A) (5/7) g sin θ
B) (1/2) g sin θ
C) (3/5) g sin θ
D) (2/3) g sin θ
E) (4/5) g sin θ
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A car of mass 1 000 kg moves with a speed of 50 m/s on a circular track of radius 100 m.What is the magnitude of its angular momentum (in kg⋅m2/s) relative to the center of the race track?
A) 5.0 × 102
B) 5.0 × 106
C) 2.5 × 104
D) 2.5 × 106
E) 5.0 × 103
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
What is the angular momentum of the moon about the Earth? The mass of the moon is 7.35 × 1022 kg,the center-to-center separation of the Earth and the moon is 3.84 × 105 km,and the orbital period of the moon is 27.3 days.Ignore the small offset of the center of mass of the system from the center of the Earth in your calculation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A torque can be exerted on a body with a fixed axis of rotation
A) only by a centripetal force.
B) only by a force directed radially outwards.
C) only by a tangential force.
D) only by a force with a component directed radially outwards.
E) by any force not pointing directly toward or away from the axis of rotation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 11-1
Two blocks of masses m1 and m2 are connected by a light cord that passes over a pulley of mass M,as shown.Block m2 slides on a frictionless horizontal surface.The blocks and pulley are initially at rest.When m1 is released,the blocks accelerate and the pulley rotates.The total angular momentum of the system of the two blocks and the pulley relative to the axis of rotation of the pulley is 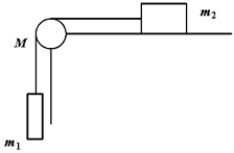 Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The total angular momentum of the system of the two blocks and the pulley relative to the axis of rotation of the pulley is
Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The total angular momentum of the system of the two blocks and the pulley relative to the axis of rotation of the pulley is
A) the same at all times.
B) proportional to l1,the length of string from the pulley to m1.
C) proportional to l2,the length of string from the pulley to m2.
D) conserved because the Earth doesn't move.
E) proportional to the speed of the blocks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A hockey puck traveling at speed v on essentially frictionless ice collides elastically with one end of a straight stick lying flat on the ice.In this collision
A) momentum is conserved.
B) angular momentum is conserved.
C) energy is conserved.
D) all of the above are conserved.
E) only momentum and angular momentum are conserved.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The object shown below has mass m and velocity 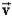 ) The direction of its angular momentum vector with respect to an axis perpendicular to the page through point O is
) The direction of its angular momentum vector with respect to an axis perpendicular to the page through point O is 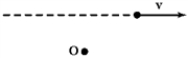
A) downwards.
B) to the right.
C) into the page.
D) up out of the page.
E) counterclockwise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid sphere,spherical shell,solid cylinder and a cylindrical shell all have the same mass m and radius R.If they are all released from rest at the same elevation and roll without slipping,which reaches the bottom of an inclined plane first?
A) solid sphere
B) spherical shell
C) solid cylinder
D) cylindrical shell
E) all take the same time
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 3.0-kg particle has a position vector given by 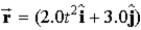 Where
Where 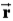 Is in meters and t is in seconds.What is the angular momentum of the particle,in kg⋅m2/s,about the origin at t = 2 s?
Is in meters and t is in seconds.What is the angular momentum of the particle,in kg⋅m2/s,about the origin at t = 2 s?
A) 72 ![]()
B) −72 ![]()
C) 24 ![]()
D) −24 ![]()
E) 22 ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Five objects of mass m move at velocity 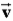 At a distance r from an axis of rotation perpendicular to the page through point A,as shown below.The one that has zero angular momentum about that axis is
At a distance r from an axis of rotation perpendicular to the page through point A,as shown below.The one that has zero angular momentum about that axis is
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A force 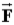 Is applied to a cylindrical roll of paper of radius R and mass M by pulling on the paper as shown.The acceleration of the center of mass of the roll of paper (when it rolls without slipping) is
Is applied to a cylindrical roll of paper of radius R and mass M by pulling on the paper as shown.The acceleration of the center of mass of the roll of paper (when it rolls without slipping) is 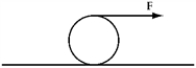
A) ![]() .
.
B) ![]() .
.
