A) as a pentose
B) as a hexose
C) as a monosaccharide
D) as a disaccharide
E) as a polysaccharide
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the 15 molecules illustrated in the figure below. Each molecule may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
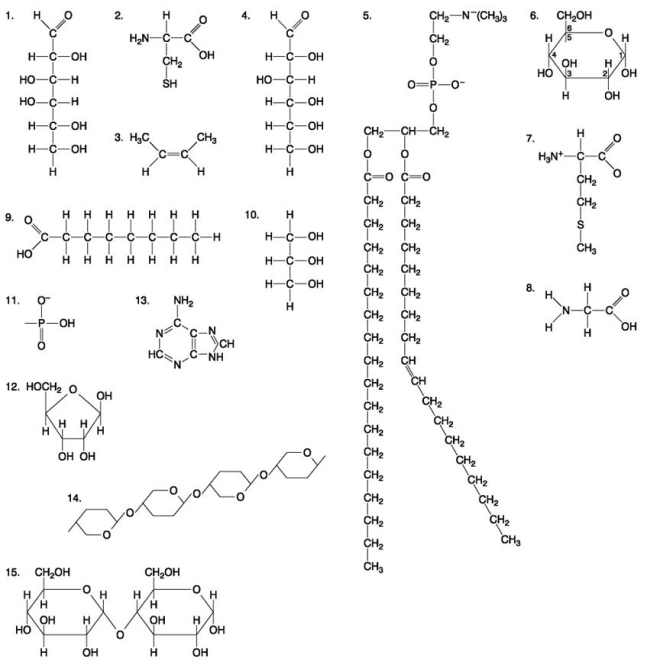 -Which of the following combinations could be linked together to form a nucleotide?
-Which of the following combinations could be linked together to form a nucleotide?
A) 1, 2, and 11
B) 3, 7, and 8
C) 5, 9, and 10
D) 11, 12, and 13
E) 12, 14, and 15
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of interaction stabilizes the α helix and the β pleated sheet structures of proteins?
A) hydrophobic interactions
B) disulphide bonds
C) ionic bonds
D) hydrogen bonds
E) peptide bonds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following figure to answer the questions below.
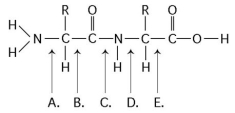 -At which bond would water need to be added to achieve hydrolysis of the peptide, back to its component amino acid?
-At which bond would water need to be added to achieve hydrolysis of the peptide, back to its component amino acid?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A new organism is discovered in the forests of Costa Rica. Scientists there determine that the polypeptide sequence of hemoglobin from the new organism has 72 amino acid differences from humans, 65 differences from a gibbon, 49 differences from a rat, and 5 differences from a frog. These data suggest that the new organism
A) is more closely related to humans than to frogs.
B) is more closely related to frogs than to humans.
C) evolved at about the same time as frogs, which is much earlier than primates and mammals.
D) is more closely related to humans than to rats.
E) is more closely related to frogs than to humans and also evolved at about the same time as frogs, which is much earlier than primates and mammals.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are human sex hormones considered to be lipids?
A) They are essential components of cell membranes.
B) They are not soluble in water.
C) They are made of fatty acids.
D) They are hydrophilic compounds.
E) They contribute to atherosclerosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which modifications of fatty acids will best keep triglycerides solid at warmer temperatures?
A) creating cis double bonds to the fatty acids
B) adding hydrogens to the fatty acids
C) creating trans double bonds to the fatty acids
D) adding hydrogens or trans double bonds to the fatty acids
E) adding cis double bonds and trans double bonds to the fatty acids
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between the sugar in DNA and the sugar in RNA is that the sugar in DNA
A) is a six-carbon sugar and the sugar in RNA is a five-carbon sugar.
B) can form a double-stranded molecule.
C) is an aldehyde sugar and the sugar in RNA is a keto sugar.
D) is in the α configuration and the sugar in RNA is in the β configuration.
E) contains one less oxygen atom.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A molecule with the chemical formula C₆H₁₂O₆ is probably a
A) carbohydrate.
B) lipid.
C) monosaccharide
D) carbohydrate and lipid only.
E) carbohydrate and monosaccharide only.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Approximately 32 different monomeric carbohydrate subunits are found in various natural polysaccharides. Proteins are composed of 20 different amino acids. DNA and RNA are each synthesized from four nucleotides. -Among these biological polymers, which has the least structural variety?
A) polysaccharides
B) proteins
C) DNA
D) RNA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following figure to answer the questions below.
 -Which bond is a peptide bond?
-Which bond is a peptide bond?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between dehydration reactions and hydrolysis?
A) Dehydration reactions assemble polymers, and hydrolysis reactions break down polymers.
B) Dehydration reactions eliminate water from lipid membranes, and hydrolysis makes lipid membranes water permeable.
C) Dehydration reactions can occur only after hydrolysis.
D) Hydrolysis creates monomers, and dehydration reactions break down polymers.
E) Dehydration reactions ionize water molecules and add hydroxyl groups to polymers; hydrolysis reactions release hydroxyl groups from polymers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of both starch and cellulose?
A) They are both polymers of glucose.
B) They are cis-trans isomers of each other.
C) They can both be digested by humans.
D) They are both used for energy storage in plants.
E) They are both structural components of the plant cell wall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of covalent bond between amino acid side chains (R groups) functions in maintaining a polypeptide's specific three-dimensional shape?
A) ionic bond
B) hydrophobic interaction
C) van der Waals interaction
D) disulphide bond
E) hydrogen bond
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many different kinds of polypeptides, each composed of 12 amino acids, could be synthesized using the 20 common amino acids?
A) 4¹²
B) 12²⁰
C) 240
D) 20
E) 20¹²
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the 15 molecules illustrated in the figure below. Each molecule may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
 -Which of the following molecules act as building blocks (monomers) of polypeptides?
-Which of the following molecules act as building blocks (monomers) of polypeptides?
A) 1, 4, and 6
B) 2, 7, and 8
C) 7, 8, and 13
D) 11, 12, and 13
E) 12, 13, and 15
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You have just had a breakfast of toast (high-fibre bread) with butter and jam (no added sugar) along with a glass of milk. -What are the two major polysaccharides you have consumed?
A) fatty acids and pectin
B) cellulose and fructose
C) starch and fructose
D) glucose and fructose
E) cellulose and starch
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Normal hemoglobin is a tetramer, consisting of two molecules of β hemoglobin and two molecules of α hemoglobin. In sickle-cell disease, as a result of a single amino acid change, the mutant hemoglobin tetramers associate with each other and assemble into large fibres. Based on this information alone, we can conclude that sickle-cell hemoglobin exhibits
A) altered primary structure.
B) altered secondary structure.
C) altered tertiary structure.
D) altered quaternary structure.
E) altered primary structure and altered quaternary structure; the secondary and tertiary structures may or may not be altered.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the 15 molecules illustrated in the figure below. Each molecule may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
 -Which of the following molecules could be joined together by a phosphodiester type of covalent bond?
-Which of the following molecules could be joined together by a phosphodiester type of covalent bond?
A) 3 and 4
B) 3 and 8
C) 6 and 15
D) 11 and 12
E) 11 and 13
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following figure to answer the questions below.
 -Which bond is closest to the amino terminus of the molecule?
-Which bond is closest to the amino terminus of the molecule?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 117
Related Exams