A) causes apoptosis when cells are at the S and G2 checkpoints.
B) inhibits the growth factor at the restriction point.
C) blocks DNA replication.
D) causes apoptosis only at the tumor site.
E) kills all tumor cells without harming healthy cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The number of chromosomes in a cell is reduced to half during
A) interphase.
B) meiosis I.
C) meiosis II.
D) fertilization.
E) mitosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the sexual life cycle called alternation of generations, an organism spends roughly equal amounts of time in the _______ and the _______ stages.
A) monosomic; trisomic
B) haploid; monosomic
C) haploid; diploid
D) prokaryotic; eukaryotic
E) haplontic; diplontic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If n = 30 for a species of beetles, then a diploid cell would have a total of _______ chromosomes.
A) 1
B) 15
C) 30
D) 60
E) 90
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure showing a phase of mitosis. 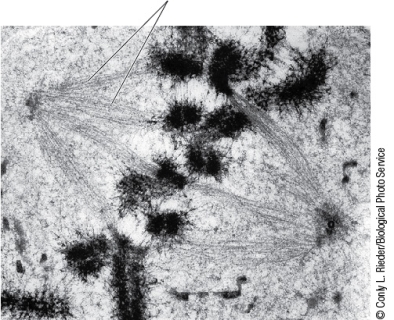 What phase is shown here?
What phase is shown here?
A) Mitosis prophase
B) Mitosis metaphase
C) Mitosis anaphase
D) Meiosis prophase I
E) Meiosis prophase II
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell in G2 has 0.8 pg of DNA.How much DNA did that cell have in G1?
A) 0.4 pg
B) 0.8 pg
C) 1.6 pg
D) 1.6 pg in animals, but 3.2 pg in plants
E) 1.6 pg in plants, but 3.2 pg in animals
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Paclitaxel
A) is an oncogene.
B) prevents the functioning of microtubules in a cell.
C) is a Cdk.
D) acts as a negative regulator.
E) produces a protein called E7.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the milestone that defines anaphase, the chromosomes
A) separate.
B) come together.
C) are at opposite poles.
D) line up.
E) cross over.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which phase of the cell cycle is not part of interphase?
A) S
B) G0
C) G1
D) G2
E) M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure showing two sexual life cycles. 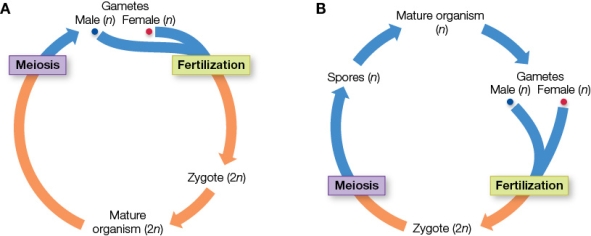 Which sexual life cycle type is not illustrated, and what is an example of that type of organism?
Which sexual life cycle type is not illustrated, and what is an example of that type of organism?
A) Haplontic; Rhizopus fungus
B) Haplontic; a sheep
C) Diplontic; a sheep
D) Alternation of generations; a fern
E) Alternation of generations; Rhizopus fungus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At the end of the first meiotic division, each chromosome consists of
A) chiasmata.
B) a homologous chromosome pair.
C) four copies of each DNA molecule.
D) two chromatids.
E) a pair of polar microtubules.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement about necrosis is true?
A) It requires ATP.
B) It does not cause inflammation.
C) It may occur when cells are damaged by toxins.
D) It produces nucleosome-sized pieces of chromatin.
E) It results in fragmentation of the cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
If a mutation renders a cyclin-Cdk more likely to phosphorylate RB, the result will be _______ (more/fewer) active RB molecules and more cells going through the checkpoint.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
In general, the division of the cell, which is called _______, follows immediately after mitosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Caspases play a role in the process of
A) autopolyploidy.
B) allopolyploidy.
C) aneuploidy.
D) necrosis.
E) apoptosis.
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Refer to the figure showing cyclin-dependent kinases regulating the progress of the cell cycle. 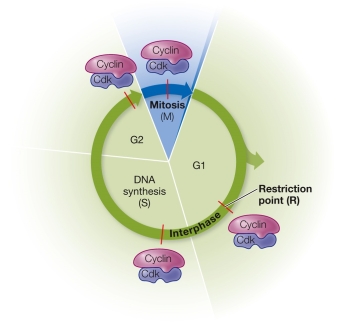 At what point is the commitment made to another cell cycle?
At what point is the commitment made to another cell cycle?
Correct Answer

verified
Late in G1...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure showing the artificial selection of wheat. 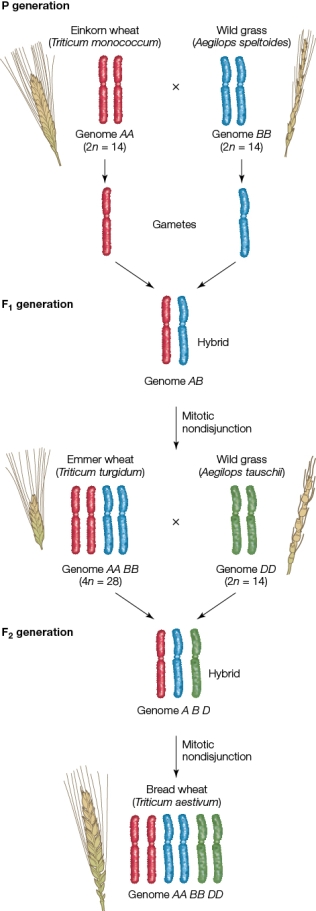 According to the figure, what is the ploidy level of the most modern form of wheat?
According to the figure, what is the ploidy level of the most modern form of wheat?
A) 1n
B) 2n
C) 3n
D) 4n
E) 6n
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA is _______ charged; thus, _______ amino acids in histones make histones more likely to bind DNA.
A) positively; positively charged
B) positively; neutral
C) positively; negatively charged
D) negatively; positively charged
E) negatively; negatively charged
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During asexual reproduction, the genetic material of the parent is passed on to the offspring by
A) homologous pairing.
B) meiosis and fertilization.
C) mitosis and cytokinesis.
D) karyotyping.
E) crossing over.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mutation in _______ can lead to aneuploidy.
A) a cyclin
B) a Cdk
C) cohesin
D) caspases
E) chromosome 21
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 260
Related Exams