A) genetic drift.
B) population bottleneck.
C) natural selection.
D) founder effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The formation of new species over many generations is an example of:
A) microevolution.
B) macroevolution.
C) gene pools.
D) allelic variants.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At its most basic level,evolution is a:
A) change in the frequency of alleles in a population.
B) change in the frequency of alleles in an individual.
C) new species arising from an existing species.
D) change in an individual's phenotype caused by mutations.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Read the statement below, and then answer the following question(s) . A small population of deer is introduced to an island. All the males have 11 to 13 points on their antlers. -If after several generations most males have antlers with 20 points,this development will have been the result of:
A) directional selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) founder effect.
D) bottleneck effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If every sexually reproducing organism has only two alleles for each gene,how can there be a range of traits seen for a physical characteristic?
A) One of the alleles in an organism is expressed at different levels, while the other is turned off.
B) Sometimes one of the alleles works, and other times the other allele works.
C) There can be more than two variations of a gene in a population.
D) In a population there are only two variations of a gene, but they are blended differently during sexual reproduction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two nearby populations in which there is some movement of individuals between the populations are an example of:
A) disruptive selection.
B) bottleneck effect.
C) genetic drift.
D) gene flow.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
________ is necessary for a population to survive over successive generations in response to environmental changes.
A) Adaptation
B) Sexual selection
C) Speciation
D) Gene flow
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The advantage a trait conveys depends on its environmental context.
B) A population will always evolve to fit current conditions.
C) All traits are simultaneously maximized in a population.
D) All traits currently in a population must have provided a reproductive advantage at some point in time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A small minority of mutations is adaptive,providing an improvement to the gene pool of the population.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The original source of variation within a population comes from ________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phenotypes that show a wide range of almost continuous variation,such as height or skin color in humans,are probably:
A) due to several sets of alleles working together.
B) due to both alleles of one gene working together.
C) acquired characteristics.
D) dominant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the question that follows.
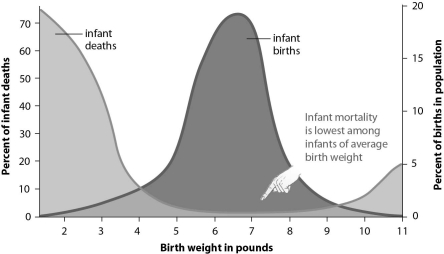 -Human birth weights are an example of:
-Human birth weights are an example of:
A) disruptive selection.
B) stabilizing selection.
C) directional selection.
D) sexual selection.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the question that follows.
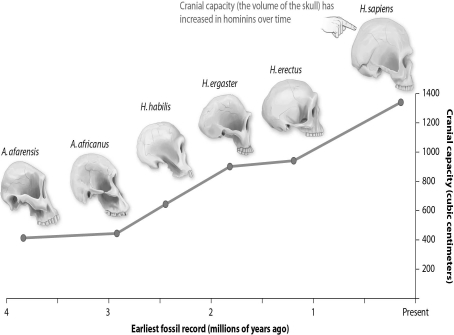 -The changes in cranial capacity over the course of human evolution are an example of:
-The changes in cranial capacity over the course of human evolution are an example of:
A) disruptive selection.
B) stabilizing selection.
C) directional selection.
D) sexual selection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Disruptive selection operates whenever:
A) a phenotype is more successful because it is rare.
B) natural selection is disrupted by genetic drift.
C) the extremes in a distribution of phenotypes are more fit than the average.
D) only the largest individuals survive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population is:
A) a group of organisms that can successfully interbreed in nature but do not interbreed with other such groups.
B) all the members of a species that live in a defined geographic region at the same time.
C) all the different species that live in a defined geographic area at the same time.
D) a group of different species that share common features.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about evolution is true?
A) Evolution involves maintaining a constant frequency of alleles in the gene pool.
B) Populations evolve.
C) Individuals evolve.
D) Evolution can proceed to a limited extent without the occurrence of mutation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Read the statement below, and then answer the following question(s) . A small population of deer is introduced to an island. All the males have 11 to 13 points on their antlers. -If after several generations all males have 12-point antlers,this development will have been due to:
A) directional selection.
B) disruptive selection.
C) founder effect.
D) stabilizing selection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term "natural selection" is not interchangeable with the term "evolution" because:
A) natural selection is just a theory, whereas evolution has been proven.
B) a population may evolve in ways other than through natural selection.
C) Darwin coined the term "natural selection," but not "evolution."
D) natural selection does not always lead to evolution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How successful an individual is at passing on its genes to the next generation is known as:
A) microevolution.
B) adaptation.
C) fitness.
D) sexual selection.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mate-attracting elaborate plumage of the male peacock is a result of:
A) genetic drift.
B) adaptation to the environment.
C) sexual selection.
D) gene flow.
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 71
Related Exams