A) It increases.
B) It decreases.
C) It remains the same.
D) It could increase, decrease or remain constant, depending on whether the firm is able to cut costs somewhere else.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue curve is downward sloping.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal revenue is
A) total revenue divided by the total quantity of output.
B) the change in profit divided by the change in the quantity of output.
C) the change in total revenue divided by the change in total cost.
D) the change in total revenue divided by the change in the quantity of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-5 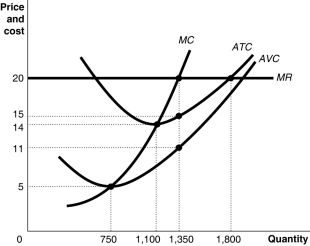 Figure 12-5 shows cost and demand curves facing a typical firm in a constant-cost, perfectly competitive industry.
-Refer to Figure 12-5. If the market price is $20, what is the firm's profit-maximizing output?
Figure 12-5 shows cost and demand curves facing a typical firm in a constant-cost, perfectly competitive industry.
-Refer to Figure 12-5. If the market price is $20, what is the firm's profit-maximizing output?
A) 750 units
B) 1,100 units
C) 1,350 units
D) 1,800 units
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ted's Pancake Kitchen suffers a short-run loss. When should Ted decide to shut down rather than continue to produce?
A) if his Kitchen's revenue is less than its variable costs
B) if his Kitchen's revenue is less than its fixed costs
C) if his Kitchen's revenue is less than its explicit costs
D) if his Kitchen's revenue is less than its total costs
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the market price is $40 in a perfectly competitive market, the marginal revenue from selling the fifth unit is
A) $8.
B) $20.
C) $40.
D) $200.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 12-4
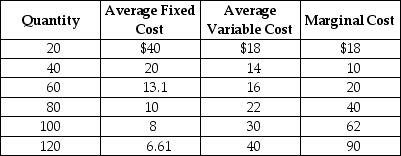 Table 12-4 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm. Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.
-Refer to Table 12-4. If the market price is $45, the firm will produce
Table 12-4 shows the short-run cost data of a perfectly competitive firm. Assume that output can only be increased in batches of 20 units.
-Refer to Table 12-4. If the market price is $45, the firm will produce
A) 60 units.
B) 80 units.
C) 100 units
D) 120 units
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-7 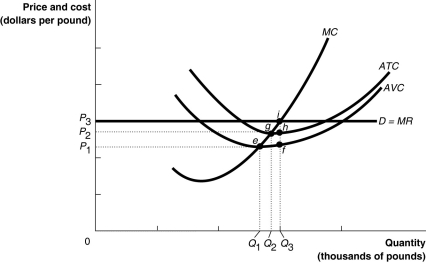 Figure 12-7 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
-Refer to Figure 12-7. If the market price is P3, the firm
Figure 12-7 illustrates the cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm.
-Refer to Figure 12-7. If the market price is P3, the firm
A) will break even.
B) will make a profit.
C) will earn enough revenue to cover its variable costs but not its fixed costs.
D) will produce a quantity of Q1.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-12 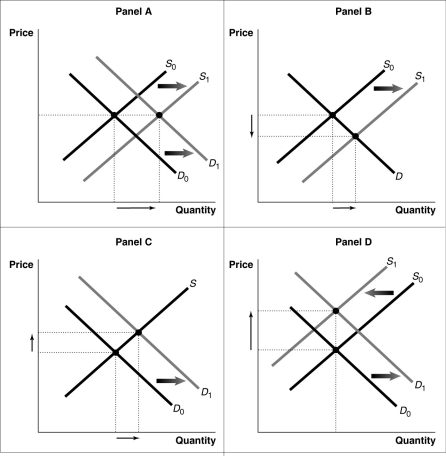 -Refer to Figure 12-12. Consider a typical firm in a perfectly competitive industry that makes short-run profits. Which of the diagrams in the figure shows the effect on the industry as it transitions to a long-run equilibrium?
