Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
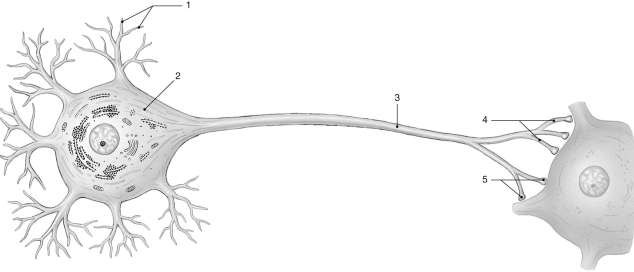 Figure 12-1 The Neuron
Use Figure 12-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "5."
Figure 12-1 The Neuron
Use Figure 12-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "5."
A) axons
B) telodendria
C) dendritic spines
D) synaptic terminals
E) collateral branch
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
________ provide information about the external environment.(Note: Be sure to capitalize the first letter of your answer).
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The ________ principle states that the size and speed of the action potential are independent of the stimulus strength.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the axolemma becomes more permeable to potassium ion:
A) the membrane will depolarize to threshold
B) a stronger stimulus will be required to cause an action potential
C) the membrane will depolarize to +30 mV
D) sodium ions will enter the cell to replace the lost potassium ions
E) the inside of the membrane will have a positive charge
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The all-or-none principle states that
A) all stimuli will produce identical action potentials.
B) all stimuli great enough to bring the membrane to threshold will produce identical action potentials.
C) the greater the magnitude of the stimuli,the greater the magnitude of the action potential.
D) only sensory stimuli can activate action potentials.
E) only motor stimuli can activate action potentials.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
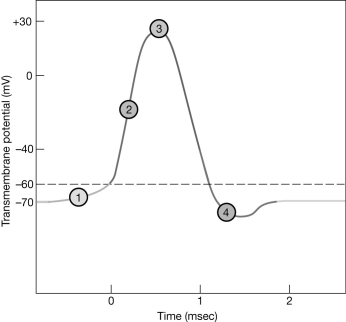 Figure 12-2 The Nerve Action Potential
Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-What is occurring at the area labeled #4?
Figure 12-2 The Nerve Action Potential
Use Figure 12-2 to answer the following questions:
-What is occurring at the area labeled #4?
A) An inhibitory stimulus has occurred.
B) Chemically-gated potassium channels have opened.
C) Excessive potassium has diffused out causing hyperpolarization.
D) Sodium ions have been pumped out of the neuron.
E) Excessive depolarization of the axon has occurred.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurons in which dendritic and axonal processes are continuous and the soma lies off to one side are called
A) anaxonic.
B) unipolar.
C) bipolar.
D) tripolar.
E) multipolar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The neuroglial cells that participate in maintaining the blood-brain barrier are the
A) astrocytes.
B) ependymal cells.
C) microglia.
D) oligodendrocytes.
E) Schwann cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The ________ division carries motor commands to muscles and glands.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Axons terminate in a series of fine extensions known as
A) telodendria.
B) terminals.
C) collaterals.
D) dendrites.
E) synapses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effect that a neurotransmitter has on the postsynaptic membrane depends on
A) the frequency of neurotransmitter release.
B) the nature of the neurotransmitter.
C) the characteristics of the receptors.
D) the quantity of neurotransmitters released.
E) All of the answers are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many medications introduced into the bloodstream cannot directly affect the neurons of the CNS because
A) oligodendrocytes form a continuous myelin sheath around the axons.
B) the endothelium of CNS capillaries forms a blood-brain barrier.
C) the neurolemma is impermeable to most molecules.
D) ependymal cells restrict the flow of interstitial fluid between the capillaries and the neurons.
E) astrocytes form a capsule around neurons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Glial cells that surround the neurons in ganglia are
A) astrocytes.
B) satellite cells.
C) oligodendrocytes.
D) microglia.
E) ependymal cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a function of the nervous system?
A) sense the internal and external environments
B) integrate sensory information
C) coordinate voluntary and involuntary activities
D) direct long-term functions,such as growth
E) control peripheral effectors
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The tiny gaps between adjacent Schwann cells are called ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a function of the neuroglia?
A) support
B) memory
C) secretion of cerebrospinal fluid
D) maintenance of blood-brain barrier
E) phagocytosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a possible drug effect on synaptic function?
A) interfere with neurotransmitter synthesis
B) interfere with neurotransmitter reuptake
C) prevent neurotransmitter inactivation
D) block neurotransmitter binding to receptors
E) change the type of receptor found in the postsynaptic membrane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Puffer fish poison blocks voltage-gated sodium channels like a cork.What effect would this neurotoxin have on the function of neurons?
A) Neurons would depolarize more rapidly.
B) Action potentials would lack a repolarization phase.
C) The absolute refractory period would be shorter than normal.
D) The axon would be unable to generate action potentials.
E) None,because the chemically-gated sodium channels would still function.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most CNS neurons lack centrioles.This observation explains
A) why CNS neurons grow such long axons.
B) why CNS neurons cannot divide to regenerate damaged tissue.
C) the ability of neurons to generate an action potential.
D) the ability of neurons to communicate with each other.
E) the ability of neurons to produce a resting potential.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 168
Related Exams