A) It is created by the direct action of natural selection.
B) It arises in response to changes in the environment.
C) It must be present in a population before natural selection can act upon the population.
D) It tends to be reduced by the processes involved when diploid organisms produce gametes.
E) A population that has a higher average heterozygosity has less genetic variation than one with a lower average heterozygosity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely to produce an African butterfly species in the wild whose members have one of two strikingly different colour patterns?
A) artificial selection
B) directional selection
C) stabilizing selection
D) disruptive selection
E) sexual selection
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In modern terminology, diversity is understood to be a result of genetic variation. Which of the following is a recognized source of variation for evolution?
A) mistakes in translation of structural genes
B) mistakes in protein folding
C) rampant changes to the dictionary of the genetic code
D) binary fission
E) recombination by crossing over in meiosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the formula for determining a population's genotype frequencies, the 2 in the term 2pq is necessary because
A) the population is diploid.
B) heterozygotes can come about in two ways.
C) the population is doubling in number.
D) heterozygotes have two alleles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If global warming permits mosquitoes to live at higher altitudes than they currently do, then in which direction should the entire plot in the correct distribution below be shifted? 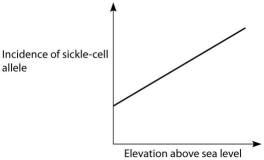 A.
A.
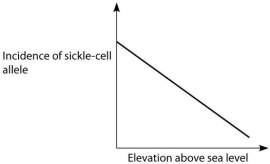 B.
B.
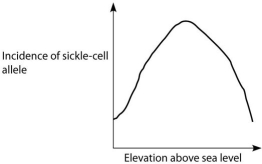 C.
C.
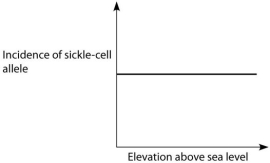 D.
D.
A) to the right
B) to the left
C) upward
D) downward
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are maintaining a small population of fruit flies in the laboratory by transferring the flies to a new culture bottle after each generation. After several generations, you notice that the viability of the flies has decreased greatly. Recognizing that small population size is likely to be linked to decreased viability, the best way to reverse this trend is to
A) cross your flies with flies from another lab.
B) reduce the number of flies that you transfer at each generation.
C) transfer only the largest flies.
D) change the temperature at which you rear the flies.
E) shock the flies with a brief treatment of heat or cold to make them more hardy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
With respect to the sickle-cell allele, what should be true of the β hemoglobin locus in U.S. populations of African-Americans whose ancestors were from equatorial Africa? 1. The average heterozygosity at this locus should be decreasing over time. 2. There is an increasing heterozygote advantage at this locus. 3. Diploidy is helping to preserve the sickle-cell allele at this locus. 4. Frequency-dependent selection is helping to preserve the sickle-cell allele at this locus.
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) 1, 2, and 3
E) 1, 2, and 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the following from most general (i.e., most inclusive) to most specific (i.e., least inclusive) : 1 natural selection 2. microevolution 3. intrasexual selection 4. evolution 5. sexual selection
A) 4, 1, 2, 3, 5
B) 4, 2, 1, 3, 5
C) 4, 2, 1, 5, 3
D) 1, 4, 2, 5, 3
E) 1, 2, 4, 5, 3
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement about variation is true?
A) All phenotypic variation is the result of genotypic variation.
B) All genetic variation produces phenotypic variation.
C) All nucleotide variability results in neutral variation.
D) All new alleles are the result of nucleotide variability.
E) All geographic variation results from the existence of clines.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Considering the overall human population of the U.S. mainland at the time when the slave trade brought large numbers of people from equatorial Africa, what was primarily acting to change the frequency of the sickle-cell allele in the overall U.S. population?
A) natural selection
B) gene flow
C) genetic drift
D) founder effect
E) Two of the responses are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The restriction enzymes of bacteria protect the bacteria from successful attack by bacteriophages, whose genomes can be degraded by the restriction enzymes. The bacterial genomes are not vulnerable to these restriction enzymes because bacterial DNA is methylated. This situation selects for bacteriophages whose genomes are also methylated. As new strains of resistant bacteriophages become more prevalent, this in turn selects for bacteria whose genomes are not methylated and whose restriction enzymes instead degrade methylated DNA. The outcome of the conflict between bacteria and bacteriophage at any point in time results from
A) frequency-dependent selection.
