A) 12
B) 10
C) 8.0
D) 11
E) 7.0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The concentration of S2O82- remaining at 400 s is __________ M.
A) +0.015
B) +0.035
C) -0.007
D) +0.045
E) +0.057
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The magnitude of the rate constant is __________.
A) 38.0
B) 0.278
C) 13.2
D) 42.0
E) 2.21
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average rate of disappearance of I- in the initial 400.0 s is __________ M/s.
A) 6.00
B) 3.8 × 10-5
C) 1.4 × 10-4
D) 2.7 × 104
E) 3.2 × 10-4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following reaction is second order in [A] and the rate constant is 0.039 M-1s-1: A → B The concentration of A was 0.30 M at 23 s. The initial concentration of A was __________ M.
A) 2.4
B) 0.27
C) 0.41
D) 3.7
E) 1.2 × 10-2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average rate of disappearance of A between 20 s and 40 s is __________ mol/s.
A) 8.5 × 10-4
B) 1.7 × 10-3
C) 590
D) 7.1 × 10-3
E) 1.4 × 10-3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The decomposition of N2O5 in solution in carbon tetrachloride proceeds via the reaction 2N2O5 (soln) → 4NO2 (soln) + O2 (soln) The reaction is first order and has a rate constant of 4.82 × 10-3 s-1 at 64°C. The rate law for the reaction is rate = __________.
A) k[N2O5]2
B) ![]()
C) k[N2O5]
D) ![]()
E) 2k[N2O5]
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The combustion of ethylene proceeds by the reaction C2H4 (g) + 3O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g) When the rate of disappearance of O2 is 0.23 Ms-1, the rate of disappearance of C2H4 is __________ Ms-1.
A) 0.15
B) 0.077
C) 0.69
D) 0.35
E) 0.46
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Reaction rates are affected by reactant concentrations and temperature. This is accounted for by the __________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which energy difference in the energy profile below corresponds to the activation energy for the forward reaction? 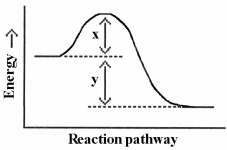
A) x
B) y
C) x + y
D) x - y
E) y - x
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 130 of 130
Related Exams