Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The patient must be NPO a minimum of ____ hours before the small bowel series.
A) 4
B) 6
C) 8
D) 24
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Overhead, radiographic projections are often not taken when using digital fluoroscopy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is classified as an irritant laxative?
A) Magnesium citrate
B) Magnesium sulfate
C) Castor oil
D) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "tapered," or "corkscrew," radiographic sign is often seen with:
A) diverticulosis.
B) neoplasm.
C) volvulus.
D) intussusception.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following procedures is considered as a functional study?
A) Barium enema (BE)
B) Enteroclysis
C) Air-contrast BE
D) Small bowel series
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which imaging modality can demonstrate abscesses in the retroperitoneum?
A) MRI
B) Nuclear medicine
C) Sonography
D) Conventional radiography
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract synthesizes and absorbs vitamins B and K?
A) Ileum
B) Duodenum
C) Jejunum
D) Large intestine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The tip of the catheter is advanced to the ____ during an enteroclysis.
A) duodenojejunal junction (ligament of Treitz)
B) C-loop of the duodenum
C) pyloric sphincter
D) ileocecal sphincter
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The ascending colon and upper rectum are intraperitoneal structures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At what stage of respiration should the enema tip be inserted into the rectum?
A) During deep breaths
B) During shallow breaths
C) Suspended inspiration
D) Suspended expiration
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Ultrasound, with graded compression, can be used in diagnosing acute appendicitis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which structure is labeled 6? 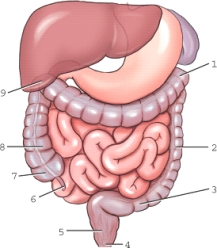
A) Cecum
B) Sigmoid colon
C) Vermiform appendix
D) Iliac colon
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following conditions may produce the "cobblestone" or "string" sign?
A) Whipple disease
B) Regional enteritis (Crohn's disease)
C) Giardiasis
D) Ileus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which radiographic sign is frequently seen with adenocarcinoma of the large intestine?
A) "Sail" sign
B) Diverticula
C) "Napkin ring" or "apple core" sign
D) Thickened mucosa
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the initial enema tip insertion, the tip is aimed:
A) toward the coccyx.
B) toward the umbilicus.
C) directly posterior.
D) directly superior.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is it important for the technologist to review the patient's chart and inform the radiologist before beginning the barium enema examination if a biopsy was performed as part of a prior sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy procedure?
A) A sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy would make the BE examination unnecessary.
B) The biopsy of the colon may weaken that portion of the colon, which could lead to a perforation during the BE examination.
C) The radiologist would want to confer with the referring physician to see whether the biopsy revealed a malignancy.
D) None of the above; the radiologist does not need to know this information before the BE examination.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following imaging modalities and/or procedures is very effective in detecting the Meckel diverticulum?
A) CT
B) Double-contrast barium enema
C) Sonography
D) Nuclear medicine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which projection and/or position is most commonly performed during an evacuative proctogram?
A) Anteroposterior (AP) erect
B) Lateral
C) Right posterior oblique (RPO) and left posterior oblique (LPO)
D) AP axial
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The "stovepipe" radiographic sign is often seen with:
A) volvulus.
B) intussusception.
C) neoplasm.
D) chronic ulcerative colitis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 83
Related Exams