C) ![]() .
.
D) ![]() .
.
E) ![]() .
.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A puck on a frictionless air hockey table has a mass of 5.0 kg and is attached to a cord passing through a hole in the surface as in the figure.The puck is revolving at a distance 2.0 m from the hole with an angular velocity of 3.0 rad/s.The angular momentum of the puck (in kg⋅m2/s) is 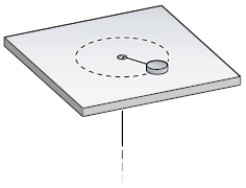
A) 80
B) 20
C) 30
D) 60
E) 50
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A merry-go-round of radius R = 2.0 m has a moment of inertia I = 250 kg⋅m2,and is rotating at 10 rpm.A child whose mass is 25 kg jumps onto the edge of the merry-go-round,heading directly toward the center at 6.0 m/s.The new angular speed (in rpm) of the merry-go-round is approximately
A) 10
B) 9.2
C) 8.5
D) 7.1
E) 6.4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an object is effectively isolated from external torques,like an ice skater twirling on the tip of one skate,the angular momentum of the object
A) can be increased by shifting mass out away from the axis of rotation.
B) can be decreased by shifting mass out away from the axis of rotation.
C) can be increased by shifting mass in toward the axis of rotation.
D) can be decreased by shifting mass in toward the axis of rotation.
E) cannot be changed except by friction at the point of contact.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A space station out beyond the solar system is rotating with constant angular velocity.A spaceship heading into the station along a diameter of the station,uses its rockets to brake,and then docks inside the station at its center.When the spaceship docks,the angular momentum of the system consisting of the station and ship
A) is less than the original angular momentum of the station.
B) is the same as the original angular momentum of the station.
C) is greater than the original angular momentum of the station.
D) is less than the original angular momentum of the station,but the angular velocity increases.
E) is greater than the original angular momentum of the station,but the angular velocity decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 11-1
Two blocks of masses m1 and m2 are connected by a light cord that passes over a pulley of mass M,as shown.Block m2 slides on a frictionless horizontal surface.The blocks and pulley are initially at rest.When m1 is released,the blocks accelerate and the pulley rotates.The total angular momentum of the system of the two blocks and the pulley relative to the axis of rotation of the pulley is  Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The total angular momentum of the system of the two blocks and the pulley relative to the axis of rotation of the pulley is
Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
-Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The total angular momentum of the system of the two blocks and the pulley relative to the axis of rotation of the pulley is
A) proportional to the radius of the pulley.
B) proportional to the speed of the blocks.
C) proportional to the length of the string.
D) to all of the above.
E) only to (a) and (b) above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particle located at the position vector 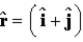 M has a force
M has a force 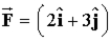 N acting on it.The torque about the origin is
N acting on it.The torque about the origin is
A) (1 ![]() ) N⋅m
) N⋅m
B) (5 ![]() ) N⋅m
) N⋅m
C) (−1 ![]() ) N⋅m
) N⋅m
D) (−5 ![]() ) N⋅m
) N⋅m
E) (2 ![]() + 3
+ 3 ![]() ) N⋅m
) N⋅m
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particle whose mass is 2 kg moves in the xy plane with a constant speed of 3 m/s in the x direction along the line y = 5.What is its angular momentum (in kg⋅m2/s) relative to the origin?
A) −30 ![]()
B) 30 ![]()
C) −15 ![]()
D) 15 ![]()
E) 45 ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid cylinder rolls without slipping down an incline as shown in the figure.The linear acceleration of its center of mass is 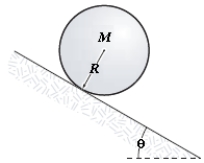
A) (5/7) g sin θ
B) (1/2) g sin θ
C) (2/3) g sin θ
D) (3/5) g sin θ
E) (4/5) g sin θ
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A hockey puck traveling at speed v on essentially frictionless ice collides with one end of a straight stick lying flat on the ice and sticks to that end.In this collision
A) momentum is conserved.
B) angular momentum is conserved.
C) energy is conserved.
D) all of the above are conserved.
E) only momentum and angular momentum are conserved.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 46
Related Exams