B) evolutionary imbalance.
C) heterozygote advantage.
D) neutral variation.
E) genetic variation being preserved by diploidy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the wild, male house finches (Carpodus mexicanus) vary considerably in the amount of red pigmentation in their head and throat feathers, with colours ranging from pale yellow to bright red. These colours come from carotenoid pigments that are found in the birds' diets; no vertebrates are known to synthesize carotenoid pigments. Thus, the brighter red the male's feathers are, the more successful he has been at acquiring the red carotenoid pigment by his food-gathering efforts (all other factors being equal) . During breeding season, one should expect female house finches to prefer to mate with males with the brightest red feathers. Which of the following is true of this situation?
A) Alleles that promote more efficient acquisition of carotenoid-containing foods by males should increase over the course of generations.
B) Alleles that promote more effective deposition of carotenoid pigments in the feathers of males should increase over the course of generations.
C) There should be directional selection for bright red feathers in males.
D) Three of the statements are correct.
E) Two of the statements are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
There are 40 individuals in population 1, all with genotype A1A1, and there are 25 individuals in population 2, all with genotype A2A2. Assume that these populations are located far from each other and that their environmental conditions are very similar. Based on the information given here, the observed genetic variation is most likely an example of
A) genetic drift.
B) gene flow.
C) disruptive selection.
D) discrete variation.
E) directional selection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Evolution
A) must happen, due to organisms' innate desire to survive.
B) must happen whenever a population is not well-adapted to its environment.
C) can happen whenever any of the conditions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are not met.
D) requires the operation of natural selection.
E) requires that populations become better suited to their environments.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement about the beak size of finches on the island of Daphne Major during prolonged drought is true?
A) Each bird evolved a deeper, stronger beak as the drought persisted.
B) Each bird's survival was strongly influenced by the depth and strength of its beak as the drought persisted.
C) Each bird that survived the drought produced only offspring with deeper, stronger beaks than seen in the previous generation.
D) The frequency of the strong-beak alleles increased in each bird as the drought persisted.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Adult male humans generally have deeper voices than do adult female humans, which is the direct result of higher levels of testosterone causing growth of the larynx. If the fossil records of apes and humans alike show a trend toward decreasing larynx size in adult females and increasing larynx size in adult males, then
A) sexual dimorphism was developing over time in these species.
B) intrasexual selection seems to have occurred.
C) stabilizing selection was occurring in these species concerning larynx size.
D) selection was acting more directly upon genotype than upon phenotype.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a Hardy-Weinberg population with two alleles, A and a, that are in equilibrium, the frequency of the allele a is 0.3. What is the percentage of the population that is homozygous for this allele?
A) 0.09
B) 0.49
C) 0.9
D) 9.0
E) 49.0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is true of natural selection?
A) Natural selection is a random process.
B) Natural selection creates beneficial mutations.
C) The only way to eliminate harmful mutations is through natural selection.
D) Mutations occur at random; natural selection can preserve and distribute beneficial mutations.
E) Mutations occur when directed by the good of the species; natural selection edits out harmful mutations and causes populations to adapt to the beneficial mutations.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use this information to answer the following questions Many species once roamed across large areas of continents, and for millions of years these species were "shaped" by their environment. Today, numerous species, especially large carnivores, are found in national parks and nature reserves that are isolated by hundreds or thousands of kilometres of land now occupied by humans. The cheetah is one example of a species that has shown several dramatic decreases in numbers over time, and now occupies a small fraction of its historic range. -Which of the following statements would most likely apply to cheetahs currently found in Kenya and South Africa?
A) Certain alleles may be under- or over-represented in cheetah populations.
B) Cheetah populations likely passed through several bottlenecks, which may have been caused by factors such as disease, competition with other predators, overhunting, poaching, and habitat loss.
C) Over time, reduced gene flow between the isolated populations would lead to aggressive encounters if the separated populations were brought together.
D) Natural selection has much more impact on large populations than on small populations.
E) A and B
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If, on average, 46% of the loci in a species' gene pool are heterozygous, then the average homozygosity of the species should be
A) 23%.
B) 46%.
C) 54%.
D) There is not enough information to say.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 86
Related Exams