A) the relevance of the law of diminishing returns.
B) at least one fixed input.
C) insufficient time for firms to enter or leave the industry.
D) the ability of the firm to change its plant size.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fast-food company spends millions of dollars to develop and promote a new hamburger on their menu only to find that consumers won't buy it because they don't like the taste. From an economic perspective, the company should
A) keep the hamburger on the menu because they've spent so much money and time developing and promoting the product.
B) spend more money to develop a more efficient way to cook the hamburger so it cooks in a shorter time.
C) pull the hamburger off the menu and treat the development and promotion expenditures as a sunk cost.
D) keep trying to sell the hamburger so that people who developed and promote it have a job with the company.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economies and diseconomies of scale explain
A) the profit-maximizing level of production.
B) why the firm's long-run average total cost curve is U-shaped.
C) why the firm's short-run marginal cost curve cuts the short-run average variable cost curve at its minimum point.
D) the distinction between fixed and variable costs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the long run, a firm can increase its output quantity, but it will be limited by the size of its existing production plant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, a firm will choose a plant size that has the
A) minimum of average fixed costs.
B) capacity to produce the largest quantity of the product.
C) minimum average total cost of producing the target level of output.
D) maximum level of resource use per unit of the total product of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Zero economic profits mean that the firm is earning
A) revenues that just cover all of its actual expenses.
B) accounting profits that are equal to its accounting costs.
C) the same amount of accounting profits as what it would have earned elsewhere.
D) revenues that are equal to its accounting profits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Introduction of the Verson Stamping Machine helped firms in the automobile industry
A) eliminate diminishing returns in production.
B) achieve greater economies of scale.
C) reach their minimum efficient scale at a lower level of production.
D) shift their AVC, ATC, and MC curves upward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-run average total cost curve
A) displays declining unit costs so long as output is increasing.
B) indicates the lowest unit costs achievable when a firm has had sufficient time to alter plant size.
C) has a shape that is the inverse of the law of diminishing returns.
D) can be derived by summing horizontally the average total cost curves of all firms in an industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the following information. TFC = Total Fixed Cost Q = Quantity of Output MC = Marginal Cost P = Product Price TVC = Total Variable Cost Average total cost is .
A)
B)
C)
D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following table shows the relationship between output and costs for two firms in the short run. 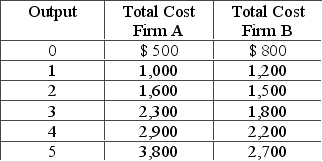 Which of the following is correct?
Which of the following is correct?
A) B has lower fixed costs than A
B) A has higher per-unit costs than B at an output level of 1.
C) A has greater marginal costs than B at each level of output.
D) B starts experiencing diminishing marginal returns with the second unit of output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the total cost of 20 units of a product is $20, and the total cost of 21 units is $21, then from 20 to 21 units of product the
A) marginal cost is decreasing.
B) marginal cost equals average total cost.
C) marginal cost equals average variable cost.
D) average total cost equals average variable cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Answer the question on the basis of the accompanying table that shows average total costs (ATC) for a manufacturing firm whose total fixed costs are $10. The profit-maximizing level of output for this firm
A) is 3.
B) is 4.
C) is 5.
D) cannot be determined from the information given.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the only variable resource used to produce output is labor. 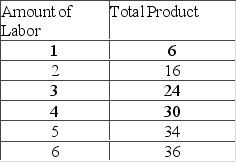 Refer to the provided table. Diminishing marginal returns set in with the addition of the
Refer to the provided table. Diminishing marginal returns set in with the addition of the
A) first unit of labor.
B) second unit of labor.
C) third unit of labor.
D) fourth unit of labor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Harvey quit his job at State University, where he earned $45,000 a year. He figures his entrepreneurial talent or forgone entrepreneurial income to be $5,000 a year. To start the business, he cashed in $100,000 in bonds that earned 10 percent interest annually to buy a software company, Extreme Gaming. In the first year, the firm sold 11,000 units of software at $75 for each unit. Of the $75 per unit, $55 goes for the costs of production, packaging, marketing, employee wages and benefits, and rent on a building. The total revenues of Harvey's firm in the first year were
A) $220,000.
B) $105,000.
C) $605,000.
D) $825,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following definitions is correct?
A) Accounting profit + economic profit = normal profit.
B) Economic profit − accounting profit = explicit costs.
C) Economic profit = accounting profit − implicit costs.
D) Economic profit − implicit costs = accounting profits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The law of diminishing returns explains diseconomies of scale.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Harvey quit his job at State University, where he earned $45,000 a year. He figures his entrepreneurial talent or forgone entrepreneurial income to be $5,000 a year. To start the business, he cashed in $100,000 in bonds that earned 10 percent interest annually to buy a software company, Extreme Gaming. In the first year, the firm sold 11,000 units of software at $75 for each unit. Of the $75 per unit, $55 goes for the costs of production, packaging, marketing, employee wages and benefits, and rent on a building. The explicit costs of Harvey's firm in the first year were
A) $755,000.
B) $605,000.
C) $705,000.
D) $825,000.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following constitutes an implicit cost to the Johnston Manufacturing Company?
A) payments of wages to its office workers
B) rent paid for the use of equipment owned by the Schultz Machinery Company
C) use of savings to pay operating expenses instead of generating interest income
D) economic profits resulting from current production
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best expresses the law of diminishing returns?
A) Because large-scale production allows the realization of economies of scale, the real costs of production vary directly with the level of output.
B) Population growth automatically adjusts to that level at which the average product per worker will be at a maximum.
C) As successive amounts of one resource (labor) are added to fixed amounts of other resources (capital) , beyond some point the resulting extra or marginal output will decline.
D) Proportionate increases in the inputs of all resources will result in a less-than-proportionate increase in total output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economic cost can best be defined as
A) any contractual obligation that results in a flow of money expenditures from an enterprise to resource suppliers.
B) those payments for resources that involve an obvious cash transaction.
C) the income the firm must provide to resource suppliers to attract resources from alternative uses.
D) the opportunity cost of using a resource already owned by the firm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 261 - 280 of 307
Related Exams