A) 3.90 × 10-6
B) 2.31 × 10-2
C) 0.990
D) 42.9
E) 42.5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
If the value for the equilibrium constant is much greater than 1, then the equilibrium mixture contains mostly __________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equilibrium expression for Kp for the reaction below is __________. N2 (g) + O2 (g)  2NO (g)
2NO (g)
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effect of a catalyst on an equilibrium is to __________.
A) increase the rate of the forward reaction only
B) increase the equilibrium constant so that products are favored
C) slow the reverse reaction only
D) increase the rate at which equilibrium is achieved without changing the composition of the equilibrium mixture
E) shift the equilibrium to the right
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At 400 K, the equilibrium constant for the reaction Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 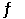 2BrCl (g)
Is Kp = 7.0. A closed vessel at 400 K is charged with 1.00 atm of Br2 (g) , 1.00 atm of Cl2 (g) , and 2.00 atm of BrCl (g) . Use Q to determine which of the statements below is true.
2BrCl (g)
Is Kp = 7.0. A closed vessel at 400 K is charged with 1.00 atm of Br2 (g) , 1.00 atm of Cl2 (g) , and 2.00 atm of BrCl (g) . Use Q to determine which of the statements below is true.
A) The equilibrium partial pressures of Br2, Cl2, and BrCl will be the same as the initial values.
B) The equilibrium partial pressure of Br2 will be greater than 1.00 atm.
C) At equilibrium, the total pressure in the vessel will be less than the initial total pressure.
D) The equilibrium partial pressure of BrCl (g) will be greater than 2.00 atm.
E) The reaction will go to completion since there are equal amounts of Br2 and Cl2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sealed 1.0 L flask is charged with 0.500 mol of I2 and 0.500 mol of Br2. An equilibrium reaction ensues: I2 (g) + Br2 (g) 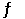 2IBr (g)
When the container contents achieve equilibrium, the flask contains 0.84 mol of IBr. The value of Keq is __________.
2IBr (g)
When the container contents achieve equilibrium, the flask contains 0.84 mol of IBr. The value of Keq is __________.
A) 11
B) 4.0
C) 110
D) 6.1
E) 2.8
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At 900.0 K, the equilibrium constant (Kp) for the following reaction is 0.345. 2SO2 + O2 (g) 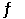 2SO3 (g)
At equilibrium, the partial pressure of SO2 is 35.0 atm and that of O2 is 15.9 atm. The partial pressure of SO3 is __________ atm.
2SO3 (g)
At equilibrium, the partial pressure of SO2 is 35.0 atm and that of O2 is 15.9 atm. The partial pressure of SO3 is __________ atm.
A) 82.0
B) 4.21 × 10-3
C) 192
D) 6.20 × 10-4
E) 40.2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following reaction at equilibrium, if Kc = 6.34 x 105 at 230.0°C, Kp = __________. 2NO (g) + O2 (g) 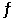 2NO2 (g)
2NO2 (g)
A) 3.67 × 10-2
B) 1.53 × 104
C) 6.44 × 105
D) 2.61 × 106
E) 2.62 × 107
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At 200°C, the equilibrium constant (Kp) for the reaction below is 2.40 × 103. 2NO (g) 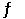 N2 (g) + O2 (g)
A closed vessel is charged with 36.1 atm of NO. At equilibrium, the partial pressure of O2 is __________ atm.
N2 (g) + O2 (g)
A closed vessel is charged with 36.1 atm of NO. At equilibrium, the partial pressure of O2 is __________ atm.
A) 294
B) 35.7
C) 17.9
D) 6.00
E) 1.50 × 10-2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of Keq for the equilibrium H2 (g) + I2 (g) 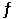 2 HI (g)
Is 794 at 25 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
1/2 H2 (g) + 1/2 I2 (g)
2 HI (g)
Is 794 at 25 °C. What is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
1/2 H2 (g) + 1/2 I2 (g) 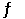 HI (g)
HI (g)
A) 397
B) 0.035
C) 28
D) 1588
E) 0.0013
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The equilibrium constant for the gas phase reaction 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 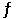 2SO3 (g)
Is Keq = 2.80 × 102 at 999 K. At equilibrium, __________.
2SO3 (g)
Is Keq = 2.80 × 102 at 999 K. At equilibrium, __________.
A) products predominate
B) reactants predominate
C) roughly equal amounts of products and reactants are present
D) only products are present
E) only reactants are present
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The value of Keq for the equilibrium H2 (g) + I2 (g) 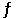 2 HI (g)
Is 794 at 25°C. At this temperature, what is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
HI (g)
2 HI (g)
Is 794 at 25°C. At this temperature, what is the value of Keq for the equilibrium below?
HI (g) 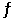 1/2 H2 (g) + 1/2 I2 (g)
1/2 H2 (g) + 1/2 I2 (g)
A) 1588
B) 28
C) 397
D) 0.035
E) 0.0013
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following equilibria, only __________ will shift to the right in response to a decrease in volume.
