A) fission reactions to generate heat to boil water.
B) fission reactions to directly generate electricity.
C) fusion reactions to generate heat to boil water.
D) fusion reactions to directly generate electricity.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At present,the total number of long-term,commercial,below-ground nuclear waste depository sites in use in the United States is
A) zero.
B) 7.
C) 23.
D) over a hundred.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following energy sources can generate the greatest additional power without contributing significantly to global climate change?
A) solar technologies
B) hydroelectric power
C) nuclear energy
D) geothermal energy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
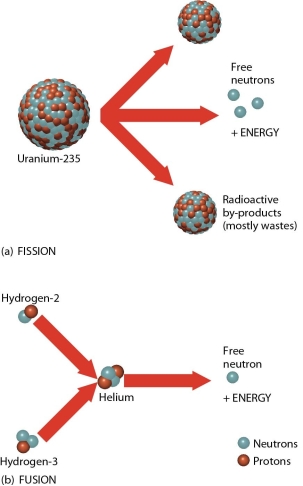 -The two reactions indicated in this figure represent
-The two reactions indicated in this figure represent
A) fusion at the top and fission at the bottom.
B) fission at the top and fusion at the bottom.
C) two types of fission reactions.
D) two types of fusion reactions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For most people living in developed countries,their greatest exposure to radiation is from
A) the natural environment.
B) dental X-rays.
C) X-rays of the bones of the body.
D) exposure to any sort of fossil fuels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a nuclear power plant,the amount of electricity that is generated is regulated by
A) moving the nuclear fuel in and out of water.
B) changing the water levels that surround the control rods.
C) releasing surplus heat out of cooling towers that are always part of nuclear power plants.
D) moving submerged control rods away from or between the submerged fuel rods.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Good stewardship of nuclear power is best promoted by
A) government oversight and international cooperation.
B) independent decisions of the countries of the world.
C) oversight provided by the companies that own the facilities.
D) limiting regulations and requirements.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Yucca Mountain in the state of Nevada is
A) the location of a leaky nuclear power plant that will cost billions of dollars to clean up.
B) the only potential site for long-term commercial nuclear waste storage in the United States,rejected for safety concerns in 2009.
C) a military base that has accumulated low-level and high-level nuclear waste for many decades.
D) the site of a lake that received illegal dumping of nuclear waste in the 1960s.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Riding along the road on your bicycle,you make a sharp right turn,hit some gravel,and tumble to the ground striking your shoulder.You are in a lot of pain.Worrying that you might have broken your shoulder blade or a rib,you walk your bike to the nearby hospital for emergency care. -Just two X-rays are taken,and the time of exposure was quite limited.According the U.S.Nuclear Regulatory Agency,your radiation exposure for the X-rays was
A) below any level to cause harm.
B) minimal,but does pose a slight health risk.
C) harmless,because medical radiation is not the same dangerous energy as radiation from nuclear energy.
D) a different type of radiation that does not cause biological damage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Riding along the road on your bicycle,you make a sharp right turn,hit some gravel,and tumble to the ground striking your shoulder.You are in a lot of pain.Worrying that you might have broken your shoulder blade or a rib,you walk your bike to the nearby hospital for emergency care. -From the 1930s to the 1950s,an X-ray machine called a shoe-fitting fluoroscope was common in shoe stores.People would try on shoes,stand with their feet in the machine,and allow the salesperson to view live images of the bones of their feet in the shoes! Sometimes the salesperson would reach down and adjust the person's shoes for a better image.These machines used X-rays and exposed the feet of customers to 5-30 seconds of radiation.Further,lower doses of radiation exposure also occurred within about 10-15 inches of the outside of the machine.If you were looking for medical problems resulting from the use of these fluoroscopes in shoe stores,where would you expect the greatest harm?
A) customers who had their feet exposed to the X-ray device
B) the salespeople who operated the machine to sell shoes
C) salespeople who worked in nearby stores
D) the salesperson who worked behind the cash register in the store
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Globally,some of the worst radioactive storage leaks have been associated with
A) military facilities in the United States and Russia.
B) hospitals in Europe.
C) nuclear power plants in China.
D) university research facilities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
New Generation III nuclear plants such as the AP1000 Advanced Passive Reactor features
A) a combination of nuclear fusion and fission in a single design.
B) a pressurized water system with many new passive safety features to prevent a LOCA.
C) a design that uses a mechanical source of X-rays for power.
D) designs based on the Fukushima Daiichi plant in Japan.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The longevity of nuclear power plants has averaged about
A) 20-25 years due to unexpectedly high levels of corrosion and embrittlement.
B) 40-50 years,longer than imagined,because neutrons tend to stabilize the building materials.
C) 10 years,only about 25% of their expected life,due to the need for new government-mandated safety designs.
D) 40 years,as expected,due to routine maintenance and the replacement with new longer-lasting materials.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Current U.S.plans for nuclear power production in 2030 are to
A) increase generating capacity by about 15%.
B) double generating capacity.
C) keep the generating capacity about the same.
D) shift to increased reliance on fossil fuels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nuclear fusion reactions
A) were used in the atomic bombs dropped on Japan in 1945.
B) require conditions that are not yet cost-efficient for the generation of electricity.
C) are widely used today in nuclear power plants.
D) can only occur in the special conditions of the sun and stars.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The worst case scenario of a disaster at a nuclear power plants is the
A) injury or death of the people working within the power plant.
B) destruction of the costly nuclear fuel used in the plant leading to a thermonuclear explosion
C) destruction of the entire nuclear power plant and loss of electrical generating capacity.
D) large scale meltdown,release and fallout of radioactive particles over thousands of square miles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Security of nuclear resources and the safe storage of nuclear wastes
A) remain a global challenge.
B) have been improved by concentrating these in four secure locations throughout the world.
C) have now been addressed by UN task forces who guard resources that are subject to terrorist attacks.
D) remain a problem only outside of the United States and Canada.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Breeder or fast-neutron reactors generate more fuel than they use because
A) these reactors capture the energy of extra neutrons released by 235U fissions.
B) the Second Law of Thermodynamics does not apply to nuclear reactions.
C) of solar collectors that invest the energy of the sun into new fuel.
D) the heat that is usually released in standard reactors is mostly recaptured.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Radioactive substance A breaks down to substance B with a half-life of 1,000 years.If we start out with four kilograms of radioactive substance A,how much of those four kilograms of substance A will remain in 3,000 years?
A) 250 grams
B) 500 grams
C) 1 kilogram
D) 2 kilograms
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The actual fission reactions that release energy in a nuclear power plant are about
A) two-thirds from uranium-235 and one-third from uranium-239.
B) one-third from uranium-235 and two-thirds from uranium-239.
C) two-thirds from uranium-235 and one-third from plutonium-239.
D) one-third from uranium-235 and two-thirds from plutonium-239.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 77
Related Exams