A) eupnea.
B) hyperpnea.
C) diaphragmatic breathing.
D) costal breathing.
E) shallow breathing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Harry suffers from cystic fibrosis and has severe breathing difficulties.His problems result from
A) genetic mutation in cilia production.
B) laryngospasms.
C) thick secretions that are difficult to transport.
D) lack of neural control of respiration.
E) reduced mucus secretions in the trachea.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Each of the following factors affects the rate of external respiration except the
A) PO₂ of the alveoli.
B) PCO₂ of the blood.
C) thickness of the respiratory membrane.
D) PN₂ of the alveoli.
E) solubility of oxygen in plasma.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
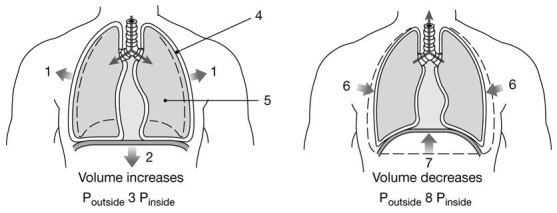 Figure 23-2 Mechanics of Ventilation
Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which muscle(s) contract(s) to cause the movement indicated by the arrows labeled "6" and "7"?
Figure 23-2 Mechanics of Ventilation
Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which muscle(s) contract(s) to cause the movement indicated by the arrows labeled "6" and "7"?
A) rectus abdominis
B) internal intercostals
C) external intercostals
D) diaphragm
E) both rectus abdominis and internal intercostals
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a function of the nasal mucosa?
A) warming the incoming air
B) trapping particulate matter
C) dehumidifying the incoming air
D) cooling outgoing air
E) None of the answers is correct; all of these are functions of the nasal mucosa.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 23-2 Mechanics of Ventilation
Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-What is the relationship between the pressures at label "3"?
Figure 23-2 Mechanics of Ventilation
Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-What is the relationship between the pressures at label "3"?
A) P outside = P inside
B) P outside > P inside
C) P outside < P inside
D) P outside + P inside
E) P outside - P inside
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The number of lobes in the right lung is
A) greater than the number of lobes in the left lung.
B) less than the number of lobes in the left lung.
C) equal to the number of lobes in the left lung.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Dalton's law of gases relates to
A) partial pressure of a gas in a mixture of gases.
B) temperature and pressure of gases.
C) solubility of gases.
D) gas pressure and saturation of hemoglobin.
E) volume and gas pressure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a patient inhales as deeply as possible and then exhales as much as possible,the volume of air expelled would be the patient's
A) tidal volume.
B) inspiratory reserve volume.
C) expiratory reserve volume.
D) reserve volume.
E) vital capacity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Figure 23-2 Mechanics of Ventilation
Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-How does the pressure "P4" at label "4" compare to the pressure "P5" at label "5"?
Figure 23-2 Mechanics of Ventilation
Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-How does the pressure "P4" at label "4" compare to the pressure "P5" at label "5"?
A) P4 is higher than P5 during inhalation and then lower during exhalation.
B) P4 is always higher than P5.
C) P4 is always lower than P5.
D) P4 always equals P5.
E) P4 is lower than P5 during inhalation and then higher during exhalation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The superior region of the pharynx is called the
A) nasal cavity.
B) nasopharynx.
C) oropharynx.
D) laryngopharynx.
E) superior nasal conchae.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The movement of chloride ions into the RBCs in exchange for bicarbonate ions is known as the chloride
A) trade.
B) shift.
C) exchange.
D) swap.
E) transport.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to the type II pneumocytes of the lungs would result in
A) a loss of surfactant.
B) an increased rate of gas exchange.
C) decreased surface tension in the alveoli.
D) expansion of alveoli.
E) All of the answers are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pneumotaxic center of the pons
A) sets the at-rest respiratory pattern.
B) prolongs inspiration.
C) modifies the rate and depth of breathing.
D) suppresses the expiratory center in the medulla.
E) stimulates the dorsal respiratory group.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Respiratory function deteriorates as a result of pneumonia because inflammation
A) causes fluids to leak into the alveoli.
B) causes respiratory bronchioles to swell and dilate.
C) causes the lungs to leak air into the thorax.
D) reduces movement of the epiglottis.
E) reduces the size of the pleural cavity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The function of pulmonary ventilation is to
A) remove carbon dioxide from the blood.
B) supply oxygen to the blood.
C) maintain adequate alveolar ventilation.
D) remove air from dead air space.
E) prevent gas exchange in the bronchioles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An acute infection of the throat that can lead to swelling and closure of the glottis and cause suffocation is known as
A) laryngitis.
B) laryngospasm.
C) acute epiglottitis.
D) strep throat.
E) acute pharyngitis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Low pH alters hemoglobin structure so that oxygen binds less strongly to hemoglobin at low PO₂.This increases the effectiveness of
A) external respiration.
B) internal respiration.
C) carbon dioxide transport.
D) hemoglobin synthesis.
E) acid-base balance.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The actual sites of gas exchange within the lungs are the
A) bronchioles.
B) terminal bronchioles.
C) spaces between the parietal and visceral pleura.
D) respiratory membranes of the alveoli.
E) interlobular septa.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prolonged inspirations can result from stimulating the ________ center.
A) apneustic
B) pneumotaxic
C) expiratory
D) baroreceptor
E) chemoreceptor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 193
Related Exams