A) toxins in the mucus.
B) the cilia.
C) stomach acids and enzymes.
D) a lack of nutrients.
E) alveolar macrophages.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The condition of low tissue oxygen levels is known as
A) cystic fibrosis.
B) hypoxia.
C) hyperventilation.
D) pneumothorax.
E) emphysema.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors would increase the amount of oxygen released by hemoglobin from the bloodstream?
A) decreased temperature and decreased pH
B) decreased pH and increased temperature
C) increased tissue ![]() and increased pH
and increased pH
D) decreased tissue ![]() and increased pH
and increased pH
E) decreased temperature and increased pH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Active tissues receive approximately ________ as much O₂ as inactive tissues.
A) 2 times
B) 3 times
C) 5 times
D) 10 times
E) 100 times
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During forced breathing,which of the following occurs during inhalation?
A) The diaphragm and external intercostal muscles relax.
B) The DRG is inhibited.
C) The expiratory center of the VRG is active.
D) The inspiratory center of the VRG is inhibited.
E) The expiratory center of the VRG is inhibited.
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Receptors in the medulla oblongata respond to which variables?
A) pH and ![]() in CSF
in CSF
B) pH and ![]() in blood
in blood
C) ![]() and pH in blood
and pH in blood
D) pH and ![]() in CSF
in CSF
E) pH and ![]() in CSF
in CSF
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is defined as the absorption of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide by cells?
A) hypoxia
B) external respiration
C) anoxia
D) pulmonary ventilation
E) internal respiration
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
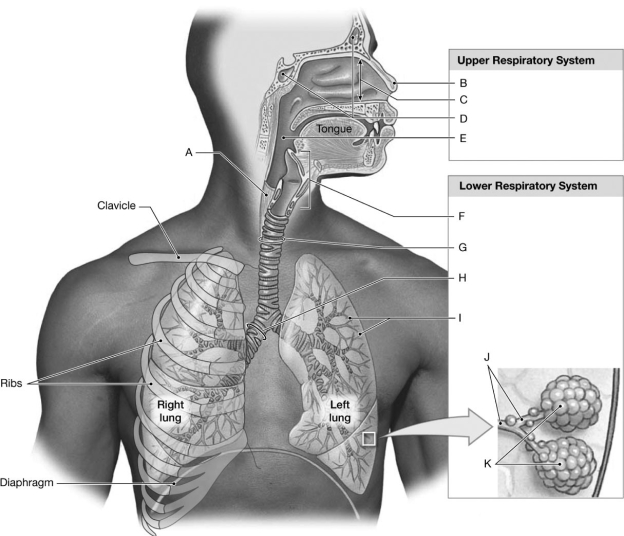 Figure 15-1 Components of the Respiratory System
Use Figure 15-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label B represents which structure(s) ?
Figure 15-1 Components of the Respiratory System
Use Figure 15-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label B represents which structure(s) ?
A) nose
B) nasal cavity
C) pharynx
D) sinuses
E) larynx
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The actual sites of gas exchange within the lungs include
A) bronchioles.
B) alveolar ducts.
C) pleural spaces.
D) alveoli.
E) capillary beds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does fluid accumulation in the lungs affect vital capacity?
A) Vital capacity increases in females but not in males.
B) Vital capacity decreases in females but not in males.
C) Vital capacity increases in both sexes equally.
D) Vital capacity decreases in both sexes equally.
E) Accumulating fluid has no effect on vital capacity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount of air that can be taken in over and above the tidal volume is the
A) vital capacity.
B) residual volume.
C) expiratory reserve volume.
D) inspiratory reserve volume.
E) minimal volume.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Someone suffering from a lack of angiotensin-converting enzyme may have a problem with their
A) endothelial cells of the alveolar capillaries.
B) septal cells of the alveolar ducts.
C) squamous epithelial cells of the alveoli.
D) alveolar macrophages within the alveolar sacs.
E) type II pneumocytes lining the respiratory bronchioles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ends of each tracheal cartilage are connected by an elastic ligament and the
A) cuneiform cartilages.
B) diaphragm.
C) arytenoid cartilages.
D) pleura.
E) trachealis muscle.
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The structure that provides posterior support to the larynx is the
A) glottis.
B) cricoid cartilage.
C) epiglottis.
D) arytenoid cartilage.
E) cuneiform cartilage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has the lowest partial pressure in inhaled dry air?
A) oxygen
B) nitrogen
C) water vapor
D) carbon dioxide
E) mercury
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 15-1 Components of the Respiratory System
Use Figure 15-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label F represents which structure(s) ?
Figure 15-1 Components of the Respiratory System
Use Figure 15-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label F represents which structure(s) ?
A) larynx
B) trachea
C) pharynx
D) bronchus
E) bronchioles
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is defined as the amount of air that remains in the lungs after a maximum exhalation?
A) minimal volume
B) inspiratory reserve volume
C) vital capacity
D) expiratory reserve volume
E) residual volume
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a patient has low compliance,it is no reference to her adhering to hospital policy,rather
A) she may suffer from pneumonia.
B) she may have an overproduction of surfactant.
C) she may have alveolar damage.
D) she may have lower energy demands while breathing.
E) she may be diagnosed with chronic epistaxis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 15-1 Components of the Respiratory System
Use Figure 15-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label G represents which structure(s) ?
Figure 15-1 Components of the Respiratory System
Use Figure 15-1 to identify the labeled part.
-Label G represents which structure(s) ?
A) larynx
B) trachea
C) pharynx
D) bronchus
E) bronchioles
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glands within the lamina propria of the respiratory mucosa secrete
A) hormones.
B) saliva.
C) mucus.
D) sweat.
E) acids.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 101
Related Exams