A) They produce products toxic to the host.
B) They replicate outside of the chromosome.
C) They replicate using the host's resources without direct benefit to the host.
D) They spread rapidly throughout the genome.
E) They produce products that prevent cooperation between cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If one wished to test the hypothesis that humans and chimps differ due to differences in the expression of a large set of shared genes,the technique to use would be
A) Southern blotting.
B) PCR.
C) DNA sequencing.
D) protein-protein interaction assays.
E) DNA microarray analysis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In comparing DNA sequences from two different eukaryotic organisms,which do you expect to vary the most?
A) sequences that code for exons
B) sequences that code for introns
C) sequences that code for a polypeptide
D) sequences that regulate transcription
E) sequences that code for micro-RNAs
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following questions is asked in functional genomics research?
A) What is the number of Drosophila genes?
B) How does the GC content of human DNA vary across the genome?
C) What is the pattern of gene expression during mouse development?
D) How many introns exist in the human CFTR gene?
E) How closely related are the visual pigment genes of mouse and human?
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In establishing paternity by DNA fingerprinting,what proportion of microsatellite repeat alleles in a child come from the father?
A) none
B) 1/4
C) 1/2
D) 3/4
E) all
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Like DNA microarrays,Northern blots analyze the levels of mRNA.However,Northern blots are almost always prepared with a probe tagged with one label,whereas DNA microarrays almost always use two groups of probes,each one tagged with a different fluorescent label.What advantage is conferred by using two labels for the microarray probes?
A) The two labels increase the sensitivity of the microarray.
B) The two labels allow the analysis of the expression of more genes.
C) The two labels allow simultaneous assay of levels of DNA and RNA.
D) The two labels allow comparison of gene expression between two samples.
E) Probing the array with two labels is equivalent to doing two experiments at once.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Although transposable elements and simple tandem repeats (STRs) are both repetitive DNAs,they differ in that
A) STRs occur within exons;transposable elements occur within introns.
B) STRs occur within introns;transposable elements occur within exons.
C) the repeated unit in STRs is clustered one after another;transposable element repeats are scattered throughout the genome.
D) the repeated unit in STRs is much larger than the repeated unit of transposable elements.
E) variation in STR repeat number comes from STR movement in the genome;variation in transposable element repeat number comes from errors in DNA replication.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The discipline that manages,analyzes,and interprets the vast amounts of sequence data generated from whole genome sequencing is
A) proteomics.
B) functional genomics.
C) evolutionary genomics.
D) bioinformatics.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The goal of annotating a whole genome sequence is to
A) establish the nucleotide sequence.
B) learn the number of nucleotides contained within the genome.
C) identify genes and their positions within the genome.
D) learn how gene products interact to produce phenotypes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What can proteomics reveal that genomics cannot?
A) The number of genes characteristic of a species.
B) The patterns of alternative splicing.
C) The set of proteins present within a cell or tissue type.
D) The levels of mRNAs present in a particular cell type.
E) The movement of transposable elements within the genome.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One surprising discovery from the analysis of bacterial genomes is that
A) very few species contain plasmids.
B) there is only one copy of each gene present within a bacterial genome.
C) there are many genes of unknown function.
D) bacterial genomes are always contained on a single circular chromosome.
E) there is almost no difference between the genomes of diverse bacteria.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 20.1 The following table from the Venter et al. paper presents the numbers of different types of genes discovered in this study.
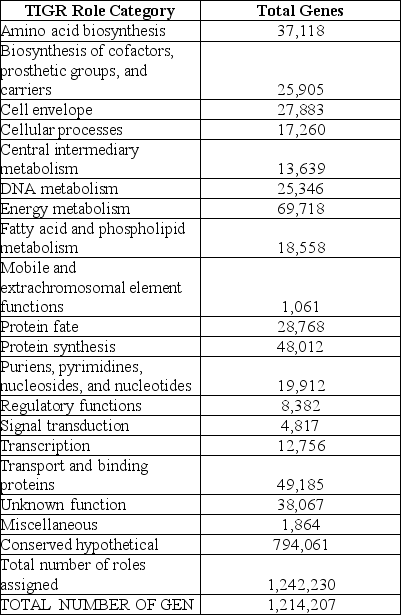 -How do you think putative genes were placed into the categories shown in the preceding table?
-How do you think putative genes were placed into the categories shown in the preceding table?
A) by searching for ORFs,especially those with translation start and stop sites
B) by searching for matches,especially of the predicted gene products,with previously identified gene products of known function
C) by expressing the cloned genes in E.coli and then running biochemical analyses of the products
D) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When gene duplication occurs to its ultimate extent by doubling all genes in a genome,what has occurred?
