A) a coenzyme
B) an allosteric inhibitor
C) the substrate
D) an intermediate
E) a competitive inhibitor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -You have discovered an enzyme that can catalyze two different chemical reactions. Which of the following is most likely to be correct?
-You have discovered an enzyme that can catalyze two different chemical reactions. Which of the following is most likely to be correct?
A) The enzyme contains α-helices and β-pleated sheets.
B) The enzyme is subject to competitive inhibition and allosteric regulation.
C) Two types of allosteric regulation occur: The binding of one molecule activates the enzyme, while the binding of a different molecule inhibits it.
D) Either the enzyme has two distinct active sites or the reactants involved in the two reactions are very similar in size and shape.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the induced fit hypothesis of enzyme catalysis, ________.
A) the binding of the substrate depends on the shape of the active site
B) some enzymes change their structure when activators bind to the enzyme
C) a competitive inhibitor can outcompete the substrate for the active site
D) the binding of the substrate changes the shape of the enzyme's active site
E) the active site creates a microenvironment ideal for the reaction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the accompanying figure. 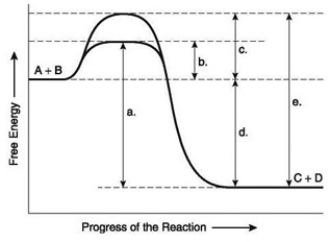 -HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. In the mid-1990s, researchers discovered an enzyme in HIV called protease. Once the enzyme's structure was known, researchers began looking for drugs that would fit into the active site and block it. If this strategy for stopping HIV infections were successful, it would be an example of what phenomenon?
-HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. In the mid-1990s, researchers discovered an enzyme in HIV called protease. Once the enzyme's structure was known, researchers began looking for drugs that would fit into the active site and block it. If this strategy for stopping HIV infections were successful, it would be an example of what phenomenon?
A) vaccination
B) denaturation
C) allosteric regulation
D) competitive inhibition
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is a logical consequence of the second law of thermodynamics?
A) If the entropy of a system increases, there must be a corresponding decrease in the entropy of the universe.
B) If there is an increase in the energy of a system, there must be a corresponding decrease in the energy of the rest of the universe.
C) Every energy transfer requires activation energy from the environment.
D) Every chemical reaction must increase the total entropy of the universe.
E) Energy can be transferred or transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a laboratory experiment, you discover that an enzyme-catalyzed reaction has a ∆G of -20 kcal/mol. If you double the amount of enzyme in the reaction, what will be the ∆G for the new reaction?
A) -40 kcal/mol
B) -20 kcal/mol
C) 0 kcal/mol
D) +20 kcal/mol
E) +40 kcal/mol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You collect data on the effect of pH on the function of the enzyme catalase in human cells. Which of the following graphs would you expect?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of potential rather than kinetic energy?
A) the muscle contractions of a person mowing grass
B) water rushing over Niagara Falls
C) light flashes emitted by a firefly
D) a molecule of glucose
E) a crawling beetle foraging for food
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increasing the substrate concentration in an enzymatic reaction could overcome which of the following?
A) the need for a coenzyme
B) allosteric inhibition
C) competitive inhibition
D) insufficient cofactors
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Enthalpy (H) is the ________.
A) total kinetic energy of a system
B) total energy in biological systems
C) system's entropy
D) cell's energy equilibrium
E) condition of a cell that is not able to react
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the question(s) below. A series of enzymes catalyze the reaction X → Y → Z → A. Product A binds to the enzyme that converts X to Y at a position remote from its active site. This binding decreases the activity of the enzyme. -Some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because ________.
A) they are able to maintain a lower internal temperature
B) high temperatures make catalysis unnecessary
C) their enzymes have high optimal temperatures
D) their enzymes are completely insensitive to temperature
E) they use molecules other than proteins or RNAs as their main catalysts
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mechanism in which the end product of a metabolic pathway inhibits an earlier step in the pathway is most precisely described as ________.
A) metabolic inhibition
B) feedback inhibition
C) allosteric inhibition
D) noncooperative inhibition
E) reversible inhibition
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the accompanying figure.  -Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in the figure?
-Which of the following terms best describes the forward reaction in the figure?
A) endergonic, ∆G > 0
B) exergonic, ∆G < 0
C) endergonic, ∆G < 0
D) exergonic, ∆G > 0
E) chemical equilibrium, ∆G = 0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is ATP an important molecule in metabolism?
A) Its hydrolysis provides an input of free energy for exergonic reactions.
B) It provides energy coupling between exergonic and endergonic reactions.
C) Its terminal phosphate group contains a strong covalent bond that, when hydrolyzed, releases free energy.
D) Its terminal phosphate bond has higher energy than the other two phosphate bonds.
E) It is one of the four building blocks for DNA synthesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A chemical reaction that has a positive ΔG is best described as ________.
A) endergonic
B) entropic
C) enthalpic
D) spontaneous
E) exergonic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -Consider the HIV enzyme called protease. The amino acid residues at the active site are highly hydrophobic. In designing a drug that would bind to the active site and jam it, researchers should use a molecule that is ________.
-Consider the HIV enzyme called protease. The amino acid residues at the active site are highly hydrophobic. In designing a drug that would bind to the active site and jam it, researchers should use a molecule that is ________.
A) hydrophobic
B) polar
C) charged
D) acidic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the accompanying figure.  -Which of the following represents the activation energy needed for the enzyme-catalyzed reverse reaction, C + D → A + B, in the figure?
-Which of the following represents the activation energy needed for the enzyme-catalyzed reverse reaction, C + D → A + B, in the figure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is TRUE of enzymes?
A) Enzyme function is increased if the 3-D structure or conformation of an enzyme is altered.
B) Enzyme function is independent of physical and chemical environmental factors such as pH and temperature.
C) Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reaction by lowering activation energy barriers.
D) Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reaction by providing activation energy to the substrate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the pair of terms that correctly completes this sentence: Catabolism is to anabolism as ________ is to ________.
A) exergonic; spontaneous
B) exergonic; endergonic
C) free energy; entropy
D) work; energy
E) entropy; enthalpy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To attach a particular amino acid to the tRNA molecule that will transport it, an enzyme, an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, is required, along with ATP. Initially, the enzyme has an active site for ATP and another for the amino acid, but it is not able to attach the tRNA. What must occur for the final attachment to occur?
A) The ATP must first have to attach to the tRNA.
B) The binding of the first two molecules must cause a 3-D change that opens another active site on the enzyme.
C) The ATP must be hydrolyzed to allow the amino acid to bind to the synthetase.
D) The tRNA molecule must alter its shape to be able to fit into the active site with the other two molecules.
E) The 3' end of the tRNA must be cleaved before it can have an attached amino acid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 60
Related Exams