A) may inherit both abnormal chromosomes from the father and would thus carry a deletion.
B) may inherit one abnormal chromosome with one normal one from the father, and would carry a deletion or duplication.
C) will inherit one abnormal chromosome from both the mother and father.
D) may inherit both normal chromosomes from the father and an abnormal one from the mother.
E) carry the same translocation as the father.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure:  -You are a genetic counselor, and a man with the translocation shown in the figure is your client. He and his partner (who has a normal karyotype) wish to have children. You explain to him that the probability of having a child with an unbalanced translocation is ______.
-You are a genetic counselor, and a man with the translocation shown in the figure is your client. He and his partner (who has a normal karyotype) wish to have children. You explain to him that the probability of having a child with an unbalanced translocation is ______.
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An embryo produced by in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be tested for genetic disorders prior to implantation. How is this accomplished?
A) Fetal cells are recovered from the mother's blood, and the DNA analyzed with a DNA microarray.
B) Amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling is performed, and a karyotype assembled.
C) A polar body is isolated and its DNA amplified by PCR for analysis by DNA microarray.
D) A single cell is removed from a 6 to 8-celled embryo, and its DNA analyzed with a DNA microarray.
E) Blood is drawn from the embryo for genetic marker analysis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following syndromes is caused by a translocation?
A) Alagille syndrome
B) invdup 15 syndrome
C) Williams syndrome
D) Cri-du-chat syndrome
E) Turner syndrome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A translocation chromosomal mutation is the exchange of segments between two homologous chromosomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Amniocentesis may be preferred over chorionic villus sampling (CVS) for karyotyping because
A) CVS takes much longer to obtain a karyotype.
B) CVS is a more invasive procedure.
C) amniocentesis has a lower risk of miscarriage than CVS.
D) amniocentesis can be performed more quickly than CVS.
E) a larger amount of tissue may be obtained through amniocentesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chromosomes for karyotyping are often obtained from a blood sample. Red blood cells, however, cannot be used for this purpose because
A) they are too small.
B) they lack nuclei.
C) white blood cells are much more common.
D) they have abnormal chromosomes.
E) they are difficult to isolate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
To perform an in vivo gene therapy treatment, cells are removed from the patient's body, normal genes are added to them, and then the cells are returned to the patient's body.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person with familial hypercholesterolemia is participating in an ex-vivo gene therapy trial. The procedure involves
A) infecting a portion of the person's liver with a retrovirus containing a normal gene for a cholesterol receptor.
B) spraying the normal gene for the cholesterol receptor into the nose.
C) insertion of the cholesterol receptor gene into a virus, then injecting the virus into the person.
D) removing a piece of the person's liver, infecting it with a retrovirus containing the normal cholesterol receptor gene, and replacing it after treatment.
E) transplanting a normal liver into the individual.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A known abnormality in a gene's sequence that can be linked to a genetic disease is called a(n)
A) genetic profile.
B) enzyme.
C) genetic marker.
D) DNA microarray.
E) genomic DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A child with bluish-purple skin is found to lack the enzyme diaphorase and is subsequently diagnosed with which genetic disorder?
A) methemoglobinemia
B) Duchenne muscular dystrophy
C) Marfan syndrome
D) sickle cell disease
E) color blindness
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chromosome 7 may lose an end piece resulting in Williams syndrome. This is an example of a(n)
A) inversion.
B) duplication.
C) deletion.
D) translocation.
E) epigenetic inheritance.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is/are the possible genotypes of the individual marked with a * on this pedigree if the mode of inheritance is autosomal recessive? 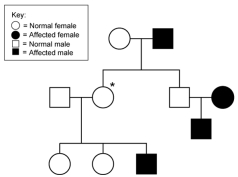
A) AA
B) AA or Aa
C) aa
D) cannot be determined
E) Aa
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Down syndrome could not be treated by gene therapy because
A) scientists do not know which faulty genes cause the syndrome.
B) Down syndrome is caused by possessing extra copies of genes of an entire chromosome, and adding more genes would not help.
C) liposomes and nasal sprays cannot be used due to abnormalities in the respiratory tract of Down syndrome individuals.
D) there are too many genes involved in the syndrome.
E) the gene therapy treatment could not be performed on an adult individual.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A man with an X-linked recessive trait has a daughter with a woman who does not exhibit the trait. What is/are the possible genotype(s) of the daughter?
A) XbXb
B) XBXB
C) XBXb or XbXb
D) XBXb
E) XBXB or XBXb
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following diseases are caused by an autosomal dominant allele?
A) cystic fibrosis and Marfan syndrome
B) Marfan syndrome and Huntington disease
C) Huntington disease and Duchenne muscular dystrophy
D) alkaptonuria and Huntington disease
E) sickle cell disease and Marfan syndrome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inversions are chromosomal mutations that
A) always result in a syndrome.
B) neither increase nor decrease the amount of genetic material in the cell.
C) rarely cause deletions or duplications during gamete formation when crossing-over occurs.
D) result from duplication of a portion of a chromosome.
E) never disrupt gene regulation or cause physical abnormalities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A genetic profile includes
A) the location of all known genes in the human genome.
B) the entire base sequence of an individual's genome.
C) all of an individual's normal genes.
D) an individual's complete genotype, including mutations.
E) all of an individual's genetic markers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the mode of inheritance for the pedigree shown here is X-linked dominant, what is/are the possible phenotype(s) of the individual marked with a *? 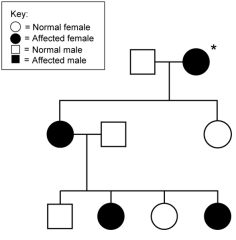
A) XBXB
B) XBXb
C) XbXb
D) XBXB or XBXb
E) cannot be determined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A female child with an unaffected father can exhibit an X-linked recessive disorder.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 50
Related Exams