A) can charge whatever price it wants
B) charges more than almost any consumer is willing to pay
C) is constrained by marginal cost in setting price
D) is constrained by demand in setting price
E) always earns an economic profit
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Price-discriminating,profit-maximizing monopolists charge higher prices to buyers who have more elastic demand curves.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolist's demand curve
A) is horizontal at the market price
B) lies above its marginal revenue curve
C) is the same as its marginal cost curve
D) indicates that the firm must raise price to sell additional units
E) lies above the marginal cost curve at all levels of output
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9-3
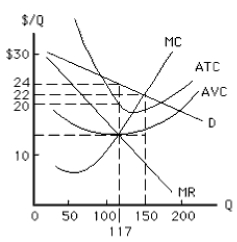 -The total cost for the firm in Exhibit 9-3,a monopolist that maximizes profit while charging all customers the same price,is
-The total cost for the firm in Exhibit 9-3,a monopolist that maximizes profit while charging all customers the same price,is
A) $3,300
B) $3,400
C) $2,808
D) $2,340
E) $1,638
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If all of a monopolist's costs are fixed costs,it will produce where demand is unit elastic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gilligan runs the only dry-cleaning business on a desert isle.If the cost of cleaning fluid falls,he can increase profit by
A) raising price
B) charging the highest price he can
C) using less cleaning fluid
D) lowering price
E) charging a price equal to marginal cost
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The demand curve a monopolist faces
A) is more elastic than a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve
B) is the market demand curve
C) is as elastic as a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve
D) is not affected by the prices of complements
E) will not shift in response to a change in consumer tastes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolist that produces in the short run and does not price discriminate,price always has to be
A) equal to marginal cost at the profit-maximizing quantity
B) equal to marginal revenue at the profit-maximizing quantity
C) greater than marginal cost at the profit-maximizing quantity
D) less than marginal cost at the profit-maximizing quantity
E) less than marginal revenue at the profit-maximizing quantity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of marginal revenue for a monopolist that charges a single price?
A) P = MR because there are no close substitutes for the monopolist's product.
B) P > MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units sold in order to sell an additional unit.
C) P < MR because the monopolist must decrease price on all units sold in order to sell an additional unit.
D) AR = MR because there are no close substitutes for the monopolist's product.
E) P = MR only at the profit-maximizing quantity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9-2
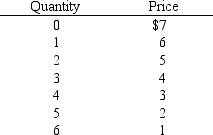 -In Exhibit 9-2,the marginal revenue of the fourth unit is
-In Exhibit 9-2,the marginal revenue of the fourth unit is
A) $12
B) $3
C) $4
D) -$4
E) $0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main reason a monopolist can earn long-run economic profit,whereas a perfectly competitive firm cannot,is that
A) monopolists operate under economies of scale
B) perfectly competitive firms have opportunity costs
C) demand for the monopolist's output is inelastic
D) demand for the monopolist's output is elastic
E) there are no barriers to entry in perfect competition
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolist,
A) marginal revenue and price are constant as quantity increases
B) marginal revenue falls but price is constant as quantity increases
C) marginal revenue is constant but price falls as quantity increases
D) both marginal revenue and price fall as quantity increases,but price falls faster
E) both marginal revenue and price fall as quantity increases,but marginal revenue falls faster
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9-17
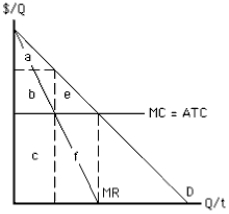 -In Exhibit 9-17,which area represents the amount of consumer surplus received by consumers under perfect price discrimination?
-In Exhibit 9-17,which area represents the amount of consumer surplus received by consumers under perfect price discrimination?
A) area a
B) area b
C) area a + b + c
D) area b + e
E) there is no consumer surplus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a perfectly competitive industry is monopolized,consumer surplus
A) can be expected to decrease
B) will usually remain constant
C) can be expected to increase
D) drops from a high value to zero
E) increases from zero to a high value
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9-5
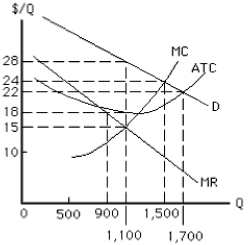 -Optimal output and price for the nondiscriminating monopolist in Exhibit 9-5 are
-Optimal output and price for the nondiscriminating monopolist in Exhibit 9-5 are
A) 90 and $18
B) 1,500 and $24
C) 1,700 and $22
D) 1,100 and $28
E) 1,500 and $22
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a monopolist,there is no supply curve because
A) the supply curve is the same as the marginal cost curve
B) the monopolist does not maximize profit
C) the quantity supplied is independent of marginal cost
D) the quantity supplied is independent of demand
E) there is no unique relationship between price and quantity supplied
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm facing a downward-sloping demand curve sells 50 units of output at $10 each.The firm's marginal revenue is
A) $500
B) more than $10 but less than $500
C) $10
D) less than $10
E) zero
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The supply curve for a monopolist
A) is its marginal cost curve
B) is vertical because there are no close substitutes for its product
C) is horizontal because there are no close substitutes for its product
D) slopes upward
E) does not exist
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 9-20
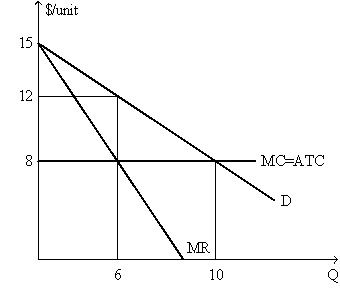 -In Exhibit 9-20,the deadweight loss with perfect price discrimination is:
-In Exhibit 9-20,the deadweight loss with perfect price discrimination is:
A) $35
B) $8
C) $10
D) $12
E) $0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Rent-seeking activities are socially wasteful because they use scarce resources but do not add to society's output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 257
Related Exams