A) GFP fusions enable one to track changes in the location of the protein in living cells; staining usually requires preserved cells.
B) GFP fusions enable higher resolution than staining with fluorescent probes.
C) GFP permits the position of the protein in the cell more precisely than fluorescent probes.
D) GFP permits visualization of protein-protein interactions; fluorescent probes do not.
E) GFP fusions are not subject to artifacts; fluorescent probes may introduce background artifacts.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The minimum distance two points can be separated and still discerned as separate is the
A) resolution.
B) magnification.
C) visibility.
D) objective magnification.
E) contrast.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference in lipid and protein composition between the membranes of the endomembrane system is largely determined by
A) the physical separation of most membranes from each other.
B) the transportation of membrane lipids among the endomembrane system by small membrane vesicles.
C) the function of the Golgi apparatus in sorting and directing membrane components.
D) the modification of the membrane components once they reach their final destination.
E) the synthesis of different lipids and proteins in each of the organelles of the endomembrane system.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which cell would be best for studying lyosomes?
A) muscle cell
B) nerve cell
C) phagocytic white blood cell
D) leaf cell of a plant
E) bacterial cell
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
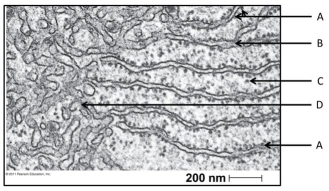 -The structure labelled D functions in
-The structure labelled D functions in
A) lipid synthesis.
B) membrane production.
C) cytosolic protein production.
D) modification of proteins for transport.
E) package of proteins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mycoplasma is an organism with a diameter between 0.1 and 1.0 µm. What does the organism's size tell you about how it might be classified?
A) It must be a single-celled protist.
B) It must be a single-celled fungus.
C) It could be almost any typical bacterium.
D) It could be a typical virus.
E) It could be a very small bacterium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What technique would be most appropriate to use to observe the movements of condensed chromosomes during cell division?
A) light microscopy
B) scanning electron microscopy
C) transmission electron microscopy
D) confocal fluorescence microscopy
E) super-resolution fluorescence microscopy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
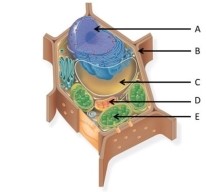 -What is the name of the structure labelled B?
-What is the name of the structure labelled B?
A) cell wall
B) plasma membrane
C) nuclear envelope
D) cytosol
E) endoplasmic reticulum
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A newspaper ad for a local toy store indicates that a very inexpensive microscope available for a small child is able to magnify specimens nearly as much as the much more costly microscope available in your college lab. What is the primary reason for the price difference?
A) The ad agency is misrepresenting the ability of the toy microscope to magnify.
B) The toy microscope does not have the same fine control for focus of the specimen.
C) The toy microscope magnifies a good deal, but has low resolution and therefore poor quality images.
D) The college microscope produces greater contrast in the specimens.
E) The toy microscope usually uses a different wavelength of light source.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cyanide binds with at least one molecule involved in producing ATP. If a cell is exposed to cyanide, most of the cyanide will be found within the
A) mitochondria.
B) ribosomes.
C) peroxisomes.
D) lysosomes.
E) endoplasmic reticulum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When biologists wish to study the internal ultrastructure of cells, they can achieve the finest resolution by using
A) a phase-contrast light microscope.
B) a scanning electron microscope.
C) a transmission electronic microscope.
D) a confocal fluorescence microscope.
E) a super-resolution fluorescence microscope.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What types of proteins are not synthesized in the rough ER?
A) endoplasmic reticulum proteins
B) extracellular matrix proteins
C) secreted proteins
D) mitochondrial proteins
E) plasma membrane proteins
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why isn't the mitochondrion classified as part of the endomembrane system?
A) It is a static structure.
B) Its structure is not derived from the ER or Golgi.
C) It has too many vesicles.
D) It is not involved in protein synthesis.
E) It is not attached to the outer nuclear envelope.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is present in a prokaryotic cell?
A) mitochondrion
B) ribosome
C) nuclear envelope
D) chloroplast
E) ER
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Golgi apparatus has a polarity or sidedness to its structure and function. Which of the following statements correctly describes this polarity?
A) Transport vesicles fuse with one side of the Golgi and leave from the opposite side.
B) Proteins in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
C) Lipids in the membrane of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
D) Soluble proteins in the cisternae (interior) of the Golgi may be sorted and modified as they move from one side of the Golgi to the other.
E) All of the above correctly describe polar characteristics of the Golgi function.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the most likely pathway taken by a newly synthesized protein that will be secreted by a cell?
A) ER → Golgi → nucleus
B) Golgi →ER →lysosome
C) nucleus →ER →Golgi
D) ER →Golgi →vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane
E) ER →lysosomes →vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a major cause of the size limits for certain types of cells?
A) limitation on the strength and integrity of the plasma membrane as cell size increases
B) the difference in plasma membranes between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
C) evolutionary progression in cell size; more primitive cells have smaller sizes
D) the need for a surface area of sufficient area to support the cell's metabolic needs
E) rigid cell walls that limit cell size expansion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following produces and modifies polysaccharides that will be secreted?
A) lysosome
B) vacuole
C) mitochondrion
D) Golgi apparatus
E) peroxisome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Tay-Sachs disease is a human genetic abnormality that results in cells accumulating and becoming clogged with very large and complex lipids. Which cellular organelle must be involved in this condition?
A) the endoplasmic reticulum
B) the Golgi apparatus
C) the lysosome
D) mitochondria
E) membrane-bound ribosomes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of organelle is found in plant cells but not in animal cells?
A) ribosomes
B) mitochondria
C) nuclei
D) plastids
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 96
Related Exams