A) eIF-2
B) eIF-2
C) eEF-1α
D) eEF-1βγ
E) eEF-2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reticulocytes control the rate of globin synthesis as a consequence of the level of heme in the cell. This prevents globin protein from being made when there are insufficient amounts of heme. Which of the following best explains the effects of heme on protein synthesis in these cells?
A) a heme-controlled phosphatase dephosphorylates cap-binding factor, which prevents recognition of globin mRNA by the ribosomes
B) a tRNA degrading enzyme is active in the absence of heme
C) heme normally activates peptidyltransferase in reticulocytes
D) RNA polymerase activity is decreased in reticulocytes by low heme
E) the initiation factor eIF-2 becomes phosphorylated, reducing its level of activity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the development of B cells there is switch from the synthesis of membrane-bound immunoglobulin to a secreted form of immunoglobulin. This change occurs because the mRNA population encodes a protein missing which of the following sequence motifs?
A) anchor sequence
B) glycosylation sites
C) leucine zipper
D) signal sequence
E) zinc-binding domain
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following translation factors is the target of an interferon-mediated translational control mechanism?
A) eEF-1α
B) eEF-2
C) eIF-2
D) eIF-4A
E) eIF-4E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Control of the rate of translational initiation can be exerted at the level of the activity of the GTPbinding and hydrolyzing initiation factor, eIF-2. The efficiency with which eIF-2 recycles between the active GTP-bound form and the inactive GDPbound form is controlled by which of the following translation factors?
A) eIF-1
B) eIF-2B
C) eIF-4A
D) eIF-4E
E) eIF-4G
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following determines the sequence of a polypeptide synthesized by the polyribosome complex?
A) aminoacyl-tRNA
B) aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
C) elongation factor 1 (eEF-1)
D) mRNA
E) peptidyltransferase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes the direction of translation of mRNAs and synthesis of protein on ribosomes?
A) Translation : 5′ → 3′
Synthesis: C-terminus → N-terminus
B) Translation: 3′ → 5′
Synthesis: C-terminus → N-terminus
C) Translation : 5′ →3′
Synthesis: N-terminus → C-terminus
D) Translation: 3′ → 5′
Synthesis: N-terminus → C-terminus
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At which of the following sites on a eukaryotic mRNA is translation most likely to begin?
A) at the cap
B) at the 3′-end of the mRNA
C) at the 5′-end of the mRNA
D) first AUG codon
E) within 5 nucleotides of the Shine-Delgarno sequence
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many proteins contain a specialized stretch of amino acids that are recognized by a protein complex called the signal recognition particle. Which of the following best describes the function of this complex during the synthesis of secretory proteins?
A) anchors the ribosome to the Golgi membrane
B) enhances the rate of protein synthesis
C) interact with the amino terminus of the nascent polypeptide
D) interacts with glycosyltransferases within the endoplasmic reticulum
E) promotes the binding of specific mRNAs to ribosomes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the process of protein synthesis the elongating peptide is transferred to the incoming aminoacyltRNA by a peptidyltransferase activity. Which of the following components of the translational machinery is most likely to possess this enzymatic activity?
A) peptidase
B) ribosomal protein L11
C) ribosomal protein S16
D) 5S rRNA
E) 28S rRNA
F) tRNA nucleotidyltransferase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are studying the function of a protein isolated from a lung tumor cell line and comparing it to the same protein from normal tissue. You find that the protein derived from the cancer cells does not carry out its correct function as a result of improper folding of the protein. Which of the following, involved in the prevention of aggregation and improper folding of newly synthesized proteins, is most likely to be defective in the lung cancer cells?
A) chaperones
B) lysozymes
C) mitochondrial precursor proteins
D) ribosomal-binding proteins
E) zymogens
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are examining the mutational changes that occurred in a breast cancer cell line. You discover that there is a mutation in the gene encoding selenoprotein translation factor B (SelB) . Which of the following is most likely defective in these cells as a result of this mutation?
A) decreased bile acid synthesis
B) decreased glycogen synthesis
C) decreased reactive oxygen species generation by pancreatic mitochondria
D) increased fatty acid incorporation into triglycerides
E) increased rate of erythrocyte lysis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the process of protein synthesis the factor eEF-2 induces the hydrolysis of GTP. The energy of this hydrolysis is coupled to which of the following?
A) amino acid activation by attachment to a tRNA
B) correct alignment of the mRNA on the 40S ribosome
C) formation of the 80S initiation complex
D) formation of the peptide bond
E) translocation of the ribosome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are studying the effects of chemical treatment of components of the translational machinery. You discover that one chemical in particular results in the conversion of the cysteine attached to a tRNA to alanine. Which of the following would best describe the results of this chemical-induced insertion of alanine into the resultant polypeptide?
A) it would not occur due to altered structure
B) it would occur randomly
C) it would occur where alanine is normally present
D) it would occur where cysteine is normally present
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reading of the genetic code is dependent on recognition of a codon on which of the following?
A) DNA by an amino acid
B) DNA by an mRNA
C) mRNA by an amino acid
D) mRNA by an aminoacyl-tRNA
E) tRNA by an amino acid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The unfolded protein response is a stress response in the ER. This stress pathway results in a halt to global protein synthesis and the activation of translation of factors required to respond to the stress inducer. Which of the following proteins of translation is the primary target of the ER stress response?
A) eIF-2
B) eIF2B
C) eIF-4E
D) eEF-1α
E) eEF-2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are studying the processes of protein synthesis via the use of a cell-free system and synthetic RNAs. You have introduced the following RNA to this system: 5′-AUAUAAUGACUAAAUAU-3′ Table of codons Aaa lysine Aau asparagine ACu threonine Aua isoleucine AuG methionine Uau tyrosine Cau leucine Using the above indicated codons, which of the following is the most likely sequence of the peptide synthesized in this system?
A) isoleucine, methionine, threonine, lysine, tyrosine
B) methionine, isoleucine, asparagine
C) methione, threonine, leucine, threonine
D) methionine, threonine, lysine, tyrosine
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You are studying the process of protein synthesis in cultures of hepatocytes. During an experiment, you Observe that translation of certain mRNAs continues until a termination codon reside in the A-site of the ribosome. The liberation of the polypeptide chain at this point involves the eukaryotic releasing factor and hydrolysis of which of the following?
A) ATP
B) CTP
C) GTP
D) TTP
E) UTP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following occurs to mRNA molecules during protein synthesis?
A) amplification in the cytoplasm to code for new proteins
B) conversion to DNA by reverse transcriptase
C) synthesis from individual ribonucleotides
D) transcription in a 3′ → 5′ direction
E) translation in a 5′ → 3′ direction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the DNA shown was transcribed and then translated in a eukaryotic in vitro translation system, what would be the composition of the resultant peptide?
5′-CATTCCATAGCATGT-3′
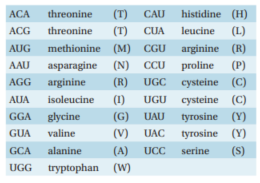
A) C-T-I-P-Y
B) H-S-I-A-C
C) M-L-W-N
D) T-C-Y-G-M
E) V-R-Y-R-T
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 43
Related Exams