A) an increase in government expenditures
B) an increase in net exports
C) an increase in investment spending
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If money demand shifted to the right and the Federal Reserve desired to return the interest rate to its original value,it could
A) buy bonds to increase the money supply.
B) buy bonds to decrease the money supply.
C) sell bonds to increase the money supply.
D) sell bonds to decrease the money supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Federal Funds rate is the interest rate
A) banks charge each other for short-term loans.
B) the Fed charges depository institutions for short-term loans.
C) the Fed pays on deposits.
D) interest rate on 3 month Treasury bills.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assuming no crowding-out,investment-accelerator,or multiplier effects,a $100 billion increase in government expenditures shifts aggregate demand
A) right by more than $100 billion.
B) right by $100 billion.
C) left by more than $100 billion.
D) left by $100 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 24-2.On the left-hand graph,MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph,AD represents aggregate demand.The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs.
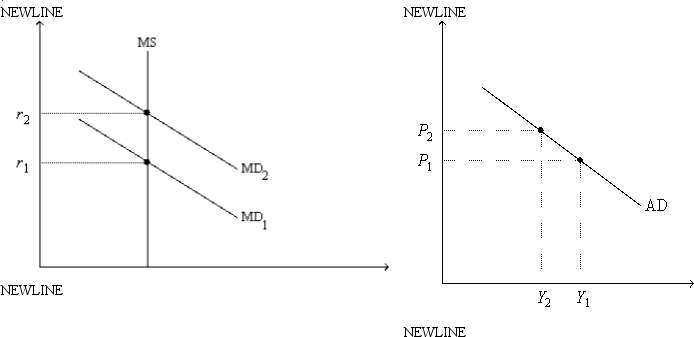 -Refer to Figure 24-2.As we move from one point to another along the money-demand curve MD1,
-Refer to Figure 24-2.As we move from one point to another along the money-demand curve MD1,
A) the price level is held fixed at P1.
B) the interest rate is held fixed at r1.
C) the money supply is changing so as to keep the money market in equilibrium.
D) the expected inflation rate is changing so as to keep the real interest rate constant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Unemployment insurance and welfare programs work as automatic stabilizers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The multiplier for changes in government spending is calculated as
A) 1/MPC.
B) 1/(1 - MPC) .
C) MPC/(1 - MPC) .
D) (1 - MPC) /MPC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed conducts open-market purchases,the money supply
A) increases and aggregate demand shifts right.
B) increases and aggregate demand shifts left.
C) decreases and aggregate demand shifts right.
D) decreases and aggregate demand shifts left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Both liquidity preference theory and classical theory assume the interest rate adjusts to bring the money market into equilibrium.
B) Both liquidity preference theory and classical theory assume the price level adjusts to bring the money market into equilibrium.
C) Liquidity preference theory assumes the interest rate adjusts to bring the money market into equilibrium; classical theory assumes the price level adjusts to bring the money market into equilibrium.
D) Liquidity preference theory assumes the price level adjusts to bring the money market into equilibrium; classical theory assumes the interest rate adjusts to bring the money market into equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If households view a tax cut as temporary,then the tax cut
A) has no affect on aggregate demand.
B) has more of an affect on aggregate demand than if households view it as permanent.
C) has the same affect as when households view the cut as permanent.
D) has less of an affect on aggregate demand than if households view it as permanent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 24-4.On the figure,MS represents money supply and MD represents money demand. 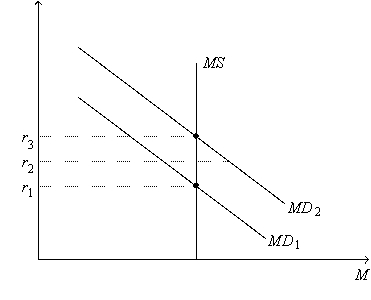 -Refer to Figure 24-4.Suppose the current equilibrium interest rate is r3.Let Y3 represent the corresponding quantity of goods and services demanded,and let P3 represent the corresponding price level.Starting from this situation,if the Federal Reserve decreases the money supply and if the price level remains at P3,then
-Refer to Figure 24-4.Suppose the current equilibrium interest rate is r3.Let Y3 represent the corresponding quantity of goods and services demanded,and let P3 represent the corresponding price level.Starting from this situation,if the Federal Reserve decreases the money supply and if the price level remains at P3,then
A) there will be an increase in the equilibrium quantity of goods and services demanded.
B) there will be a decrease in the equilibrium interest rate.
C) the aggregate-demand curve will shift to the right.
D) fewer firms will choose to borrow to build new factories and buy new equipment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the multiplier is 5 and that the crowding-out effect is $20 billion.An increase in government purchases of $10 billion will shift the aggregate-demand curve to the
A) right by $150 billion.
B) right by $70 billion.
C) right by $30 billion.
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory,if there were a shortage of money,then
A) the interest rate would be above equilibrium and the quantity of money demanded would be too large for equilibrium.
B) the interest rate would be above equilibrium and the quantity of money demanded would be too small for equilibrium.
C) the interest rate would be below equilibrium and the quantity of money demanded would be too small for equilibrium.
D) the interest rate would be below equilibrium and the quantity of money demanded would be too large for equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the multiplier is 6 and if there is no crowding-out effect,then a $60 billion increase in government expenditures causes aggregate demand to
A) increase by $250 billion.
B) increase by $333 billion.
C) increase by $360 billion.
D) None of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 24-2.On the left-hand graph,MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph,AD represents aggregate demand.The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs.
 -Refer to Figure 24-2.Assume the money market is always in equilibrium.Under the assumptions of the model,
-Refer to Figure 24-2.Assume the money market is always in equilibrium.Under the assumptions of the model,
A) the quantity of goods and services demanded is higher at P2 than it is at P1.
B) the quantity of money is higher at Y1 than it is at Y2.
C) an increase in r from r1 to r2 is associated with a decrease in Y from Y1 to Y2.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the liquidity preference theory,an increase in the overall price level of 10 percent
A) increases the equilibrium interest rate,which in turn decreases the quantity of goods and services demanded.
B) decreases the equilibrium interest rate,which in turn increases the quantity of goods and services demanded.
C) increases the quantity of money supplied by 10 percent,leaving the interest rate and the quantity of goods and services demanded unchanged.
D) decreases the quantity of money demanded by 10 percent,leaving the interest rate and the quantity of goods and services demanded unchanged.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed conducts open-market sales,which of the following quantities increase(s) ?
A) interest rates,prices,and investment spending
B) interest rates and prices,but not investment spending
C) interest rates and investment,but not prices
D) interest rates,but not investment or prices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 24-4.On the figure,MS represents money supply and MD represents money demand.  -Refer to Figure 24-4.Suppose the current equilibrium interest rate is r1.Which of the following events would cause the equilibrium interest rate to increase?
-Refer to Figure 24-4.Suppose the current equilibrium interest rate is r1.Which of the following events would cause the equilibrium interest rate to increase?
A) The Federal Reserve increases the money supply.
B) Money demand increases.
C) The price level decreases.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A policy that results in slow and steady growth of the money supply is an example of
A) an "easy" monetary policy.
B) a "passive" monetary policy.
C) a "practical" monetary policy.
D) an "active" monetary policy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the inflation rate is zero,then the nominal and real interest rate are the same.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 341 - 360 of 415
Related Exams