A) the heart
B) a blood vessel in the skin
C) a sweat gland
D) the liver
E) the salivary glands
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sympathomimetic drugs might be used to
A) decrease heart rate.
B) decrease blood pressure.
C) dilate airways.
D) increase gastric motility.
E) reduce blood sugar levels.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Drugs known as beta-blockers may be useful for treating
A) constipation.
B) diarrhea.
C) excessive salivation.
D) excessive heart rate.
E) prostate disorders.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Parasympathetic stimulation
A) increases heart rate.
B) increases gastric motility.
C) causes sweat glands to secrete.
D) causes blood vessels in the skin to dilate.
E) causes the pupils to dilate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Long-term memories that are with you for a lifetime are called ________ memories.
A) tertiary
B) reflexive
C) consolidated
D) multilobar
E) secondary
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is essential for memory consolidation?
A) occipital lobe
B) basal nuclei
C) hippocampus
D) insula
E) prefrontal lobe
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Parasympathetic functions include all of the following, except
A) decrease in the rate of cardiac contraction.
B) constriction of the pupils.
C) dilation of the airways.
D) stimulation of urination.
E) stimulation of defecation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The adrenal medullae secrete
A) medullin.
B) epinephrine.
C) norepinephrine.
D) renin.
E) both epinephrine and norepinephrine.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sympathetic preganglionic fibers are ________ and have ________ axons.
A) short; myelinated
B) short; unmyelinated
C) long; myelinated
D) long; unmyelinated
E) intermediate; small
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A pedestrian narrowly avoids being hit by an oncoming car. He notices that it takes a little while for hisheart rate and respiratory rate to return to normal. This is likely because
A) the parasympathetic nervous system has become activated.
B) sympathetic activation of the adrenal medulla has released epinephrine and norepinephrine into the bloodstream.
C) the splanchnic nerves have become activated.
D) somatic motor neurons have increased the heart and respiratory rate.
E) the corticospinal pathway has become activated.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Intramural ganglia in the digestive, urinary, and reproductive organs are innervated by the ________ nerves.
A) spinal
B) splanchnic
C) chain
D) pelvic
E) collateral
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Autonomic tone is an important aspect of ANS function because it
A) allows ANS neurons to be silent under normal conditions.
B) allows ANS neurons to increase activity on demand but not decrease their activity.
C) allows ANS neurons to decrease their activity on demand but not increase their activity.
D) allows ANS neurons to increase or decrease their activity, providing a range of control options.
E) provides for a narrow range of control options that keeps target tissues constantly active.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sympathetic nerves contain postganglionic fibers that innervate organs in which cavity?
A) thoracic
B) pelvic
C) abdominal
D) cranial
E) abdominopelvic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most vital organs receive ________ innervation. That is, they receive input from both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
A) single
B) dual
C) biaxial
D) ambitonic
E) autonomic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mary accidentally ate poisonous mushrooms that contain muscarine. You would expect to observe all of thefollowing symptoms except
A) diarrhea.
B) salivation.
C) very fast heart rate.
D) sweating.
E) low blood pressure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Descending branches of the vagus and splanchnic nerves travel through the ________ plexus.
A) cardiac
B) pulmonary
C) hypogastric
D) esophageal
E) celiac
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Preganglionic fibers of parasympathetic neurons are present in all of the following cranial nerves except
A) III.
B) VII.
C) IX.
D) X.
E) XII.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 16-1 ANS Pathway
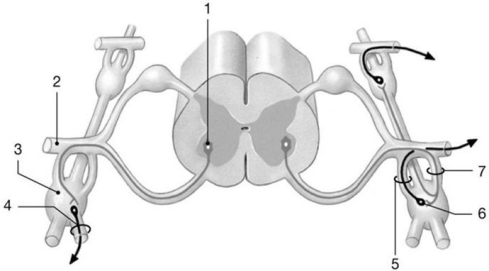 Use Figure 16-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "6."
Use Figure 16-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "6."
A) somatic motor neuron
B) preganglionic neuron
C) sensory neuron
D) ganglionic neuron
E) astrocyte
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alzheimer's disease is characterized by all of the following except that it
A) is the most common cause of senile dementia.
B) is characterized by a progressive loss of memory.
C) has a clear genetic basis.
D) is associated with the formation of plaques and neurofibrillary tangles.
E) may be associated with damage to the nucleus basalis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Avisceral motor neuron whose cell body is within the CNS is called a(n) ________ neuron.
A) upper motor
B) lower motor
C) preganglionic
D) postganglionic
E) somatomotor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 129
Related Exams