A) Break the cough drop into little pieces and put them all in your mouth. Since each little piece must be dissolved separately, the drop will last longer.
B) Keep the cough drop whole. This maintains the largest surface-to-volume ratio and slows the dissolution of the cough drop.
C) Break the cough drop into little pieces and put them all in your mouth. This decreases the surface-to-volume ratio and slows the dissolution of the cough drop.
D) It doesn't matter if the cough drop is in one piece or many pieces; the total amount of cough drop is all that matters.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tay-Sachs disease
A) causes an accumulation of lipids in brain cells.
B) involves damage to liver cells.
C) is due to the absence of an enzyme that digests polysaccharides.
D) prevents the breakdown of glycogen.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about internal membranes in eukaryotic cells is false?
A) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes greatly increase a cell's total membrane area.
B) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes provide an additional area for many metabolic processes to occur.
C) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes form membranous compartments called organelles.
D) In eukaryotic cells, internal membranes standardize the internal environment of all cellular organelles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
GPCRs are receptor proteins found in the plasma membrane that are important for cellular communication. What cellular structure makes GPCRs?
A) the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
B) the rough endoplasmic reticulum
C) Golgi apparatus
D) mitochondria
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A basal body is
A) composed of nine microtubule triplets surrounding a central pair of microtubules.
B) similar in structure to centrioles.
C) composed of nine microtubule doublets surrounding a central pair of microtubules.
D) identical in structure to cilia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Much of the intracellular structure of a eukaryote cell is involved in protein synthesis. The accompanying figure shows the amounts of protein in cells at different parts of the cell cycle between two cell divisions. G1 is a stage just after the cell has divided, and G2 is the stage just before the cell divides again. S is a stage when the cell is synthesizing material such as DNA, mitochondria, and other organelles. -The protein measured in the cells was likely synthesized by
A) mitochondria.
B) the nucleolus.
C) the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
D) ribosomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about lysosomes is false?
A) Lysosomes help to digest worn-out or damaged organelles.
B) Lysosomes synthesize proteins from the recycled amino acids.
C) Lysosomes fuse with food vacuoles to expose nutrients to lysosomal enzymes.
D) Lysosomes destroy harmful bacteria engulfed by white blood cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The function of chloroplasts is
A) cellular respiration.
B) lipid synthesis.
C) photosynthesis.
D) intracellular digestion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Insulin is a protein that is produced by pancreatic cells and secreted into the bloodstream. Which of the following options correctly lists the order of the structures through which insulin passes from its production to its exit from the cell?
A) rough ER, transport vesicles, Golgi apparatus, transport vesicles, cell membrane
B) rough ER, lysosomes, transport vesicles, cell membrane
C) rough ER, Golgi apparatus, smooth ER, cell membrane
D) rough ER, transport vesicles, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, cell membrane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dynein feet
A) are present in cilia but not in flagella.
B) are knobs of carbohydrate that are essential to the movement of cilia and flagella.
C) are found on microtubules in cilia and flagella and cause movement by grabbing and pulling at adjacent microtubule doublets.
D) are the anchoring proteins in basal bodies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Skin cells are fastened into strong sheets by
A) basal bodies.
B) anchoring junctions.
C) tight junctions.
D) gap junctions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
A) stores calcium ions in muscle cells.
B) is the major site of carbohydrate synthesis in eukaryotic cells.
C) produces proteins for cell membranes.
D) helps assemble ribosomes for protein synthesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A woman is having trouble becoming pregnant. Examination of her partner's sperm indicates that dynein feet are missing from the flagella in his sperm cells. A physician explains that this could interfere with fertility by
A) preventing the sperm from attaching to the egg cell.
B) preventing the sperm from swimming to the egg cell.
C) preventing the sperm from producing enough energy to power swimming.
D) interfering with the attachment of the flagella to the sperm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell is exposed to a substance that prevents it from dividing. The cell becomes larger and larger. This situation
A) should present no problem to the cell, since it can continue to perform all other necessary functions.
B) should present no problem to the cell, because the surface area of the cell will increase as the volume of the cell increases.
C) will eventually be problematic, since the cell's ability to absorb nutrients through its outer membrane will not increase as quickly as its cytoplasmic needs.
D) should be beneficial, since the cell will be able to divert the ATP normally used for cell division to other processes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
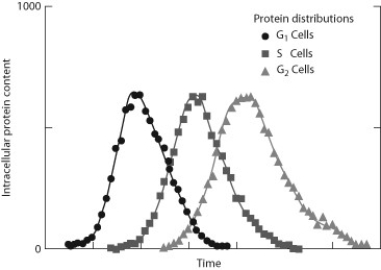 Much of the intracellular structure of a eukaryote cell is involved in protein synthesis. The accompanying figure shows the amounts of protein in cells at different parts of the cell cycle between two cell divisions. G1 is a stage just after the cell has divided, and G2 is the stage just before the cell divides again. S is a stage when the cell is synthesizing material such as DNA, mitochondria, and other organelles.
-The data show that
Much of the intracellular structure of a eukaryote cell is involved in protein synthesis. The accompanying figure shows the amounts of protein in cells at different parts of the cell cycle between two cell divisions. G1 is a stage just after the cell has divided, and G2 is the stage just before the cell divides again. S is a stage when the cell is synthesizing material such as DNA, mitochondria, and other organelles.
-The data show that
A) at any given time there are more cells in G2 than G1.
B) protein used in G1 is recycled to produce protein in S.
C) not all cells at any given stage have the same amount of protein.
D) protein levels in cells remain constant throughout the cell cycle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ cells lack a membrane-enclosed nucleus.
A) Plant
B) Prokaryotic
C) Eukaryotic
D) Fungal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As cell size increases, the
A) volume and surface area decrease.
B) volume increases proportionally more than the surface area.
C) surface area increases proportionally more than the volume.
D) ratio of surface area to volume stays the same.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bacterial cell's DNA is found in its
A) ribosomes.
B) nucleus.
C) nucleoid.
D) capsule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unlike animal cells, plant cells have ________ and ________. Unlike plant cells, animal cells have ________.
A) chloroplasts; cell walls; centrioles
B) centrioles; chloroplasts; cell walls
C) chloroplasts; cell walls; a nucleus
D) centrioles; cell walls; large central vacuoles
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A drug that interferes with microtubule formation is likely to completely disrupt
A) the amoeboid motion of a cell.
B) the function of lysosomes.
C) contraction of muscle cells.
D) the movements of sperm cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 93
Related Exams