A) surface
B) body
C) shear
D) compressional
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The quantity of offset that occurs along a fault is termed ____________.
A) fault gouge
B) the fault gauge
C) displacement
D) accumulation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following scales was used to measure the intensity of the listed earthquakes? 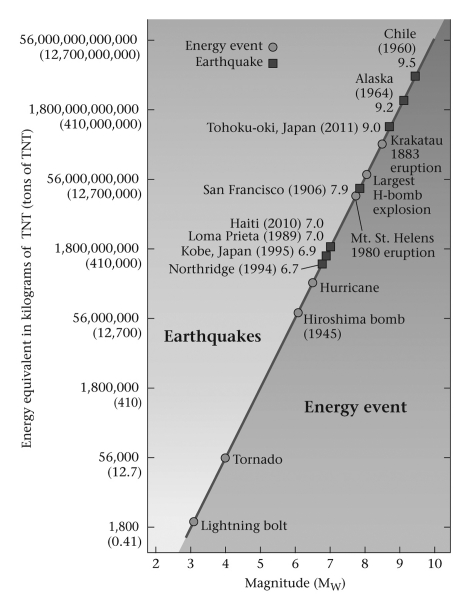
A) Mercalli
B) Seismic-moment
C) Richter
D) None of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The point within Earth where an earthquake takes place is termed the ____________.
A) hypocenter (focus)
B) epicenter
C) eye of the fault
D) vertex
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Seismic retrofitting is the process of __________.
A) predicting earthquakes
B) strengthening existing buildings and structures
C) mapping areas prone to earthquakes
D) releasing energy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Short-term predictions of earthquake behavior ____________.
A) have saved millions of lives in the past decade alone
B) have been largely unreliable
C) are primarily based on the behavior patterns of farm animals
D) are correct approximately 50% of the time
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A primary force opposing motion on all faults is ____________.
A) magnetic attraction among iron-rich minerals
B) gravity
C) friction
D) van der Waals force
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Body waves include ____________.
A) both S- and P-waves
B) both L- and R-waves
C) both surface and interior waves
D) P-waves only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aftershocks following a major earthquake ____________.
A) may continue for days after the initial earthquake
B) are mostly much smaller than the original earthquake
C) may occur on the same fault as the original earthquake, or a different fault
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What geological setting(s) would you expect to produce seismic activity?
A) rift valley
B) basin
C) collisional mountain belt
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long-term prediction of earthquake behavior ____________.
A) is based on past earthquake activity
B) works on the principle that zones of past seismicity will be active in the future
C) includes the notion of seismic gaps-places where an earthquake is "overdue"
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Generally,which type of earthquake waves travel fastest?
A) interior waves
B) R-waves
C) surface waves
D) body waves
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The key to finding the location of an earthquake's epicenter is measuring the ____________.
A) difference between the time that the P-wave arrives and the time that the S-wave arrives at the seismometer station
B) total time it takes for the P-wave and then the S-wave to arrive at the seismometer station
C) difference between the time the S-wave has reached one seismometer station and the time the S-wave has reached another station
D) difference between the time the P-wave has reached one seismometer station and the time the P-wave has reached another station
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the following,which causes the most earthquakes?
A) the sudden formation of a new fault
B) a sudden slip on an existing fault
C) the explosion of a volcano
D) a giant landslide
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Geologists who specifically study earthquakes are called ____________.
A) seismologists
B) paleontologists
C) vulcanologists
D) speleologists
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The stress that builds on a preexisting fault that has previously ruptured _____________.
A) is great enough to cause new fractures
B) must overcome the force of friction to cause an earthquake
C) is analogous to a broken stick
D) is nonexistent
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How can damage and injury be minimized in areas prone to seismic activity?
A) earthquake zoning
B) engineering controls
C) warning systems
D) All of the above are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sandy substrate is susceptible to ____________ during an earthquake.
A) displacement
B) collapse
C) liquifaction
D) faulting
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An earthquake occurs with an epicenter in the town of New Madrid,Missouri,in the interior of the North American Plate.Where might the hypocenter of this earthquake plausibly be found?
A) in New Madrid ("hypocenter" and "epicenter" mean precisely the same thing)
B) 10 km south of New Madrid
C) 20 km beneath New Madrid
D) 200 km beneath New Madrid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these areas of the United States would you expect to have the highest occurrence of seismic activity? 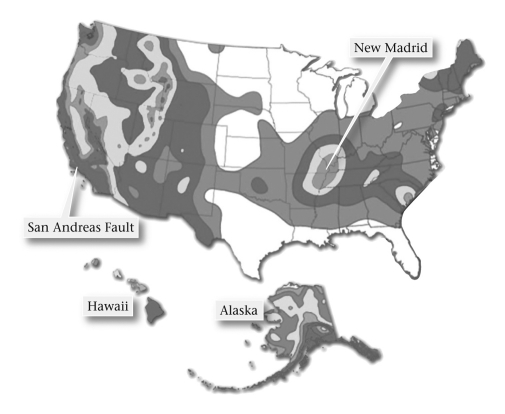
A) Southeast
B) West
C) Northeast
D) Central
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 60
Related Exams