A) gently upward sloping.
B) mound shaped.
C) flat.
D) bowl shaped.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions :
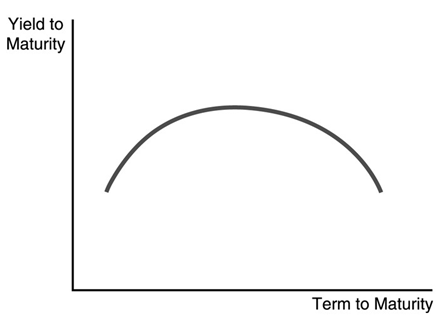 -The mound-shaped yield curve in the figure above indicates that short-term interest rates are expected to
-The mound-shaped yield curve in the figure above indicates that short-term interest rates are expected to
A) rise in the near-term and fall later on.
B) fall moderately in the near-term and rise later on.
C) fall sharply in the near-term and rise later on.
D) remain unchanged in the near-term and fall later on.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A key assumption in the segmented markets theory is that bonds of different maturities
A) are not substitutes at all.
B) are perfect substitutes.
C) are substitutes only if the investor is given a premium incentive.
D) are substitutes but not perfect substitutes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When short-term interest rates are expected to fall sharply in the future,the yield curve will
A) slope up.
B) be flat.
C) be inverted.
D) be an inverted U shape.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements are true?
A) A decrease in default risk on corporate bonds lowers the demand for these bonds,but increases the demand for default-free bonds.
B) The expected return on corporate bonds decreases as default risk increases.
C) A corporate bond's return becomes less uncertain as default risk increases.
D) As their relative riskiness increases,the expected return on corporate bonds increases relative to the expected return on default-free bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When yield curves are downward sloping,
A) long-term interest rates are above short-term interest rates.
B) short-term interest rates are above long-term interest rates.
C) short-term interest rates are about the same as long-term interest rates.
D) medium-term interest rates are above both short-term and long-term interest rates.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a "flight to quality"
A) the spread between Treasury bonds and Baa bonds increases.
B) the spread between Treasury bonds and Baa bonds decreases.
C) the spread between Treasury bonds and Baa bonds is not affected.
D) the change in the spread between Treasury bonds and Baa bonds cannot be predicted.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the liquidity premium theory,a yield curve that is flat means that
A) bond purchasers expect interest rates to rise in the future.
B) bond purchasers expect interest rates to stay the same.
C) bond purchasers expect interest rates to fall in the future.
D) the yield curve has nothing to do with expectations of bond purchasers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Over the next three years,the expected path of 1-year interest rates is 4,1,and 1 percent.The expectations theory of the term structure predicts that the current interest rate on 3-year bond is
A) 1 percent.
B) 2 percent.
C) 3 percent.
D) 4 percent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the expectations theory of the term structure
A) the interest rate on long-term bonds will exceed the average of short-term interest rates that people expect to occur over the life of the long-term bonds,because of their preference for short-term securities.
B) interest rates on bonds of different maturities move together over time.
C) buyers of bonds prefer short-term to long-term bonds.
D) buyers require an additional incentive to hold long-term bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the expected path of 1-year interest rates over the next five years is 1 percent,2 percent,3 percent,4 percent,and 5 percent,the expectations theory predicts that the bond with the highest interest rate today is the one with a maturity of
A) two years.
B) three years.
C) four years.
D) five years.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements are true?
A) A liquid asset is one that can be quickly and cheaply converted into cash.
B) The demand for a bond declines when it becomes less liquid,decreasing the interest rate spread between it and relatively more liquid bonds.
C) The differences in bond interest rates reflect differences in default risk only.
D) The corporate bond market is the most liquid bond market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the expectations theory of the term structure
A) when the yield curve is steeply upward sloping,short-term interest rates are expected to remain relatively stable in the future.
B) when the yield curve is downward sloping,short-term interest rates are expected to remain relatively stable in the future.
C) investors have strong preferences for short-term relative to long-term bonds,explaining why yield curves typically slope upward.
D) yield curves should be equally likely to slope downward as slope upward.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In actual practice,short-term interest rates and long-term interest rates usually move together; this is the major shortcoming of the
A) segmented markets theory.
B) expectations theory.
C) liquidity premium theory.
D) separable markets theory.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Corporate bonds are not as liquid as government bonds because
A) fewer corporate bonds for any one corporation are traded,making them more costly to sell.
B) the corporate bond rating must be calculated each time they are traded.
C) corporate bonds are not callable.
D) corporate bonds cannot be resold.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The segmented markets theory can explain
A) why yield curves usually tend to slope upward.
B) why interest rates on bonds of different maturities tend to move together.
C) why yield curves tend to slope upward when short-term interest rates are low and to be inverted when short-term interest rates are high.
D) why yield curves have been used to forecast business cycles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists' attempts to explain the term structure of interest rates
A) illustrate how economists modify theories to improve them when they are inconsistent with the empirical evidence.
B) illustrate how economists continue to accept theories that fail to explain observed behavior of interest rate movements.
C) prove that the real world is a special case that tends to get short shrift in theoretical models.
D) have proved entirely unsatisfactory to date.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Everything else held constant,if the tax-exempt status of municipal bonds were eliminated,then
A) the interest rates on municipal bonds would still be less than the interest rate on Treasury bonds.
B) the interest rate on municipal bonds would equal the rate on Treasury bonds.
C) the interest rate on municipal bonds would exceed the rate on Treasury bonds.
D) the interest rates on municipal,Treasury,and corporate bonds would all increase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the liquidity premium theory of the term structure
A) bonds of different maturities are not substitutes.
B) if yield curves are downward sloping,then short-term interest rates are expected to fall by so much that,even when the positive term premium is added,long-term rates fall below short-term rates.
C) yield curves should never slope downward.
D) interest rates on bonds of different maturities do not move together over time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As their relative riskiness ________,the expected return on corporate bonds ________ relative to the expected return on default-free bonds,everything else held constant.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; decreases
D) decreases; does not change
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 102
Related Exams