A) sets the at-rest respiratory pattern.
B) prolongs inspiration.
C) modifies the rate and depth of breathing.
D) suppresses the expiratory center in the medulla.
E) stimulates the dorsal respiratory group.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these factors does not affect hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen?
A) RBC metabolic activity
B) temperature
C) electrolyte balance
D) the PO2 of blood
E) blood pH
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The condition resulting from inadequate production of surfactant and the resultant collapse of alveoli is
A) respiratory distress syndrome.
B) COPD.
C) anoxia.
D) pulmonary embolism.
E) pneumothorax.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 23-2 Mechanics of Ventilation
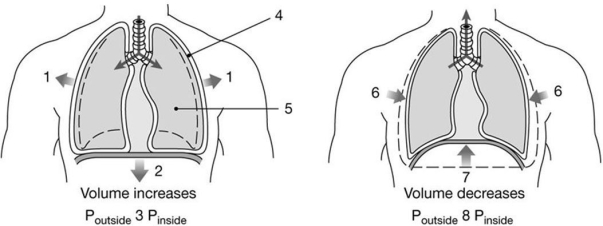 Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which muscle(s) produce(s) the movement labeled "1"?
Use Figure 23-2 to answer the following questions:
-Which muscle(s) produce(s) the movement labeled "1"?
A) rectus abdominis
B) internal intercostals
C) external intercostals
D) diaphragm
E) both rectus abdominis and external intercostals
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An acute infection of the throat that can lead to swelling and closure of the glottis and cause suffocationis known as
A) laryngitis.
B) laryngospasm.
C) acute epiglottitis.
D) strep throat.
E) acute pharyngitis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 23-1 The Upper Airways
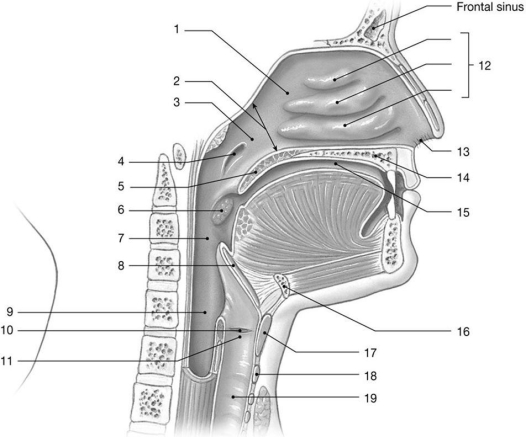 Use Figure 23-1 to answer the following questions:
-What is the function of the structure labeled "5"?
Use Figure 23-1 to answer the following questions:
-What is the function of the structure labeled "5"?
A) help olfaction
B) improve warming of air
C) cause air to swirl within the respiratory passageway
D) prevent food from entering the larynx
E) prevent food from entering the nasopharynx
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a true statement?
A) The DRG primarily controls inspiration.
B) The VRG primarily controls expiration.
C) The DRG functions in forced breathing only.
D) The VRG functions in forced breathing only.
E) The DRG controls external intercostals and the diaphragm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
JJ is suffering from laryngitis. He will most likely experience which of the following symptoms?
A) coughing
B) hoarseness
C) sneezing
D) suffocation
E) impaired swallowing
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following factors would increase the amount of oxygen discharged by hemoglobin to peripheraltissues?
A) decreased temperature
B) decreased pH
C) increased tissue PO2
D) decreased amounts of BPG
E) decreased temperature and decreased amounts of BPG
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The beating of the cilia of the respiratory passages in the direction of the pharynx forms a(n)
A) debris filter.
B) mucus escalator.
C) respiratory rhythmicity center.
D) smooth slick surface allowing particles to slide.
E) increased surface area for gas exchange.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -Name the primary muscles of inspiration. (Figure 23-14)
A) internal intercostal muscles and external intercostal muscles
B) diaphragm and internal intercostal muscles
C) diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
D) rectus abdominis and transversus thoracis
E) serratus anterior and rectus abdominus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Boyle's law states that the pressure of a gas is
A) inversely proportional to the volume of its container.
B) always higher in the atmosphere than in the lungs.
C) directly proportional to temperature.
D) inversely proportional to temperature.
E) directly proportional to the volume of its container.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which pressure remains negative throughout the respiratory cycle?
A) intrapulmonary
B) intrapleural
C) intra-alveolar
D) atmospheric
E) intrapulmonary and intra-alveolar
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Quiet breathing is to ________ as shallow breathing is to ________.
A) eupnea; diaphragmatic breathing
B) eupnea; costal breathing
C) costal breathing; eupnea
D) costal breathing; diaphragmatic
E) diaphragmatic breathing; eupnea
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ________ is lined by stratified squamous epithelium.
A) nasopharynx
B) trachea
C) oropharynx
D) larynx
E) nasal cavity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Higher brain centers that alter the activity of the respiratory centers include all of the following except
A) cortical association areas.
B) the precentral motor gyrus.
C) the limbic system.
D) the hypothalamus.
E) Broca's center.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a choking episode, most foreign objects are lodged in the ________ bronchus due to its larger diameter and steeper angle.
A) right primary
B) left primary
C) right lobar
D) left lobar
E) medial
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is one atmosphere of pressure?
A) 760 mm Hg
B) 1000 mm Hg
C) 105 mm Hg
D) 45 mm Hg
E) 650 mm Hg
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The openings to the nasal cavity are the
A) external nares.
B) internal nares.
C) nasal meatuses.
D) nasal conchae.
E) nasal sinuses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient with a connective tissue disease experiences increased pulmonary vascular resistance. Over a period of time, you would expect to observe
A) increased cardiac output from the right ventricle.
B) increased cardiac output from the left ventricle.
C) increased thickness of the right ventricular wall.
D) distension of the pulmonary veins from the right lung.
E) no appreciable changes in heart structure or function.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 200
Related Exams