A) myosin
B) tropomyosin
C) sarcomeres
D) intercalated discs
E) striations
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagram,where is the axon terminal? 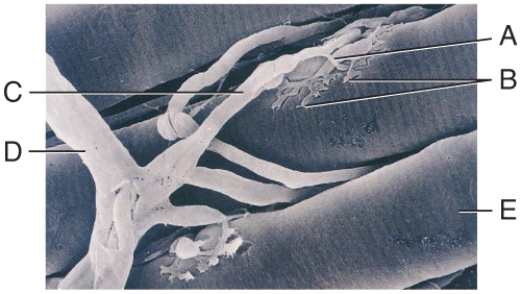
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The different types of muscle tissue differ from each other by
A) microscopic anatomy.
B) location.
C) type of Control.
D) both microscopic anatomy and location.
E) All of these choices are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
How does a nerve impulse elicit a muscle action potential?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagram,a bundle of muscle fibers form which structure? 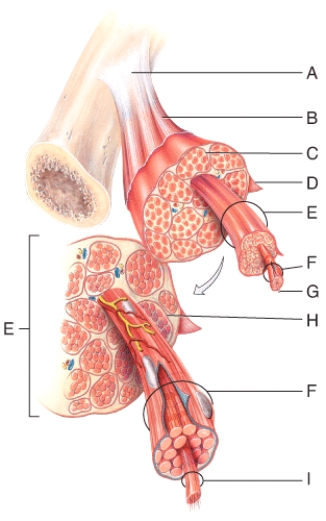
A) E
B) F
C) G
D) H
E) I
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What regulatory proteins can be found in the thin filaments of skeletal muscle fibers?
A) troponin and titin
B) tropomyosin and troponin
C) myosin and titin
D) titin and tropomyosin
E) tropomyosin and myosin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smooth muscle tone is maintained by the prolonged presence of ______ in the muscle cell's cytosol?
A) ATP
B) calcium ions
C) phosphate ions
D) myoglobin
E) None of these choices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which figure exhibits isometric contraction of the biceps brachii muscle? 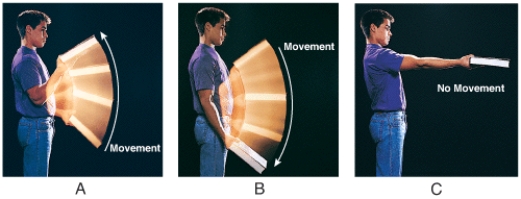
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) none of these choices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After several visits to the gym and serious "iron pumping" (strength training) you notice that your biceps have enlarged.Which one of the following has happened to your muscles?
A) atrophy
B) dystrophy
C) hyperplasia
D) hypertrophy
E) heterotrophy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Biceps are predominantly composed of this type of muscle fiber.
A) slow oxidative
B) fast glycolytic
C) fast oxidative-glycolytic
D) slow glycolytic
E) fast oxidative
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This is the least powerful type of skeletal muscle fiber.
A) slow oxidative fiber
B) fast oxidative fiber
C) fast glycolytic fiber
D) slow glycolytic fiber
E) None of these choices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
List the four steps of the contraction cycle in order of occurrence.What is needed for these steps to continuously repeat?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A period of sustained skeletal muscle contraction in which individual twitches cannot be detected is called
A) unfused tetanus.
B) muscle atrophy.
C) flaccidity.
D) fused tetanus.
E) wave summation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is a correct sequence of events in the onset of rigor mortis?
A) Cellular membranes become leaky -> myosin heads bind to actin -> calcium ions leak into the sarcoplasm -> muscles are in a state of rigidity.
B) Cellular membranes become leaky -> calcium ions leak into the sarcoplasm -> myosin heads bind to actin -> muscles are in a state of rigidity.
C) Myosin heads bind to actin -> cellular membranes become leaky -> calcium ions leak into the sarcoplasm -> muscles are in a state of rigidity.
D) Calcium ions leak into the sarcoplasm -> cellular membranes become leaky -> myosin heads bind to actin -> muscles are in a state of rigidity.
E) Calcium ions leak into the sarcoplasm -> myosin heads bind to actin -> muscles are in a state of rigidity -> cellular membranes become leaky.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the labeled structures on the diagram holds muscles with similar functions together,allows free movement of muscles,carries nerves,blood vessels and lymphatic vessels,and fills spaces between muscles? 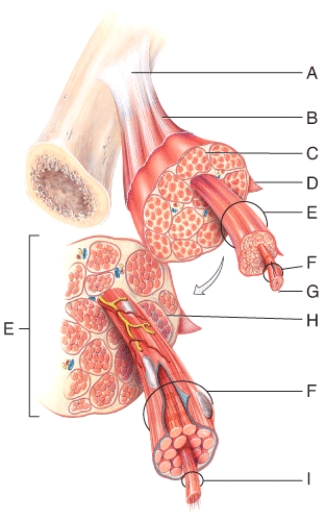
A) A
B) B
C) E
D) G
E) H
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the diagram,where would you find stored Ca2+? 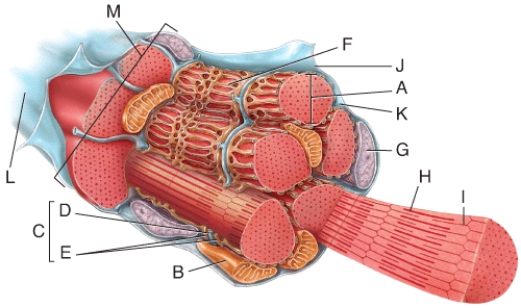
A) B
B) D
C) G
D) F
E) K
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After prolonged strenuous exercise has stopped,heavy breathing will often continue for several minutes in order to provide the oxygen needed to
A) convert the lactic acid produced during exercise back into glycogen.
B) resynthesize creatine phosphate.
C) replace oxygen displaced from muscle myoglobin.
D) All of these choices
E) None of these choices
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The contractile organelles of a skeletal muscle fiber are thread-like structures called
A) myofibrils.
B) myoglobin.
C) mitochondria.
D) Z discs.
E) M lines.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Not Answered
What are the three ways that ATP can be produced in muscle fibers?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How much of the total body weight of an average adult is muscle tissue?
A) 20-30%
B) 30-40%
C) 40-50%
D) 50-60%
E) 60-70%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 109
Related Exams