A) articulation (speech production) .
B) reading.
C) language comprehension.
D) language reception.
E) translation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The strongest evidence for the linguistic theory of cerebral asymmetry comes from the study of
A) deaf people who use American Sign Language and subsequently suffer unilateral brain damage.
B) split-brain deaf people.
C) deaf monkeys with unilateral brain damage.
D) split-brain people with right-hemisphere damage.
E) deaf people with bilateral brain damage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The discovery of the lateralization of language abilities is usually attributed to __________ although Dax preceded him.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bavalier et al.(1997) used a particularly sensitive fMRI procedure to study reading.They found that the areas of cerebral activity
A) in individual volunteers were patchy.
B) varied both from individual to individual and within individuals from trial to trial.
C) were widespread over the lateral surfaces of brain.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a result of mounting evidence that broad categories of cognitive function are not lateralized, research on the lateralization of function has started to focus on
A) language.
B) constituent cognitive processes.
C) emotion.
D) spatial ability.
E) cognitive tasks.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
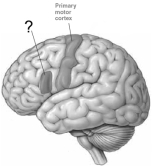 -Broca's area is in the
-Broca's area is in the
A) left hemisphere.
B) frontal lobe.
C) inferior prefrontal cortex.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The hemispheres of split-brain patients can communicate with one another externally, through their behavior; this is called __________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The language abilities of many right hemispheres of split-brain patients tend to be comparable to those of
A) chimpanzees.
B) male teenagers.
C) preschool children.
D) football players.
E) 2-year-old children.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cognitive neuroscientists interested in the brain mechanisms of language search for the specific parts of the brain that mediate
A) phonemes.
B) language production.
C) language comprehension.
D) language's constituent cognitive processes.
E) both B and C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order to establish that the dichotic listening test is a valid test of language lateralization, Kimura showed that
A) patients shown to be right-hemisphere dominant for speech by the sodium amytal test display a left-ear superiority for the recall of dichotically presented digits.
B) most people display a right ear superiority for the recall of dichotically presented melodies.
C) only left-handers display a left-ear superiority for the recall of dichotically presented digits.
D) all of the above
E) both A and B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The left planum temporale roughly corresponds to
A) Wernicke's area.
B) Broca's area.
C) the frontal operculum.
D) Heschl's gyrus.
E) primary auditory cortex.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One way of using the Z lens to test the left hemisphere's comprehension of spoken words is to
A) read words to the left ear.
B) read words to the right ear.
C) present visual stimuli in the right visual field, then verbally instruct the patient to respond to the visual stimuli.
D) both A and B
E) both B and C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most widely used behavioral test of language lateralization for healthy subjects is Kimura's adaptation of the
A) dichotic listening test.
B) sodium amytal test.
C) unilateral-lesion procedure.
D) token test.
E) split-brain test.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The corpus callosum is the largest cerebral __________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The inability to pronounce simple nonsense words is a symptom of __________ dyslexia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the ground-breaking experiment of Myers and Sperry on the learning of a visual discrimination by split-brain cats, when the eye patch was shifted to the other eye, the performance of all cats
A) in the experiment fell to 50% correct.
B) with transected corpus callosums fell to 50% correct.
C) with both their optic chiasms and their corpus callosums transected fell to 50% correct.
D) with transected optic chiasms fell to 50% correct.
E) with both their optic chiasms and their corpus callosums transected fell to zero correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The study of lateralization of function has focused on the right hemisphere because
A) most people are right-handed.
B) most people are dextrals.
C) the right hemisphere is dominant.
D) the special abilities of the left hemisphere have been more apparent.
E) both A and B
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following observations supports Kimura's motor theory of cerebral asymmetry?
A) Lesions that disrupt speech often produce other motor deficits.
B) Language-comprehension areas are located in primary sensory cortex.
C) Patients with reading difficulties often display auditory deficits..
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The left-hemisphere is dominant for speech in
A) all left-handers and a few right-handers.
B) nearly all left-handers and a few right-handers.
C) nearly all right-handers and the majority of left-handers.
D) nearly all right-handers and only a few left-handers.
E) a few right-handers and even fewer left-handers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most cases of dyslexia are
A) developmental.
B) semantic.
C) agnostic.
D) auditory.
E) acquired.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 170
Related Exams