A) pseudogene creation
B) creation of a gene cluster
C) creation of a polyploid
D) creation of an aneuploid
E) creation of a diploid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine that your goal is to isolate mouse mutants that stabilize microsatellite repeat sequences (i.e.,lower the frequency at which their repeat number changes) .Which of the following mutations would you predict to have this stabilizing effect?
A) a mutation that reduces the rate of transcription
B) a mutation that reduces the rate of translation
C) a mutation that increases the rate of DNA synthesis
D) a mutation that reduces the occurrence of homologous recombination
E) a mutation that inactivates reverse transcriptase and/or integrase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sequencing eukaryotic genomes is more difficult than sequencing genomes of bacteria or archaea because of
A) the large size of eukaryotic genomes.
B) the large amount of eukaryotic repetitive DNA.
C) the high proportion of G-C base pairs in eukaryotic DNA.
D) A and B only.
E) all of the above.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As with many new endeavors,concerns have been raised by some that genomics will fundamentally change the way biological research is practiced.Examine the full reference for the Venter et al.paper and consider the way this work was done.Now think of some seminal works in the history of biology,for example,Darwin's On the Origin of Species and Watson and Crick's publication on DNA structure.What do you think the concern might be that has been voiced about genomics?
A) Genomics will offer deep insights too rapidly for the biological community to comprehend.
B) Genomics is so based in technology that it cannot possibly reveal important knowledge of biology.
C) Genomics makes biology a "big-team science" that will squeeze out innovative individuals or small groups of scientists who traditionally have provided our greatest insights.
D) Genomics is really computer science,not biology,and therefore offers little for understanding life.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If alternative splicing did not occur,a prediction would be that
A) the human genome would contain many more genes.
B) the yeast genome would contain many fewer genes.
C) there would be little correlation between the complexity of organisms and genome size.
D) there would be many fewer genes devoted to metabolism in Arabidopsis and yeast.
E) there would be many fewer genes devoted to DNA replication and modification in humans.
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If practical applications arise from this or similar metagenomic studies,what might these be?
A) New genes with useful properties may be identified and ultimately put to use.
B) New microbial species could be isolated from seawater.
C) An increased knowledge of the diversity of marine ecosystems could lead to increased appreciation of diversity in all ecosystems.
D) Species discovered in the Sargasso Sea may also be found to inhabit less-remote waters.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 20.1 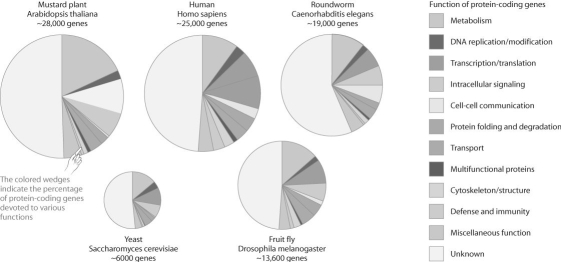 -The figure above compares the proportion of genes devoted to various functions in a set of model organisms.Based on this figure,which one of the following statements is FALSE?
-The figure above compares the proportion of genes devoted to various functions in a set of model organisms.Based on this figure,which one of the following statements is FALSE?
A) The function of roughly half of eukaryotic genes is unknown.
B) Humans have the highest proportion of genes devoted to defense and immunity.
C) The mustard plant and yeast have a small fraction of genes devoted to cell communication.
D) A relatively small but similar proportion of genes are devoted to transcription and translation in all these organisms.
E) Drosophila is unusual in having so few genes devoted to protein folding and degradation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 20.2 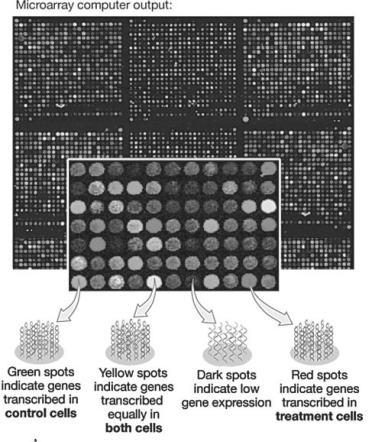 -In the microarray shown in the figure above,if you were searching for genes whose expression was inhibited by hormone treatment,you would search for sequences spotted on the array that showed ________ fluorescence.
-In the microarray shown in the figure above,if you were searching for genes whose expression was inhibited by hormone treatment,you would search for sequences spotted on the array that showed ________ fluorescence.
A) no
B) high levels of
C) green
D) red
E) yellow
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 41
Related Exams