there are 20 chromatids in a cell, how many centromeres are there?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 40
E) 80
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 63
Related Exams