A) upper respiratory tract.
B) lower respiratory tract.
C) lungs.
D) alveoli.
E) bronchioles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term ________ describes the result from an injury that permits air to leak into the intrapleural space.
A) pleurisy
B) pneumonia
C) pneumothorax
D) pulmonary edema
E) emphysema
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One way to improve respiratory performance with age is to
A) eat smaller meals.
B) stop smoking.
C) sleep longer.
D) maintain normal glucose levels.
E) produce less surfactant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following changes does not occur at birth when an infant takes his or her first breaths?
A) Blood flow to the lungs decreases.
B) The resistance in the pulmonary arteries decreases.
C) Changes in blood flow cause the foramen ovale to close.
D) Air enters the alveoli.
E) Gas diffuses across the alveolar-capillary membrane.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The superior region of the pharynx is called the
A) nasal cavity.
B) nasopharynx.
C) oropharynx.
D) laryngopharynx.
E) superior nasal conchae.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 23-2 Mechanics of Ventilation
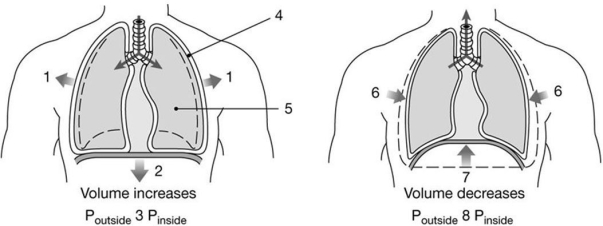 Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-What is the relationship between the pressures at label "8"?
Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-What is the relationship between the pressures at label "8"?
A) P outside = P inside
B) P outside > P inside
C) P outside < P inside
D) P outside + P inside
E) P outside - P inside
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lungs are held tightly to the wall of the thorax due to
A) the diaphragm and intercostal muscle contractions.
B) tight junctions between the lungs and the thorax.
C) surface tension of the pleural fluid and negative pressure in the cavity.
D) atmospheric pressure pushing on the lungs.
E) pulmonary ligaments that anchor the lungs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The portion of the nasal cavity contained within the flexible tissues of the external nose is the
A) nasopharynx.
B) vestibule.
C) internal chamber.
D) conchae.
E) nasal septum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood is approximately
A) 40 mm Hg.
B) 45 mm Hg.
C) 50 mm Hg.
D) 70 mm Hg.
E) 100 mm Hg.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
While playing in an intramural football game, Joe is tackled so hard that he breaks a rib. He can actuallyfeel a piece of the rib sticking through the skin and he is having a difficult time breathing. Joe is probably suffering from
A) a collapsed trachea.
B) an obstruction in the bronchi.
C) a pneumothorax.
D) decreased surfactant production.
E) a bruised diaphragm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -What type of epithelium lines the conducting portion of the respiratory tract? (Figure 23-2)
A) simple squamous epithelium
B) simple columnar epithelium
C) stratified ciliated columnar epithelium
D) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
E) stratified squamous epithelium
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The blood air barrier consists of
A) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
B) 1 layer of moist cuboidal epithelium.
C) 2 layers of simple squamous epithelium.
D) stratified squamous epithelium.
E) surfactant cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Physical damage to the lamina propria of the nasal mucosa is likely to result in
A) epistaxis.
B) nasal congestion.
C) nosebleeds.
D) a deviated septum.
E) epistaxis or nosebleeds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ involves active inspiratory and expiratory movements and calls on accessory muscles to assistwith inhalation, while exhalation involves contraction of the internal intercostal muscles and sometimes abdominal muscles, too.
A) Eupnea
B) Forced breathing
C) Costal breathing
D) Vital breathing
E) Passive breathing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The respiratory epithelium of the conducting airways consists of
A) pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
B) moist cuboidal epithelium.
C) simple squamous epithelium.
D) ciliated squamous epithelium.
E) stratified squamous epithelium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these is not part of the upper respiratory system?
A) larynx
B) pharynx
C) nasal cavity
D) nose
E) sinuses
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The entire array of protective mechanisms in the respiratory system is called the
A) respiratory immunity.
B) macrophage complex.
C) respiratory defense system.
D) acquired respiratory defense.
E) mucus escalator.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide is greatest in
A) venous blood.
B) alveolar air.
C) expired air.
D) inspired air.
E) arterial blood.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Air moves out of the lungs when the pressure inside the lungs is
A) greater than intraalveolar pressure.
B) less than the pressure in the atmosphere.
C) less than intrapulmonic pressure.
D) equal to the pressure in the atmosphere.
E) greater than the pressure in the atmosphere.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following organs is not part of the lower respiratory system?
A) pharynx
B) trachea
C) larynx
D) bronchi
E) alveoli
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 200
Related Exams