A) H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) ![]() 2 HCl (g)
2 HCl (g)
B) 2 SO3 (g) ![]() 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
C) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) ![]() 2 NH3 (g)
2 NH3 (g)
D) 2 Fe2O3 (s) ![]() 4 Fe (s) + 3 O2 (g)
4 Fe (s) + 3 O2 (g)
E) 2HI (g) ![]() H2 (g) + I2 (g)
H2 (g) + I2 (g)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given the following reaction: CO (g) + 2H2(g) 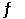 CH3OH (g)
In an experiment, 0.42 mol of CO and 0.42 mol of H2 were placed in a 1.00-L reaction vessel. At equilibrium, there were 0.29 mol of CO remaining. Keq at the temperature of the experiment is __________.
CH3OH (g)
In an experiment, 0.42 mol of CO and 0.42 mol of H2 were placed in a 1.00-L reaction vessel. At equilibrium, there were 0.29 mol of CO remaining. Keq at the temperature of the experiment is __________.
A) 2.80
B) 0.357
C) 14.5
D) 17.5
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Q does not change with temperature.
B) Keq does not change with temperature, whereas Q is temperature dependent.
C) K does not depend on the concentrations or partial pressures of reaction components.
D) Q does not depend on the concentrations or partial pressures of reaction components.
E) Q is the same as Keq when a reaction is at equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? (NH4) 2Se (s) ![Which of the following expressions is the correct equilibrium-constant expression for the reaction below? (NH<sub>4</sub>) <sub>2</sub>Se (s) 2NH<sub>3</sub> (g) + H<sub>2</sub>Se (g) A) [NH<sub>3</sub>][H<sub>2</sub>Se] / [(NH<sub>4</sub>) <sub>2</sub>Se] B) [(NH<sub>4</sub>) <sub>2</sub>Se] / [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>Se] C) 1 / [(NH<sub>4</sub>) <sub>2</sub>Se] D) [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>Se] E) [NH<sub>3</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[H<sub>2</sub>Se] / [(NH<sub>4</sub>) <sub>2</sub>Se]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1822/11ea7ce9_fb24_5e12_b46a_9b48cf15e3dc_TB1822_11.jpg) 2NH3 (g) + H2Se (g)
2NH3 (g) + H2Se (g)
A) [NH3][H2Se] / [(NH4) 2Se]
B) [(NH4) 2Se] / [NH3]2[H2Se]
C) 1 / [(NH4) 2Se]
D) [NH3]2[H2Se]
E) [NH3]2[H2Se] / [(NH4) 2Se]
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2NH3 (g) 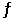 N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ΔH° = +92.4 kJ
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that adding N2 (g) to the system at equilibrium will result in __________.
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ΔH° = +92.4 kJ
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that adding N2 (g) to the system at equilibrium will result in __________.
A) a decrease in the concentration of NH3 (g)
B) a decrease in the concentration of H2 (g)
C) an increase in the value of the equilibrium constant
D) a lower partial pressure of N2
E) removal of all of the H2 (g)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Kp for the reaction below is 1.49 × 108 at 100.0°C: CO (g) + Cl2 (g) 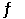 COCl2 (g)
In an equilibrium mixture of the three gases, PCO = PCl2 = 2.22 × 10-4 atm. The partial pressure of the product, phosgene (COCl2) , is __________ atm.
COCl2 (g)
In an equilibrium mixture of the three gases, PCO = PCl2 = 2.22 × 10-4 atm. The partial pressure of the product, phosgene (COCl2) , is __________ atm.
A) 7.34
B) 3.02 × 1015
C) 3.31 × 10-16
D) 3.31 × 104
E) 6.67 × 1011
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following equilibrium. 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)  2SO3 (g)
The equilibrium cannot be established when __________ is/are placed in a 1.0-L container.
2SO3 (g)
The equilibrium cannot be established when __________ is/are placed in a 1.0-L container.
A) 0.25 mol SO2 (g) and 0.25 mol O2 (g)
B) 0.75 mol SO2 (g)
C) 0.25 mol of SO2 (g) and 0.25 mol of SO3 (g)
D) 0.50 mol O2 (g) and 0.50 mol SO3 (g)
E) 1.0 mol SO3 (g)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following reaction at equilibrium: 2NH3 (g) 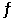 N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that the moles of H2 in the reaction container will increase with __________.
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Le Châtelier's principle predicts that the moles of H2 in the reaction container will increase with __________.
A) some removal of NH3 from the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
B) a decrease in the total pressure (T constant)
C) addition of some N2 to the reaction vessel (V and T constant)
D) a decrease in the total volume of the reaction vessel (T constant)
E) an increase in total pressure by the addition of helium gas (V and T constant)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 92
Related Exams