A) attack of C-2 carbonyl group by the amine of lysine
B) deprotonation of C-3 hydroxyl by aspartate
C) protonation of C-2 carbonyl oxygen by histidine
D) attack of C-2 carbonyl group by the thiol of cysteine
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following glycolytic reactions is freely reversible?
A) hexokinase
B) phosphofructokinase
C) triose phosphate isomerase
D) pyruvate kinase
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If unregulated, which of the following pairs of enzymes would represent a futile cycle?
A) pyruvate kinase and pyruvate carboxylase
B) pyruvate carboxylase and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase
C) pyruvate kinase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
D) fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and phosphofructokinase
E) glucose-6-phosphatase and phosphofructokinase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Conversion of pyruvate to acetaldehyde requires _______ while conversion of acetaldehyde to ethanol requires _______.
A) thiamine pyrophosphate; NAD+
B) pyridoxal phosphate; FADH2
C) biotin; NADH
D) biotin; FAD
E) thiamine pyrophosphate; NADH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs of phosphorylated molecules contains an intermediate of glycolysis with high phosphate transfer potential and one with low phosphate transfer potential?
A) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and fructose-6-phosphate
B) phosphoenolpyruvate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
C) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate
D) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate and phosphoenolpyruvate
E) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate and pyruvate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
For the interconversion of an aldose and ketose, show the intermediate of the reaction. 
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Fill in the missing two intermediates of glycolysis: 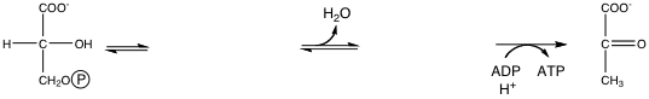
Correct Answer

verified
11ea7cd4_c4b1_82c4_a2ab_9b802765ee08_TB2679_00
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the mammalian liver, hexokinase IV is sequestered in _______ when glucose concentrations are low. When glucose concentrations are high, it is found in the cytosol bound to the enzyme ________.
A) nucleus; PFK-2
B) Golgi apparatus; PFK-2
C) endoplasmic reticulum; PFK-2
D) nucleus; PFK-1
E) Golgi apparatus; PFK-1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate requires two reactions. Which of the following correctly identifies the types of reactions in the proper order of glycolysis?
A) isomerization, hydration
B) hydration, isomerization
C) dehydration, isomerization
D) isomerization, dehydration
E) mutation, dehydration
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When glucagon binds to receptors on mammalian liver cells, which of the following occurs due to enzyme phosphorylation?
A) activation of PFK-2 followed by activation of glycolysis
B) activation of FBPase-2 followed by inhibition of gluconeogenesis
C) activation of PFK-2 followed by activation of gluconeogenesis
D) activation of FBPase-2 followed by activation of gluconeogenesis
E) activation of PFK-2 followed by inhibition of glycolysis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which isoform of hexokinase is found in the vertebrate liver?
A) hexokinase I
B) hexokinase II
C) hexokinase III
D) hexokinase IV
E) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In its non-phosphorylated state, glycogen phosphorylase can be activated by which of the following molecules?
A) ATP
B) glucose-6-phosphate
C) glucose
D) AMP
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the energy investment phase of glycolysis, _____ reaction(s) use ATP as a substrate while during the energy generation phase, _____ reactions produce ATP as a product.
A) 2; 2
B) 2; 4
C) 1; 2
D) 1; 4
E) 0; 2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following enzymes is activated when acted on by phosphoprotein phosphatase 1?
A) glycogen synthase
B) glycogen phosphorylase
C) phosphorylase kinase
D) phosphoprotein phosphatase inhibitor 1
E) protein kinase A
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conversion of ribulose-5-phosphate to xylulose-5-phosphate requires what enzyme?
A) phosphopentose isomerase
B) phosphopentose epimerase
C) transketolase
D) transaldolase
E) lactonase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A transketolase enzyme transfers a _____ carbon fragment from a(n) ________ to a(n) ________.
A) 2; aldose; ketose
B) 2; ketose; aldose
C) 2; ketose; ketose
D) 3; aldose; ketose
E) 3; ketose; aldose
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Experiments that investigated the Pasteur effect showed that when oxygen is introduced to cells where glycolysis is occurring, all intermediates beginning with ________ become depleted due to inhibition of the enzyme _________.
A) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; phosphofructokinase
B) glucose-6-phosphate: hexokinase
C) fructose-6-phosphate; phosphofructokinase
D) fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase
E) phosphoenolpyruvate; pyruvate kinase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correctly paired with the glycolytic intermediate that serves as its precursor?
A) ribulose-5-phosphate: fructose-6-phosphate
B) serine: phosphoenolpyruvate
C) glycogen: glucose-6-phosphate
D) glycerol-3-phosphate: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
E) glucosamine: fructose-1,6-bisphosphate
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With respect to carbons 1 and 2 of the intermediate in the conversion of glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate, which of the following would best describe this intermediate?
A) vicinal diol
B) enediol
C) aldehyde
D) ketone
E) enol
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under conditions of strenuous exercise, gluconeogenesis occurs primarily in the _______ using _______ formed in the skeletal muscle
A) kidney; alanine
B) muscle; glycerol
C) liver; propionate
D) kidney; acetyl-CoA
E) liver; lactate
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 41
Related Exams