A) Species 2 wins.
B) If species 1 begins with a higher abundance,it wins.
C) If species 2 begins with a higher abundance,it wins.
D) Species 1 wins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two organisms using a portion of the same resource simultaneously is referred to as
A) niche overlap.
B) competitive release.
C) intraspecific competition.
D) territoriality.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Encounter competition results from the behavioral exclusion of some individuals by others from a specific space that is defended.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Competition typically
A) only involves two closely related species.
B) involves a predator and prey.
C) is a complex interaction of biotic and abiotic factors.
D) is random.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The diagonal line that represents dN/dt = 0 in the graphical depiction of the Lotka-Volterra competitions equations is called
A) a competition coefficient.
B) the carrying capacity.
C) a zero-growth isocline.
D) a competitive exclusion parameter.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A shift in the morphology,behavior,or physiology of a species in response to resource competition is referred to as ________ displacement.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
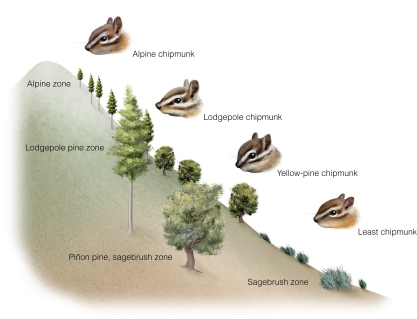 The different chipmunk species correspond to the different tree species along an elevational gradient.This is likely because
The different chipmunk species correspond to the different tree species along an elevational gradient.This is likely because
A) each chipmunk species depends on the specific tree species for habitat.
B) lodgepole trees and lodgepole chipmunks prefer warmer temperatures.
C) the fundamental niche of yellow-pine chipmunks is limited to middle elevation.
D) several resource factors for both groups change with elevation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
When a species expands its niche in response to the removal of a competitor,the species has experienced competitive ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is a zero-growth isocline?
A) when the population size of species 1 exceeds species 2
B) the set of values where α = β
C) the set of values of two population sizes where the growth rate is 0
D) the set of values where the carrying capacity is reached for one of the two species
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Studying competition in the laboratory is more complex than studying competition in the field.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The portion of the fundamental niche that an organism actually exploits in the presence of competitors is called its ________ niche.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Species A prefers a more dry habitat but grows in a wet habitat.Why might this be?
A) Species B outcompetes A in the dry habitat.
B) Species A's fundamental niche is restricted to a wet habitat.
C) Species A requires large amounts of moisture to grow.
D) Species B prefers a wet habitat.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two bird species compete in the forest for the same seeds.If α = 0.75 and β = 0.25,then (assuming the same carrying capacity for both)
A) the rate of seed consumption is the same for both species.
B) the environment can supply both species since the sum of competition coefficients equals 1.
C) species 1 "wins" and will outcompete species 2.
D) species 2 "wins" and will outcompete species 1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Two or more organisms using a portion of the same resource simultaneously is referred to as resource partitioning.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Interspecific ________ occurs when the competition for space between two species influences access to food and nesting sites.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
According to the competitive ________ principle,two "complete competitors" cannot coexist.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Various species of scavengers fighting over the carcass of a dead animal is referred to as
A) consumption competition.
B) preemptive competition.
C) encounter competition.
D) overgrowth competition.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Demonstrating the occurrence of interspecific competition during a field study is problematic for all of the following reasons,except
A) it is difficult to know whether a population is at carrying capacity.
B) competition is impossible to measure in a natural setting.
C) scientists cannot control the environment.
D) scientists lack full knowledge of the life history requirements of natural populations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One effect of decreasing wolf populations in North America is
A) decreased deer populations.
B) range expansion for coyotes.
C) range retraction for elk.
D) increased bear populations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Chemical interaction competition in plants is called ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 65
Related Exams