A) the increase in total product divided by the increase in energy used.
B) total product divided by the quantity of energy used.
C) the slope of the total product curve.
D) the slope of the marginal product curve.
E) the difference between the total product and the marginal product of energy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal product of capital is the
A) change in total product resulting from a 1-unit increase in the quantity of labour employed, holding the quantity of the capital constant.
B) change in total product resulting from a 1-unit increase in the quantity of capital employed, holding the quantity of the labour constant.
C) total product divided by the total quantity of capital employed, holding the quantity of the labour constant.
D) total product divided by the total quantity of labour employed, holding the quantity of the capital constant.
E) change in the quantity of capital used resulting from a 1-unit increase in total product, holding constant the quantity of labour.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, a firm can vary
A) all of its factors of production.
B) labour but not capital.
C) capital but not labour.
D) labour and capital but not land.
E) labour, capital and entrepreneurship but not land.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is false?
A) The marginal cost curve intersects the average variable cost curve and the average total cost curve at their maximum points.
B) When marginal cost is greater than average variable cost, average variable cost is increasing.
C) When marginal cost is greater than average total cost, average total cost is increasing.
D) The average total cost curve is U-shaped.
E) The average fixed cost curve is downward sloping.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long run refers to a time period
A) of one year or less.
B) in which all factors of production are variable.
C) in which labour is variable, but plant is fixed.
D) when there is at least one variable factor of production.
E) of at least 5 years.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ernie's Earmuffs produces 200 earmuffs per year at a total cost of $2,000 and $400 of this cost is fixed.What is Ernie's average variable cost?
A) $400
B) $8
C) $2
D) $2,400
E) $1,600
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The ATC curve shifts upward if
A) factor prices rise.
B) a new technology is introduced.
C) more workers are hired.
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The steeper the slope of the total product curve,
A) the smaller the average product.
B) the smaller the marginal product.
C) the greater the total cost.
D) the more efficient the technology employed.
E) the greater the marginal product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
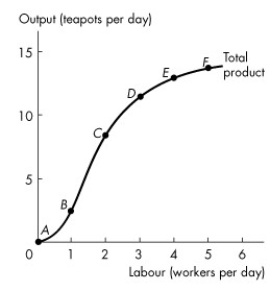 Figure 11.2.1
-Refer to Figure 11.2.1 which illustrates Tania's total product curve.Marginal product of labour reaches its maximum when the number of workers increases from
Figure 11.2.1
-Refer to Figure 11.2.1 which illustrates Tania's total product curve.Marginal product of labour reaches its maximum when the number of workers increases from
A) zero to 1.
B) 1 to 2.
C) 2 to 3.
D) 3 to 4.
E) 4 to 5.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 11.2.3
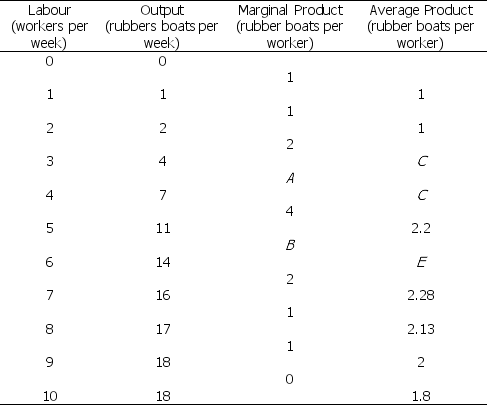 -Refer to Table 11.2.3.The maximum value of marginal product occurs where output equals ________, while the maximum value of average product occurs where output equals ________.
-Refer to Table 11.2.3.The maximum value of marginal product occurs where output equals ________, while the maximum value of average product occurs where output equals ________.
A) 5; 6
B) 6; 5
C) 7; 14
D) 9; 14
E) 14; 11
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
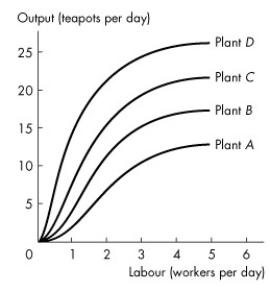 Figure 11.4.1
-Refer to Figure 11.4.1, which illustrates the total product curves for four different plant sizes.One of the fundamental technological facts reflected in the shape of each of the total product curves is the
Figure 11.4.1
-Refer to Figure 11.4.1, which illustrates the total product curves for four different plant sizes.One of the fundamental technological facts reflected in the shape of each of the total product curves is the
A) price of the inputs.
B) price of the output.
C) law of diminishing marginal returns.
D) law of economies of scale.
E) fact that capital and labour cannot be substituted for each other.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal cost is the amount that
A) total cost increases when one more labourer is hired.
B) fixed cost increases when one more labourer is hired.
C) variable cost increases when one more labourer is hired.
D) total cost increases when one more unit of output is produced.
E) fixed cost increases when one more unit of output is produced.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 11.2.1
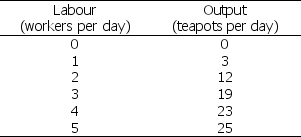 -Refer to Table 11.2.1 which gives Tania's total product schedule.Marginal product of labour reaches its maximum when the number of workers increases from
-Refer to Table 11.2.1 which gives Tania's total product schedule.Marginal product of labour reaches its maximum when the number of workers increases from
A) 0 to 1.
B) 1 to 2.
C) 2 to 3.
D) 3 to 4.
E) 4 to 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If ATC is rising then MC must be
A) rising.
B) falling.
C) equal to ATC.
D) above ATC.
E) both A and D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The short run is a time frame in which
A) the firm is not able to hire more workers.
B) the amount of output produced is fixed.
C) there is a shortage of most factors of production.
D) at least one factor of production is fixed.
E) there is not enough time to make all of the decisions necessary to maximize profit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Total cost is $20 at 4 units of output and $36 at 6 units of output.Between 4 and 6 units of output, marginal cost
A) is less than average total cost.
B) is equal to average total cost.
C) is equal to average variable cost.
D) is greater than average total cost.
E) equals average fixed cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal cost
A) is constantly increasing, but as output increases it increases by smaller and smaller amounts.
B) decreases at low outputs until it reaches its minimum value, then remains constant.
C) decreases at low outputs and increases at high outputs.
D) increases at low outputs until it reaches its maximum value, then remains constant.
E) is constantly decreasing, but as output increases it decreases by smaller and smaller amounts.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
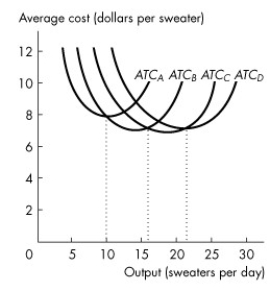 Figure 11.4.2
-Refer to Figure 11.4.2, which illustrates the short-run average total cost curves for four different plant sizes.Which curve represents the average total cost for the largest of the four plant sizes?
Figure 11.4.2
-Refer to Figure 11.4.2, which illustrates the short-run average total cost curves for four different plant sizes.Which curve represents the average total cost for the largest of the four plant sizes?
A) ATCA
B) ATCB
C) ATCC
D) ATCD
E) either ATCC or ATCD
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a graph that shows the total cost curve and the total variable cost curve.As output increases, the vertical distance between these two curves
A) increases.
B) decreases.
C) becomes smaller and then larger.
D) becomes larger and then smaller.
E) is constant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cost that has been incurred and cannot be recovered is a
A) marginal cost.
B) sunk cost.
C) variable cost.
D) business cost.
E) significant cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 142
Related Exams