-Refer to Figure 12-12. Consider a typical firm in a perfectly competitive industry that makes short-run profits. Which of the diagrams in the figure shows the effect on the industry as it transitions to a long-run equilibrium?
A) Panel A
B) Panel B
C) Panel C
D) Panel D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-9 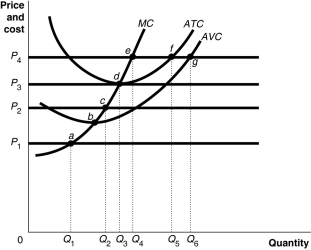 Figure 12-9 shows cost and demand curves facing a profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm.
-If total revenue exceeds fixed cost, a firm
Figure 12-9 shows cost and demand curves facing a profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm.
-If total revenue exceeds fixed cost, a firm
A) should produce in the short run.
B) has covered its variable cost.
C) is making short-run profits.
D) may or may not produce in the short run, depending on whether total revenue covers variable cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a firm in a perfectly competitive market, price is
A) equal to both average revenue and marginal revenue.
B) equal to average revenue but greater than marginal revenue.
C) greater than marginal revenue but less than average revenue.
D) less than both average revenue and marginal revenue.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Max Shreck, an accountant, quit his $80,000-a-year job and bought an existing tattoo parlor from its previous owner, Sylvia Sidney. The lease has five years remaining and requires a monthly payment of $4,000. The lease
A) is a fixed cost of operating the tattoo parlor.
B) is a variable cost of operating the tattoo parlor.
C) is an implicit cost of operating the tattoo parlor.
D) is part of the marginal cost of operating the tattoo parlor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A perfectly competitive industry achieves allocative efficiency in the long run. What does allocative efficiency mean?
A) Each firm produces up to the point where the price of the good equals the marginal cost of producing the last unit.
B) Each firm produces up to the point where all scale economies are exhausted.
C) Production occurs at the lowest average total cost.
D) Firms use an input combination that minimizes cost and maximizes output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Profit is the difference between
A) marginal revenue and marginal cost.
B) total revenue and variable cost.
C) total revenue and total explicit cost.
D) total revenue and total cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true for a firm in perfect competition?
A) Profit equals total revenue minus total cost.
B) Price equals average revenue.
C) Average revenue is greater than marginal revenue.
D) Marginal revenue equals the change in total revenue from selling one more unit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes the difference between the market demand curve for a perfectly competitive industry and the demand curve for a firm in this industry?
A) The market demand curve is a horizontal line; the firm's demand curve is downward sloping.
B) The market demand curve is downward sloping; the firm's demand curve is a vertical line.
C) The market demand curve cannot have a constant slope; the firm's demand curve has a slope equal to zero.
D) The market demand curve is downward sloping; the firm's demand curve is a horizontal line.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in a firm's fixed cost will not change the firm's profit-maximizing output in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not hold true for a perfectly competitive firm in long-run equilibrium?
A) Its economic profit will be zero.
B) It will minimize average total cost.
C) It will charge a price equal to marginal cost.
D) Marginal cost will be minimized.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-9  Figure 12-9 shows cost and demand curves facing a profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm.
-Refer to Figure 12-9. At price P1, the firm would
Figure 12-9 shows cost and demand curves facing a profit-maximizing, perfectly competitive firm.
-Refer to Figure 12-9. At price P1, the firm would
A) lose an amount equal to its fixed cost.
B) lose an amount more than fixed cost.
C) lose an amount less than fixed cost.
D) break even.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12-10 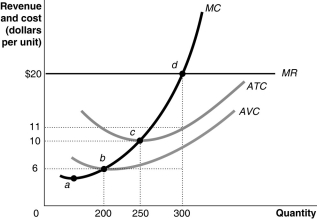 -Refer to Figure 12-10. The total cost at the profit-maximizing output level equals
-Refer to Figure 12-10. The total cost at the profit-maximizing output level equals
A) $4,800.
B) $3,300.
C) $2,500.
D) $1,800.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 298
Related Exams