A) substantial barriers to international commodity arbitrage exist.
B) tariffs and quotas imposed on international trade can explain at least some of the evidence.
C) shipping costs can make it difficult to directly compare commodity prices.
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The benefit to forecasting exchange rates
A) are greatest during periods of fixed exchange rates.
B) are nonexistent now that the euro and dollar are the biggest game in town.
C) accrue to, and are a vital concern for, MNCs formulating international sourcing, production, financing and marketing strategies.
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Assume that you are a retail customer 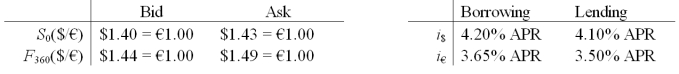 Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-There is (at least)one (smallish)profitable arbitrage at these prices.What is it?
Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-There is (at least)one (smallish)profitable arbitrage at these prices.What is it?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The random walk hypothesis suggests that
A) the best predictor of the future exchange rate is the current exchange rate.
B) the best predictor of the future exchange rate is the current forward rate.
C) both a) and b) are consistent with the efficient market hypothesis.
D) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the monetary approach,what matters in exchange rate determination are
A) the relative money supplies.
B) the relative velocities of monies.
C) the relative national outputs.
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Assume that you are a retail customer 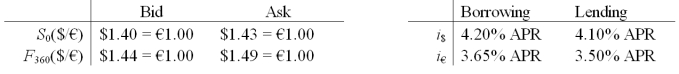 Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-If you had €1,000,000 and traded it for USD at the spot rate,how many USD will you get?
Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-If you had €1,000,000 and traded it for USD at the spot rate,how many USD will you get?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a foreign county experiences a hyperinflation,
A) its currency will depreciate against stable currencies.
B) its currency may appreciate against stable currencies.
C) its currency may be unaffected-it's difficult to say.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
 Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-There is (at least)one profitable arbitrage at these prices.What is it?
Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-There is (at least)one profitable arbitrage at these prices.What is it?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Covered Interest Arbitrage (CIA) activities will result in
A) an unstable international financial markets.
B) restoring equilibrium quite quickly.
C) a disintermediation.
D) no effect on the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The International Fisher Effect suggests that
A) any forward premium or discount is equal to the expected change in the exchange rate.
B) any forward premium or discount is equal to the actual change in the exchange rate
C) the nominal interest rate differential reflects the expected change in the exchange rate.
D) an increase (decrease) in the expected inflation rate in a country will cause a proportionate increase (decrease) in the interest rate in the country.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
 Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-If you had borrowed $1,000,000 and traded for euro at the spot rate,how many € do you receive?
Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-If you had borrowed $1,000,000 and traded for euro at the spot rate,how many € do you receive?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A formal statement of IRP is
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Fisher effect can be written for the United States as:
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Efficient Markets Hypothesis states
A) markets tend to evolve to low transactions costs and speedy execution of orders.
B) current asset prices (e.g.exchange rates) fully reflect all the available and relevant information.
C) current exchange rates cannot be explained by such fundamental forces as money supplies, inflation rates and so forth.
D) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Assume that you are a retail customer 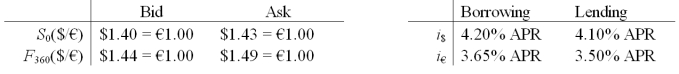 Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-If you borrowed €1,000,000 for one year,how much money would you owe at maturity?
Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-If you borrowed €1,000,000 for one year,how much money would you owe at maturity?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Assume that you are a retail customer (i.e. you buy at the ask and sell at the bid). 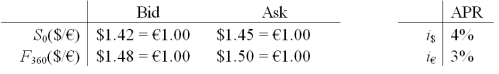 Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-USING YOUR PREVIOUS ANSWERS and a bit more work,find the 1-year forward BID exchange rate in $ per € that satisfies IRP from the perspective of a customer.
Please note that your answers are worth zero points if they do not include currency symbols ($, €)
-USING YOUR PREVIOUS ANSWERS and a bit more work,find the 1-year forward BID exchange rate in $ per € that satisfies IRP from the perspective of a customer.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main approaches to forecasting exchange rates are
A) Efficient market, Fundamental, and Technical approaches.
B) Efficient market and Technical approaches.
C) Efficient market and Fundamental approaches.
D) Fundamental and Technical approaches.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Generating exchange rate forecasts with the fundamental approach involves
A) looking at charts of the exchange rate and extrapolating the patterns into the future
B) estimation of a structural model
C) substituting the estimated values of the independent variables into the estimated structural model to generate the forecast
D) both b) and c)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A U.S.-based currency dealer has good credit and can borrow $1,000,000 for one year.The one-year interest rate in the U.S.is i$ = 2% and in the euro zone the one-year interest rate is i€ = 6%.The spot exchange rate is $1.25 = €1.00 and the one-year forward exchange rate is $1.20 = €1.00.Show how to realize a certain dollar profit via covered interest arbitrage.
A) Borrow $1,000,000 at 2%.Trade $1,000,000 for €800,000; invest at i€ = 6%; translate proceeds back at forward rate of $1.20 = €1.00, gross proceeds = $1,017,600.
B) Borrow €800,000 at i€ = 6%; translate to dollars at the spot, invest in the U.S.at i$ = 2% for one year; translate €848,000 back into euro at the forward rate of $1.20 = €1.00.Net profit $2,400.
C) Borrow €800,000 at i€ = 6%; translate to dollars at the spot, invest in the U.S.at i$ = 2% for one year; translate €850,000 back into euro at the forward rate of $1.20 = €1.00.Net profit €2,000.
D) Both c) and b)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If IRP fails to hold
A) pressure from arbitrageurs should bring exchange rates and interest rates back into line.
B) it may fail to hold due to transactions costs.
C) it may be due to government-imposed capital controls.
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 100
Related Exams