A) an increase in the interest rate or an increase in the price level
B) an increase in the interest rate, but not an increase in the price level
C) an increase in the price level, but not an increase in the interest rate
D) neither an increase in the interest rate nor an increase in the price level
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-2. On the left-hand graph, MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph, AD represents aggregate demand. The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs. 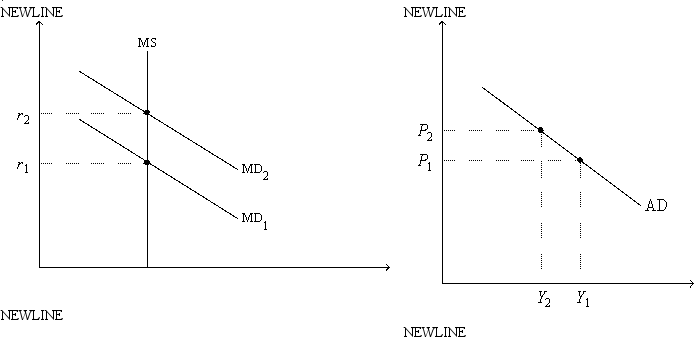 -Refer to Figure 21-2. As we move from one point to another along the money-demand curve MD1,
-Refer to Figure 21-2. As we move from one point to another along the money-demand curve MD1,
A) the price level is held fixed at P1.
B) the interest rate is held fixed at r1.
C) the money supply is changing so as to keep the money market in equilibrium.
D) the expected inflation rate is changing so as to keep the real interest rate constant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory, if the price level increases, then the equilibrium interest rate
A) rises and the aggregate quantity of goods demanded rises.
B) rises and the aggregate quantity of goods demanded falls.
C) falls and the aggregate quantity of goods demanded rises.
D) falls and the aggregate quantity of goods demanded falls.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Employment Act of 1946 states that
A) the Fed should use monetary policy only to control the rate of inflation.
B) the government should promote full employment and production.
C) the government should periodically increase the minimum wage and unemployment insurance benefits.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the theory of liquidity preference, which variable adjusts to balance the supply and demand for money?
A) interest rate
B) money supply
C) quantity of output
D) price level
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the MPC is 0.75. Assuming only the multiplier effect matters, a decrease in government purchases of $100 billion will shift the aggregate demand curve to the
A) left by $200 billion.
B) left by $400 billion.
C) right by $800 billion.
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Fed lowers the growth rate of the money supply, it must take into account
A) only the short-run effect on production.
B) only the short-run effects on inflation and production.
C) only the long-run effect on inflation.
D) the long-run effect on inflation as well as the short-run effect on production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following sequences best represents the crowding-out effect?
A) government purchases GDP supply of money equilibrium interest rate quantity of goods and services demanded
B) government purchases GDP demand for money equilibrium interest rate quantity of goods and services demanded
C) government purchases GDP demand for money equilibrium interest rate quantity of goods and services demanded
D) taxes GDP demand for money equilibrium interest rate quantity of goods and services demanded
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory, the slope of the money demand curve is explained as follows:
A) Interest rates rise as the Fed reduces the quantity of money demanded.
B) Interest rates fall as the Fed reduces the supply of money.
C) People will want to hold less money as the cost of holding it falls.
D) People will want to hold more money as the cost of holding it falls.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There is an increase in government expenditures financed by taxes and its overall short-run effect on output is larger than the change in government spending. Which of the following is correct?
A) By themselves, both the change in output and the change in the interest rate increase desired investment.
B) By themselves, both the change in output and the change in the interest rate decrease desired investment.
C) By itself, the change in output increases desired investment spending and by itself the change in the interest rate decreases desired investment spending.
D) By itself, the change in output decreases desired investment spending and by itself the change in the interest rate increases desired investment spending.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the Fed sells government bonds, the reserves of the banking system
A) increase, so the money supply increases.
B) increase, so the money supply decreases.
C) decrease, so the money supply increases.
D) decrease, so the money supply decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, which of the following responses would we expect to result from an decrease in U.S. interest rates?
A) U.S. citizens decide to hold more foreign bonds.
B) People choose to hold more currency.
C) You decide to purchase a new oven for your cookie factory.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Fed conducts open-market sales, which of the following quantities increase(s) ?
A) interest rates, prices, and investment spending
B) interest rates and prices, but not investment spending
C) interest rates and investment, but not prices
D) interest rates, but not investment or prices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of the investment accelerator involves
A) positive feedback from aggregate demand to investment.
B) negative feedback from aggregate demand to investment.
C) positive feedback from aggregate supply to investment.
D) negative feedback from aggregate supply to investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the interest rate is below the equilibrium level,
A) the quantity of money that the Federal Reserve has supplied exceeds the quantity of money that people want to hold.
B) people respond by selling interest-bearing bonds or by withdrawing money from interest-bearing bank accounts.
C) bond issuers and banks respond by lowering the interest rates they offer.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following actions might we logically expect to result from rising stock prices?
A) Jim increases his consumption spending.
B) Firms sell fewer shares of new stock.
C) Firms spend less on investment.
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the theory of liquidity preference, an increase in the price level causes the
A) interest rate and investment to rise.
B) interest rate and investment to fall.
C) interest rate to rise and investment to fall.
D) interest rate to fall and investment to rise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Other things the same, which of the following happens if the price level falls?
A) Money demand shifts rightward.
B) Initially there is an excess demand for money in the money market.
C) The interest rate falls.
D) None of the above is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 21-6. On the left-hand graph, MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph, AD represents aggregate demand. The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs. 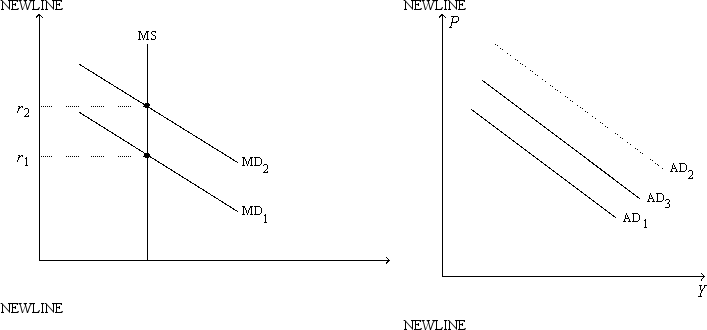 -Refer to Figure 21-6. Suppose the graphs are drawn to show the effects of an increase in government purchases. If it were not for the increase in r from r1 to r2, then
-Refer to Figure 21-6. Suppose the graphs are drawn to show the effects of an increase in government purchases. If it were not for the increase in r from r1 to r2, then
A) there would be no crowding out.
B) the full multiplier effect of the increase in government purchases would be realized.
C) the AD curves that actually apply, before and after the change in government purchases, would be separated horizontally by the distance equal to the multiplier times the change in government purchases.
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to liquidity preference theory, if there were a shortage of money, then
A) the interest rate would be above equilibrium and the quantity of money demanded would be too large for equilibrium.
B) the interest rate would be above equilibrium and the quantity of money demanded would be too small for equilibrium.
C) the interest rate would be below equilibrium and the quantity of money demanded would be too small for equilibrium.
D) the interest rate would be below equilibrium and the quantity of money demanded would be too large for equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 240 of 416
Related Exams