A) $15.
B) $25.
C) $40.
D) $65.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists use the phrase ceteris paribus to express the assumption
A) "all else equal."
B) "everything affects everything else."
C) "scarcity is a fact of life."
D) "there is no such thing as a free lunch."
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fallacy of composition is
A) the belief that if Event A happens before Event B happens, then Event A causes Event B to occur.
B) the belief that what is true for the whole is necessarily true of the parts.
C) the belief that what is true for a part is necessarily true for the whole.
D) the belief that it is impossible to draw generalizations about cause and effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An efficient market is characterized by the fact that
A) output is steady or growing and there is low inflation.
B) profit opportunities are eliminated almost instantaneously.
C) there are no opportunity costs.
D) wealth is distributed fairly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The study of economics
A) is a very narrow endeavor.
B) is a way of analyzing decision-making processes caused by scarcity.
C) is concerned with proving that capitalism is better than socialism.
D) focuses on how a business should function.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Opportunity costs arise due to scarce resources.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to Scenario 1.1 below to answer the questions that follow. SCENARIO 1.1: An economist wants to understand the relationship between minimum wages and the level of teenage unemployment. The economist collects data on the values of the minimum wage and the levels of teenage unemployment over time. The economist concludes that a 1% increase in minimum wage causes a 0.2% increase in teenage unemployment. From this information he concludes that the minimum wage is harmful to teenagers and should be reduced or eliminated to increase employment among teenagers. -Refer to Scenario 1.1. The statement that an increase in the minimum wage causes an increase in teenage unemployment is an example of
A) a fallacy.
B) an economic theory.
C) normative economics.
D) deductive reasoning.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 1.3 below to answer the questions that follow. 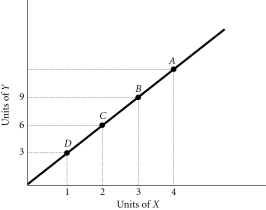 Figure 1.3
-Refer to Figure 1.3. At Point A the slope of the line is 3, so at Point D the slope would be
Figure 1.3
-Refer to Figure 1.3. At Point A the slope of the line is 3, so at Point D the slope would be
A) greater than 3.
B) less than 3.
C) equal to 3.
D) indeterminate from this information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Redistribution of income from the rich to the poor is achieved from a tax system that requires taxes to rise with income. Which of the following criteria best explains the goal of this tax system?
A) efficiency
B) equity
C) growth
D) stability
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 1.4 below to answer the questions that follow. 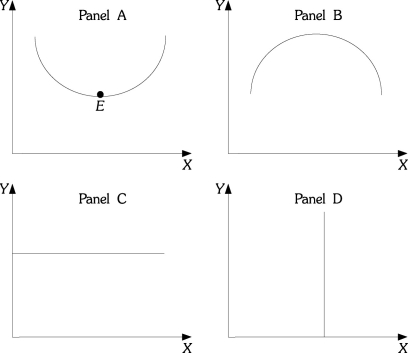 Figure 1.4
-Refer to Figure 1.4. At Point E in panel A, the slope is
Figure 1.4
-Refer to Figure 1.4. At Point E in panel A, the slope is
A) zero.
B) infinite.
C) negative.
D) indeterminate from this information.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you observe that Event A happens before Event B happens, and you conclude that Event A caused Event B, you would be guilty of an error called the
A) fallacy of composition.
B) fallacy of inductive reasoning.
C) fallacy of ceteris paribus.
D) post hoc, ergo propter hoc fallacy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The four criteria that are frequently used in judging the outcome of economic policy are
A) efficiency, equity, stability, and economic growth.
B) efficiency, equality, stability, and economic growth.
C) efficiency, equality, profitability, and stability.
D) efficiency, equity, profitability, and stability.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT one of the three fundamental concepts of economics?
A) profit maximization
B) marginalism
C) opportunity cost
D) the working of efficient markets
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 1.5 below to answer the questions that follow. 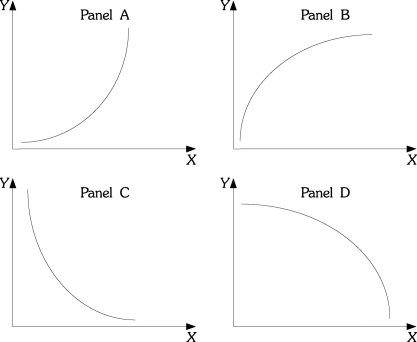 Figure 1.5
-Refer to Figure 1.5. In many industries, as firms produce additional units, average costs of production decline as the firm produces an additional unit, but average costs declines by a smaller and smaller amount as production continues to increase. If output is graphed on the horizontal axis and average costs are graphed on the vertical axis, the relationship between average costs and output would be like which of the following panels?
Figure 1.5
-Refer to Figure 1.5. In many industries, as firms produce additional units, average costs of production decline as the firm produces an additional unit, but average costs declines by a smaller and smaller amount as production continues to increase. If output is graphed on the horizontal axis and average costs are graphed on the vertical axis, the relationship between average costs and output would be like which of the following panels?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The slope of a straight line is not constant unless the line is vertical or horizontal.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If your tuition is $25,000 this semester, your books cost $1,500, you can only work 20 rather than 40 hours per week during the 15 weeks you are taking classes and you make $15 per hour, and your room and board is $7,500 this semester (same as if not attending college) , then your opportunity cost of attending college this semester is
A) $26,500.
B) $26,800.
C) $31,000.
D) $38,500.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An efficient economy is an economy
A) in which output is steady or growing and there is low inflation.
B) that produces what consumers demand and does so at the least possible cost.
C) that distributes output equally among all consumers.
D) in which there is a fair distribution of wealth.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An efficient market is a market
A) in which everyone always gets what they want.
B) in which profit opportunities are eliminated almost instantaneously.
C) in which profits are always very high and persistent.
D) in which opportunity costs are zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the information provided in Figure 1.1 below to answer the questions that follow. 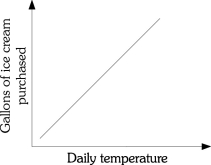 Figure 1.1
-Refer to Figure 1.1. There is ________ relationship between the daily temperature and the number of gallons of ice cream purchased.
Figure 1.1
-Refer to Figure 1.1. There is ________ relationship between the daily temperature and the number of gallons of ice cream purchased.
A) a negative
B) a positive
C) both a negative and a positive
D) an inverse
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Related to the Economics in Practice on page 10: Prior to joining a fraternity, James spent most of his evenings and weekends studying for his classes. Once he joined the fraternity, James spent a majority of his evenings and weekends going to parties. This change in behavior is best described by
A) the fallacy of composition.
B) the post hoc ergo propter hoc fallacy.
C) the problem of causality.
D) the ceteris paribus error.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 120
Related Exams