A) airborne chemicals.
B) pain.
C) pressure.
D) chemicals dissolved in saliva.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The thin, light-sensitive membrane that lies at the back of the eye and contains the sensory receptors for light is the:
A) fovea.
B) optic disk.
C) retina.
D) optic nerve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the fast pain pathway, signals travel to the thalamus, and then to the:
A) hypothalamus.
B) somatosensory cortex.
C) amygdala.
D) multimodal area.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _____ develop from brain tissue and combine, analyze, and encode visual information in the retina.
A) ganglion cells
B) bipolar cells
C) cones
D) trichromatic cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The greatest number of nociceptors are located in the:
A) cochlea.
B) skin.
C) vestibular sacs.
D) joints and muscles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What region of the eye has the largest concentration of cones?
A) the periphery
B) the iris
C) the optic nerve
D) the fovea
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vibrations from the oval window are relayed to the:
A) eardrum.
B) hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup.
C) pinna.
D) cochlea.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Chapter 3 prologue story was about a man named Mike May, who recovered partial vision in one eye after being completely blind for over 40 years. After regaining partial vision, how did Mike respond to the images shown below? 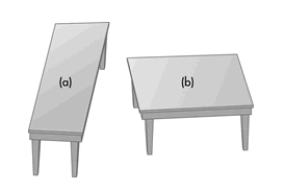
A) Unlike most people, Mike thought tabletop (b) was longer.
B) Like most people, Mike thought tabletop (a) was longer.
C) Mike thought the two tabletops were of identical size and shape.
D) Mike failed to perceive the separation between the two tables and saw the image as a misshaped "T."
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Complex tastes result from the activation of:
A) a special kind of taste bud.
B) temperature, flavor, and texture receptors.
C) nociceptors and Pacinian corpuscles.
D) different combinations of basic taste receptors.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which perceptual principles are used to help explain the moon illusion?
A) overlap and size constancy
B) brightness constancy and shape constancy
C) distance illusion and size illusion
D) the Müller-Lyer principle and the law of similarity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rods are to cones as _____ are to _____.
A) peripheral vision and night vision; color vision and visual acuity
B) color vision and night vision; bright light conditions
C) bipolar cells; ganglion cells
D) color vision and visual acuity; peripheral vision and night vision
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Flying in an airplane you look out your window and notice that everything on the ground far below looks hazy and blurred. This is an example of which depth perception cue?
A) motion parallax
B) relative size
C) aerial perspective
D) linear perspective
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the spinal cord, endorphins and enkephalins affect the pain response by:
A) increasing heart rate, muscle tension, and breathing rate.
B) releasing substance A.
C) opening the gates.
D) inhibiting the transmission of pain signals.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Feedback from the muscles of the eye can help us judge the distance of an object, because the lens of the eye thickens when we change our focus from a distant object to a nearby object. This visual cue is called:
A) relative size.
B) accommodation.
C) linear perspective.
D) motion parallax.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When psychologists refer to the visible spectrum, they mean:
A) red, orange, and yellow light waves.
B) the visual field, including peripheral vision.
C) ultraviolet rays, gamma rays, and radio waves.
D) the narrow range of wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum that are visible to the human eye.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From the optic chiasm, visual information travels first to the:
A) olfactory bulb.
B) thalamus.
C) primary visual cortex.
D) hypothalamus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You catch a whiff of freshly popped popcorn as you enter the movie theater. The process by which the odor of popcorn is converted into neural signals that your brain can interpret as the smell of popcorn is called:
A) sensory adaptation.
B) proprioception
C) transduction.
D) accommodation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine trying to assemble a jigsaw puzzle one piece at a time without knowing what the final picture will be. To accomplish this task, you would work with the individual pieces to build the image using _____ processing.
A) extrasensory
B) top-down
C) kinesthetic
D) bottom-up
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As you go to sleep at night, you realize that you can hear your roommate's wristwatch ticking. Out of curiosity, you keep a record of when you hear the watch ticking and find out that you can hear it about half the time. Your ability to hear your roommate's wristwatch about half the time is an example of:
A) a difference threshold.
B) an absolute threshold.
C) Weber's law.
D) sensory adaptation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nina was trying to convince a skeptical friend that she has ESP. "So how can you explain what happened yesterday when I knew it was Connor on the phone before I answered it?" she demanded. Nina's friend explained that we tend to remember coincidental events that seem to confirm our beliefs about unusual phenomena and to forget all the instances that do not. This tendency is called:
A) the mere exposure effect.
B) precognition.
C) the law of Prägnanz.
D) the fallacy of positive instances.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 305
Related Exams